Product Description
Customized Type Gear Coupling Mechanical Industry Coupling
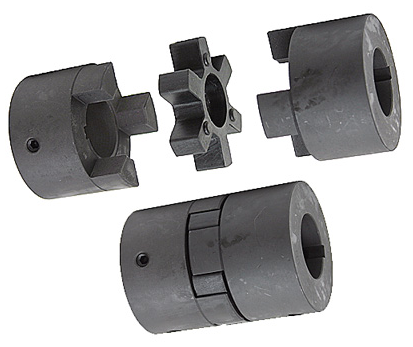
Product show
| Product Name | Densen customized GIICL gear motor shaft coupling,machine shaft coupling,flexible gear coupling |
| DN mm | 16-1040mm |
| Rated Torque | 0.4~4500 kN·m |
| Allowalbe Speed | 4000~460RPM |
| Material | 45# Steel or 42CrMo |
| Application | Widely used in metallurgy, mining, engineering and other fields. |
Why Choose Us
1. One stop service:
We have 5 own factories and 50+ sub-contractors located in different areas of China to offer you one-stop manufacturing and purchasing services to help you save time and reduce procurement cost.
2. Your eyes in China:
Our commitment to quality permeates from quoting, scheduling, production, inspection to deliver into your warehouse, our QC team will remark the errors if has on QC documents for your checking before delivery as your 3rd party.
3. Your R&Dconsultant:
With professional engineers team and 29 years manufacture experience ,we would help you work out problems during new parts’ development, optimize design and recommend the most cost-effective solution.
4. Your Emergency Solver:
With continued grown factories team and our QC teams located in different areas, if customers need to expedite the delivery, we would be able to adopt another factory to produce together immediately.
5. Quality Guaranty:
No matter how long time the products delivered, we are responsible for the quality. In case the products be rejected, we would replace them or return fund according to your demand without hesitation
FAQQ1. Are you a manufacturer or a trader?
Manufacture, we have 5 own foundries, 4 in ZheJiang Province, 1 in ZHangZhoug Province
Q2. Do you have MOQ request?
1 pcs per order is ok with us , unless material is seldom used.
Q3. If I only have a sample,without drawings, can you quote then manufacture for me?
Just send us the sample, we would have the sample simulated and measured by professional equipment then issue formal drawings for
you , at the same time, we could help you optimize the design according to your demand and related processes’ feasibility.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

How to Select the Right Shaft Coupling for Specific Torque and Speed Requirements
Selecting the appropriate shaft coupling involves considering the specific torque and speed requirements of the application. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the right coupling:
1. Determine Torque and Speed:
Identify the torque and speed requirements of the application. Torque is the rotational force required to transmit power between the shafts, usually measured in Nm (Newton-meters) or lb-ft (pound-feet). Speed refers to the rotational speed of the shafts, typically measured in RPM (revolutions per minute).
2. Calculate Torque Capacity:
Check the torque capacity of various shaft couplings. Manufacturers provide torque ratings for each coupling type and size. Ensure that the selected coupling has a torque capacity that exceeds the application’s torque requirements.
3. Consider Misalignment:
If the application involves significant shaft misalignment due to thermal expansion, vibration, or other factors, consider flexible couplings with good misalignment compensation capabilities. Elastomeric or beam couplings are popular choices for such applications.
4. Assess Operating Speed:
For high-speed applications, choose couplings with high rotational speed ratings to avoid resonance issues and potential coupling failure. High-speed couplings may have specialized designs, such as disk or diaphragm couplings.
5. Evaluate Environmental Conditions:
If the coupling will operate in harsh environments with exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures, select couplings made from corrosion-resistant materials or with protective coatings.
6. Check Torsional Stiffness:
In applications requiring precision motion control, consider couplings with high torsional stiffness to minimize torsional backlash and maintain accurate positioning. Bellows or Oldham couplings are examples of couplings with low torsional backlash.
7. Size and Space Constraints:
Ensure that the selected coupling fits within the available space and aligns with the shaft dimensions. Be mindful of any installation limitations, especially in confined spaces or applications with limited radial clearance.
8. Consult Manufacturer’s Data:
Refer to the manufacturer’s catalogs and technical data sheets for detailed information on each coupling’s torque and speed ratings, misalignment capabilities, materials, and other relevant specifications.
