Product Description
Product Description
Product Parameters
| product | Wd Type Cross Shaft Universal Coupling for Industrial Vehicle |
| material | stainless steel , iron , aluminum ,bronze ,carbon steel ,brass etc . |
| size | ISO standard ,customer requirements |
| kind | expansion sleeve Z1/Z2/Z3/Z4/Z5/Z6/Z7/Z8/Z9/Z10/Z11/Z12/Z13/Z14/Z18/Z19 |
| BORE | Finished bore, Pilot Bore, Special request |
| surface treatment | Carburizing and Quenching,Tempering ,Tooth suface high quenching Hardening,Tempering |
| Processing Method | Molding, Shaving, Hobbing, Drilling, Tapping, Reaming, Manual Chamfering, Grinding etc |
| Heat Treatment | Quenching & Tempering, Carburizing & Quenching, High-frequency Hardening, Carbonitriding…… |
| Package | Wooden Case/Container and pallet, or made-to-order |
| Certificate | ISO9001 ,SGS |
| Machining Process | Gear Hobbing, Gear Milling, Gear Shaping, Gear Broaching, Gear Shaving, Gear Grinding and Gear Lapping |
| Applications | Toy, Automotive, instrument, electrical equipment, household appliances, furniture, mechanical equipment,daily living equipment, electronic sports equipment, , sanitation machinery, market/ hotel equipment supplies, etc. |
| Testing Equipment | Rockwell hardness tester 500RA, Double mesh instrument HD-200B & 3102,Gear measurement center instrument CNC3906T and other High precision detection equipments |
workshop & equipment
Production process
Certifications
Our Advantages
1 . Prioritized Quality
2 .Integrity-based Management
3 .Service Orientation
4 .150+ advanced equipment
5 .10000+ square meter factory area
6 .200+ outstanding employees
7 .90% employees have more than 10 year- working experience in our factory
8 .36 technical staff
9 .certificate ISO 9001 , SGS
10 . Customization support
11 .Excellent after-sales service
shipping
sample orders delivery time:
10-15 working days as usual
15-20 working days in busy season
large order leading time :
20-30 working days as usual
30-40 working days in busy season
FAQ
1. why should you buy products from us not from other suppliers?
We are a 32 year-experience manufacturer on making the gear, specializing in manufacturing varieties of gears, such as helical gear ,bevel gear ,spur gear and grinding gear, gear shaft, timing pulley, rack, , timing pulley and other transmission parts . There are 150+ advanced equipment ,200+ excellent employees ,and 36 technical staff . what’s more ,we have got ISO9001 and SGS certificate .
2 .Do you accept small order?
If your order bearings are our standard size, we accept even 1pcs.
3 .How long is the delivery?
A: Small orders usually takes 10-15 working days,big order usually 20-35 days, depending on orders quantity and whether are standard size.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
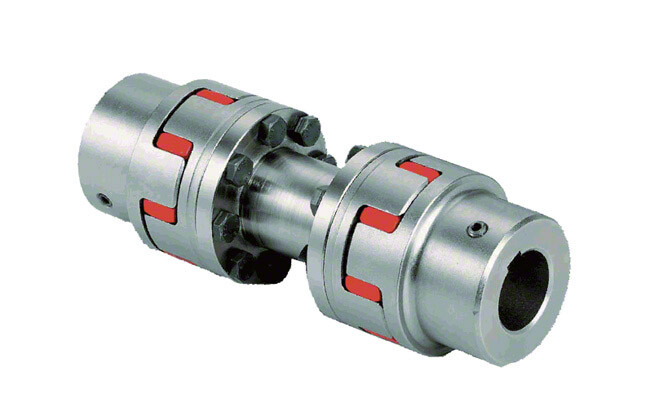

Is It Possible to Replace a Shaft Coupling Without Professional Assistance?
Yes, it is possible to replace a shaft coupling without professional assistance, especially if you have some mechanical knowledge and the necessary tools. However, the ease of replacement can vary depending on the type of coupling and the complexity of the equipment. Here are some general steps to guide you through the process:
1. Safety First:
Before starting any work, ensure that the equipment is turned off and disconnected from the power source. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to protect yourself from potential hazards.
