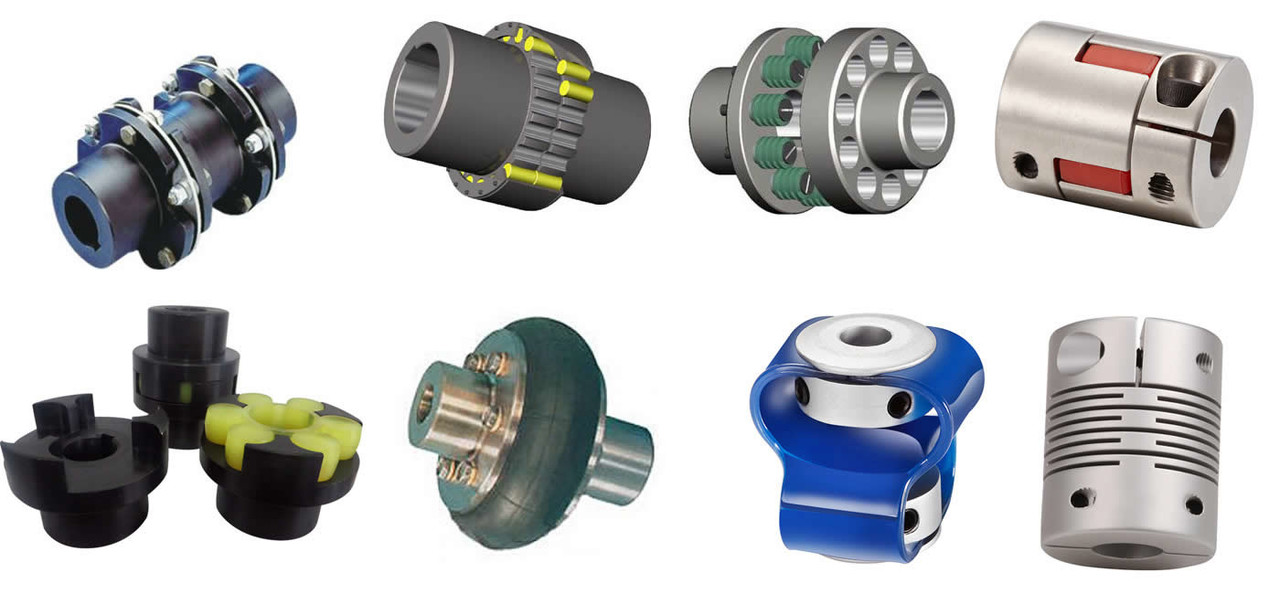
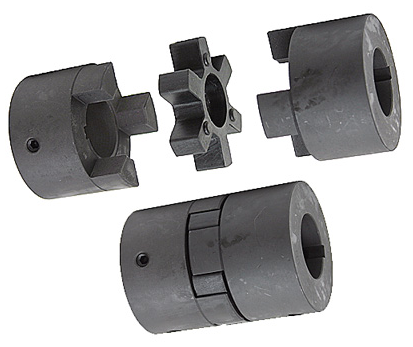
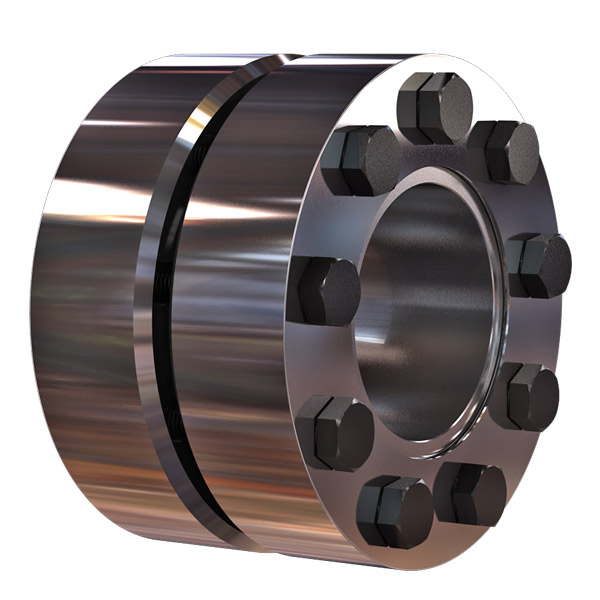
Product Description
Original Excavator Parts Coupling CF-a Series Rubber Flexible Torsionally Steel Universal Shaft Coupling for Centafle
Product Display:
| Model | Outer Diameter(mm) | Inner Diameter(mm) | Hight(mm) | Diameter from Hole to Hole(mm) | Weight(kg) |
| 4A/4AS | 103 | 53 | 28 | 68 | 0.18 |
| 8A/8AS | 134 | 71 | 32 | 88 | 0.26 |
| 16A/16AS | 160 | 80 | 41 | 110 | 0.54 |
| 22A/22AS | 165 | 86 | 41 | 128 | 0.66 |
| 25A/25AS | 183 | 102 | 46 | 123 | 0.78 |
| 28A/AS | 0.88 | ||||
| 30A/30AS | 213 | 117 | 57 | 145 | 1.28 |
| 50A/50AS | 220 | 123 | 57 | 165 | 1.48 |
| 80A/80As | 225 | 120 | 65 | 167 | 1.92 |
| 90A/90As | 278 | 148 | 70 | 190 | 3.1 |
| 140A/140AS | 285 | 151 | 71 | 215 | 3.42 |
| 250A/250AS | 6.6 | ||||
| 284B | 6.34 | ||||
| 4, 4655134, EX3, ZAX460MTH, ZAX480MTH, 4636444, ZX470-3, EX470, ZAX470, ZAX450-3, ZAX450-3F, ZAX5, Atlas Copco,,
AC 385, AC 396, AC415, AC416, AC 455, AC485, AC 486, AC86, AC836, AC976, AC 6-712, 4DNV98 Chinese Brand Excavators: LGK: 6085, 200 CLG 60, 205, 220, 906, 907, 908, 920, 925, 936, CLG906C, CLG922LG YC50-8, YC60-8, YC60-8, YC135-8, YC230, YC230-8, YC230LC-8, YC360, YC85, YC50, YC85-7, YC60-7, YC135 SW50, 60, 70, 150 FR85-7, FR65, FR80, FR150-7, ZL 60, 205, 230, 360 SY55, SY60, SY215, SY230, SY210, SY220, SY310 /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Specific Safety Precautions When Working with Shaft CouplingsWorking with shaft couplings involves handling rotating machinery and mechanical components. To ensure the safety of personnel and prevent accidents, specific safety precautions should be followed during installation, maintenance, and operation: 1. Lockout-Tagout (LOTO):Prior to any work on machinery involving couplings, implement a lockout-tagout procedure to isolate the equipment from its power source. This ensures that the machinery cannot be accidentally energized during maintenance or repair, protecting workers from potential hazards. 2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety goggles, gloves, and appropriate clothing, when working with shaft couplings. PPE helps protect against potential hazards such as flying debris, sharp edges, or contact with moving parts. 3. Proper Training and Supervision:Only trained and authorized personnel should work with shaft couplings. Ensure that workers have the necessary knowledge and experience to handle the equipment safely. Adequate supervision may be required, especially for less-experienced personnel. 4. Inspection and Maintenance:Regularly inspect shaft couplings and associated components for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Address any issues promptly to prevent equipment failure and potential accidents. 5. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:Adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines for installation, operation, and maintenance of the specific coupling model. Improper use or deviation from recommended procedures may compromise safety and void warranties. 6. Avoid Overloading:Do not exceed the torque and speed limits specified by the coupling manufacturer. Overloading a coupling can lead to premature failure and pose safety risks to operators and nearby equipment. 