9. Consider Cost and Maintenance:
Compare the costs and maintenance requirements of different couplings. While some couplings may have higher upfront costs, they could offer longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in the long run.
By following these steps and considering the specific torque and speed requirements of your application, you can select the right shaft coupling that will ensure efficient power transmission and reliable performance for your mechanical system.
“`
Can Shaft Couplings Handle Reversing Loads and Shock Loads Effectively?
Yes, shaft couplings are designed to handle both reversing loads and shock loads effectively, but the capability depends on the specific type of coupling and its design.
Reversing Loads:
Many shaft couplings, such as elastomeric couplings, gear couplings, and grid couplings, can handle reversing loads without any issue. Reversing loads occur when the direction of the torque changes periodically, causing the shafts to rotate in opposite directions. The flexibility of elastomeric couplings and the sturdy design of gear and grid couplings allow them to accommodate these reversing loads while maintaining reliable torque transmission.
Shock Loads:
Shock loads are sudden and high-magnitude forces that occur during start-up, sudden stops, or impact events. Shaft couplings with shock-absorbing features, such as elastomeric couplings and grid couplings, excel at handling shock loads. The elastomeric material in elastomeric couplings and the grid element in grid couplings act as shock absorbers, reducing the impact on the connected equipment and minimizing the risk of damage to the coupling itself.
It’s essential to select the appropriate coupling type based on the specific application’s requirements, including the magnitude and frequency of reversing loads and shock loads. Some couplings may have limitations on the amount of shock load they can handle, so it’s crucial to refer to the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines for proper coupling selection.
In heavy-duty applications with high reversing loads and shock loads, it may be necessary to consider specialized couplings designed explicitly for such conditions, like disc couplings or fluid couplings, which can offer even better performance in handling these challenging load conditions.
“`
Diagnosing and Fixing Common Issues with Shaft Couplings
Regular inspection and maintenance of shaft couplings are essential to detect and address common issues that may arise during operation. Here are steps to diagnose and fix some common coupling problems:
1. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:
If you notice unusual noise or excessive vibration during equipment operation, it may indicate misalignment, wear, or damage in the coupling. Check for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks or deformations, and inspect the coupling for proper alignment.
Diagnosis:
Use a vibration analysis tool to measure the vibration levels and identify the frequency of the abnormal vibrations. This can help pinpoint the source of the problem.
Fix:
If misalignment is the cause, adjust the coupling to achieve proper alignment between the shafts. Replace any damaged or worn coupling components, such as spiders or elastomeric inserts, as needed.
2. Excessive Heat:
Feeling excessive heat on the coupling during operation can indicate friction, improper lubrication, or overload conditions.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the coupling and surrounding components for signs of rubbing, lack of lubrication, or overloading.
Fix:
Ensure proper lubrication of the coupling, and check for any interference between the coupling and adjacent parts. Address any overloading issues by adjusting the equipment load or using a coupling with a higher torque capacity.
3. Shaft Movement:
If you observe axial or radial movement in the connected shafts, it may indicate wear or improper installation of the coupling.
Diagnosis:
Check the coupling’s set screws, keyways, or other fastening methods to ensure they are secure and not causing the shaft movement.
Fix:
If the coupling is worn or damaged, replace it with a new one. Ensure proper installation and use appropriate fastening methods to secure the coupling to the shafts.
4. Sheared Shear Pin:
In shear pin couplings, a sheared shear pin indicates overloading or shock loads that exceeded the coupling’s torque capacity.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the shear pin for damage or breakage.
Fix:
Replace the sheared shear pin with a new one of the correct specifications. Address any overloading issues or adjust the equipment to prevent future shearing.
5. Coupling Wear:
Regular wear is normal for couplings, but excessive wear may lead to decreased performance and increased misalignment.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the coupling components for signs of wear, such as worn elastomeric elements or damaged teeth.
Fix:
Replace the worn or damaged components with new ones of the appropriate specifications.
Remember, regular maintenance and periodic inspection are key to diagnosing issues early and preventing severe problems. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and replacement schedules to ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the shaft coupling.
“`

editor by CX 2024-04-12