2. Assess the Coupling Type:
Different types of couplings may have specific installation and removal methods. Identify the type of coupling you need to replace, and consult the manufacturer’s documentation or online resources for guidance.
3. Gather Tools and Materials:
Collect the necessary tools, such as wrenches, sockets, and a puller (if required), to safely remove the old coupling. Have the new coupling ready for installation, ensuring it matches the specifications of the old one.
4. Disassembly:
If your coupling is a split or clamp-style coupling, you may be able to replace it without fully disassembling the connected equipment. Otherwise, you may need to remove other components to access the coupling.
5. Remove Fasteners:
Loosen and remove any fasteners, such as set screws, that secure the old coupling to the shafts. Take care not to damage the shafts during this process.
6. Extraction:
If the old coupling is tightly fitted on the shafts, you may need to use a coupling puller or other appropriate extraction tools to safely remove it.
7. Clean and Inspect:
After removing the old coupling, clean the shaft ends and inspect them for any signs of damage or wear. Also, check for any misalignment issues that may have contributed to the old coupling’s failure.
8. Install New Coupling:
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installing the new coupling. Apply appropriate lubrication and ensure the coupling is correctly aligned with the shafts.
9. Fasten Securely:
Tighten the fasteners to the manufacturer’s recommended torque values to securely attach the new coupling to the shafts.
10. Test Run:
After installation, perform a test run of the equipment to ensure the new coupling operates smoothly and without issues.
While it is possible to replace a shaft coupling without professional assistance, keep in mind that some couplings and equipment may require specialized knowledge and tools for safe and proper replacement. If you are uncertain about the process or encounter any difficulties, it is advisable to seek help from a qualified professional or technician to avoid potential damage to the equipment or injury to yourself.
“`
Comparing Shaft Couplings with Other Types of Couplings in Performance
Shaft couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, and their performance characteristics vary depending on the coupling type. Let’s compare shaft couplings with other common types of couplings:
1. Shaft Couplings:
Shaft couplings come in various designs, including flexible and rigid couplings. They are widely used in a broad range of applications due to their ability to transmit torque and accommodate misalignments between rotating shafts. Flexible shaft couplings, with elastomeric or metallic elements, offer good misalignment compensation and damping characteristics. Rigid couplings, on the other hand, provide precise torque transmission and are ideal for applications where shafts are well-aligned.
2. Gear Couplings:
Gear couplings are robust and designed for heavy-duty applications. They consist of two external gear hubs with internal gear teeth that mesh together. Gear couplings can handle high torque, high-speed, and angular misalignment. They are often used in demanding industries such as steel, mining, and paper manufacturing.
3. Grid Couplings:
Grid couplings feature a flexible grid element between the two halves of the coupling. They provide excellent shock absorption and misalignment compensation. Grid couplings are commonly used in pumps, compressors, and other industrial machinery.
4. Disc Couplings:
Disc couplings utilize flexible metallic discs to transmit torque and compensate for misalignment. They offer high torsional stiffness, making them suitable for applications requiring precise motion control, such as robotics and CNC machines.
5. Jaw Couplings:
Jaw couplings consist of two hubs with elastomeric spider inserts. They are easy to install, have good misalignment capabilities, and offer electrical isolation between shafts. Jaw couplings are widely used in light to medium-duty applications.
6. Oldham Couplings:
Oldham couplings have three discs—two outer discs with slots and a central disc with a tongue that fits into the slots. They provide excellent angular misalignment compensation while maintaining constant velocity between shafts. Oldham couplings are commonly used in printing machines and conveyors.
7. Beam Couplings:
Beam couplings are made from a single piece of flexible material with spiral cuts. They offer good misalignment compensation and torsional flexibility, making them suitable for precision equipment like encoders and servo motors.
The choice of coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application, including torque, speed, misalignment compensation, environmental conditions, and space limitations. Each coupling type has its strengths and limitations, and selecting the right coupling is crucial to ensure optimal performance and reliability in the mechanical system.
“`
How Does a Flexible Shaft Coupling Differ from a Rigid Shaft Coupling?