7. Shaft Guards and Enclosures:Install appropriate guards and enclosures to prevent accidental contact with rotating shafts and couplings. These safety measures help reduce the risk of entanglement and injuries. 8. Zero Energy State:Ensure that all stored energy in the equipment, such as compressed air or hydraulic pressure, is released and the equipment is in a zero energy state before starting work. 9. Avoid Loose Clothing and Jewelry:Remove or secure loose clothing, jewelry, and other items that could get caught in moving parts. 10. Maintain a Clean Work Area:Keep the work area clean and free from clutter to avoid tripping hazards and facilitate safe movement around the machinery. By following these safety precautions, personnel can minimize the risks associated with working with shaft couplings and create a safer working environment for everyone involved. “` Comparing Shaft Couplings with Other Types of Couplings in PerformanceShaft couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, and their performance characteristics vary depending on the coupling type. Let’s compare shaft couplings with other common types of couplings: 1. Shaft Couplings:Shaft couplings come in various designs, including flexible and rigid couplings. They are widely used in a broad range of applications due to their ability to transmit torque and accommodate misalignments between rotating shafts. Flexible shaft couplings, with elastomeric or metallic elements, offer good misalignment compensation and damping characteristics. Rigid couplings, on the other hand, provide precise torque transmission and are ideal for applications where shafts are well-aligned. 2. Gear Couplings:Gear couplings are robust and designed for heavy-duty applications. They consist of two external gear hubs with internal gear teeth that mesh together. Gear couplings can handle high torque, high-speed, and angular misalignment. They are often used in demanding industries such as steel, mining, and paper manufacturing. 3. Grid Couplings:Grid couplings feature a flexible grid element between the two halves of the coupling. They provide excellent shock absorption and misalignment compensation. Grid couplings are commonly used in pumps, compressors, and other industrial machinery. 4. Disc Couplings:Disc couplings utilize flexible metallic discs to transmit torque and compensate for misalignment. They offer high torsional stiffness, making them suitable for applications requiring precise motion control, such as robotics and CNC machines. 5. Jaw Couplings:Jaw couplings consist of two hubs with elastomeric spider inserts. They are easy to install, have good misalignment capabilities, and offer electrical isolation between shafts. Jaw couplings are widely used in light to medium-duty applications. 6. Oldham Couplings:Oldham couplings have three discs—two outer discs with slots and a central disc with a tongue that fits into the slots. They provide excellent angular misalignment compensation while maintaining constant velocity between shafts. Oldham couplings are commonly used in printing machines and conveyors. 7. Beam Couplings:Beam couplings are made from a single piece of flexible material with spiral cuts. They offer good misalignment compensation and torsional flexibility, making them suitable for precision equipment like encoders and servo motors. The choice of coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application, including torque, speed, misalignment compensation, environmental conditions, and space limitations. Each coupling type has its strengths and limitations, and selecting the right coupling is crucial to ensure optimal performance and reliability in the mechanical system. “` Types of Shaft Couplings and Their Applications in Various IndustriesShaft couplings come in various types, each designed to meet specific application requirements and address different types of misalignment. Here are some common types of shaft couplings and their applications in various industries: 1. Jaw Couplings:Applications: Jaw couplings are widely used in power transmission applications, including conveyor systems, pumps, compressors, and industrial machinery. They are suitable for moderate torque requirements and provide good misalignment compensation. 2. Gear Couplings:Applications: Gear couplings are used in heavy-duty industrial applications such as steel mills, paper mills, and mining equipment. They offer high torque capacity and can handle significant misalignments. 3. Disc Couplings:Applications: Disc couplings are commonly used in precision machinery and automation systems, such as printing presses, machine tools, and robotics. They provide excellent torsional stiffness and are ideal for applications requiring precise positioning. 4. Grid Couplings:Applications: Grid couplings are used in various industrial applications, including fans, pumps, and compressors. They offer high torque capacity and good shock absorption. 5. Oldham Couplings:Applications: Oldham couplings are used in applications requiring high misalignment compensation, such as stepper motor drives and motion control systems. 6. Diaphragm Couplings:Applications: Diaphragm couplings are used in critical applications that demand high torque transmission accuracy, such as aerospace, medical equipment, and semiconductor manufacturing. 7. Elastomeric Couplings:Applications: Elastomeric couplings, like spider couplings, find applications in general industrial machinery, HVAC systems, and conveyor systems. They provide damping properties and flexibility to accommodate misalignments. 8. Torsionally Rigid Couplings:Applications: Torsionally rigid couplings are used in applications requiring precise torque transmission, such as precision machining equipment and high-speed spindles. 9. Fluid Couplings:Applications: Fluid couplings are used in heavy machinery and drivetrains, such as mining equipment, crushers, and marine propulsion systems. They provide smooth acceleration and dampening of shock loads. 10. Magnetic Couplings:Applications: Magnetic couplings are used in applications where hermetic sealing is required, such as chemical processing, pumps, and mixers. They allow for torque transmission without direct physical contact. The selection of the appropriate shaft coupling type depends on factors such as torque requirements, speed, misalignment, operating conditions, and the specific needs of the application. Using the right coupling ensures efficient power transmission, protects equipment from misalignment-related issues, and enhances the overall reliability and performance of industrial machinery and systems. “` |