Flexible shaft couplings and rigid shaft couplings are two distinct types of couplings, each designed to serve different purposes in mechanical power transmission. Here are the key differences between the two:
1. Flexibility:
The most significant difference between flexible and rigid shaft couplings is their flexibility. Flexible couplings are designed with elements that can deform or flex to accommodate misalignments between the shafts. This flexibility allows for angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, making them suitable for applications where shafts are not perfectly aligned. In contrast, rigid couplings do not have this flexibility and require precise alignment between the shafts.
2. Misalignment Compensation:
Flexible couplings excel in compensating for misalignments, making them ideal for applications with dynamic conditions or those prone to misalignment due to thermal expansion or vibrations. Rigid couplings, on the other hand, are used in applications where perfect alignment is critical to prevent vibration, wear, and premature failure.
3. Damping Properties:
Flexible couplings, particularly those with elastomeric or flexible elements, offer damping properties, meaning they can absorb and reduce shocks and vibrations. This damping capability helps protect the connected equipment from damage and enhances system reliability. Rigid couplings lack this damping ability and can transmit shocks and vibrations directly between shafts.
4. Torque Transmission:
Both flexible and rigid couplings are capable of transmitting torque from the driving shaft to the driven shaft. However, the torque transmission of flexible couplings can be limited compared to rigid couplings, especially in high-torque applications.
5. Types of Applications:
Flexible couplings find applications in a wide range of industries, especially in situations where misalignment compensation, vibration damping, and shock absorption are essential. They are commonly used in conveyors, pumps, compressors, printing presses, and automation systems. Rigid couplings are used in precision machinery and applications that demand perfect alignment, such as high-speed spindles and certain types of precision equipment.
6. Installation:
Flexible couplings are relatively easier to install due to their ability to accommodate misalignment. On the other hand, rigid couplings require careful alignment during installation to ensure proper functioning and prevent premature wear.
The choice between a flexible and a rigid shaft coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application. If misalignment compensation, damping, and flexibility are critical, a flexible coupling is the preferred choice. If precision alignment and direct torque transmission are essential, a rigid coupling is more suitable.
“`

editor by CX 2024-03-07
China best Kc Type Spline Shaft Roller Chain Rigid Shaft Coupling
Product Description
Product Description
|
Product name |
Chain coupling |
|||
|
Material |
Carbon steel material |
|||
|
Structure |
Roller chain+sprocket+cover |
|||
|
Size |
KC3012, KC4012, KC4014, KC4016, KC5014, KC5016, KC5018, KC6018, KC6571, KC6571, KC8018, KC8571, KC8571, KC1571, KC12018, KC12571, KC16018, KC16571, KC20018, KC20571, KC24026 |
|||
|
Other type |
Flexible coupling |
|||
|
Application |
Shaft transmission |
|||
|
Feature |
High performance, light weight, convenient assembly |
|||
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
ZheJiang Haorongshengye Electrical Equipment Co., Ltd.
1. Was founded in 2008
2. Our Principle:
“Credibility Supremacy, and Customer First”
3. Our Promise:
“High quality products, and Excellent Service”
4. Our Value:
“Being Honesty, Doing the Best, and Long-lasting Development”
5. Our Aim:
“Develop to be a leader in the power transmission parts industry in the world”
|
6.Our services: |
1).Competitive price |
|||
|
2).High quality products |
||||
|
3).OEM service or can customized according to your drawings |
||||
|
4).Reply your inquiry in 24 hours |
||||
|
5).Professional technical team 24 hours online service |
||||
|
6).Provide sample service |
||||
Main products
Machines
Exbihition
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Are There Any Safety Considerations When Using Rigid Couplings in Rotating Machinery?
Yes, there are several safety considerations to keep in mind when using rigid couplings in rotating machinery. While rigid couplings offer various advantages, their use in certain applications requires careful attention to safety measures to prevent accidents and equipment damage. Here are some important safety considerations:
– Secure Installation: Proper installation of rigid couplings is crucial to ensure safety. The coupling must be securely mounted and aligned with the shafts to prevent any slippage or disengagement during operation. Use of appropriate mounting hardware, such as high-strength bolts, is essential to maintain the coupling’s integrity under high-speed and high-torque conditions.
– Shaft Alignment: Accurate shaft alignment is necessary to avoid excessive forces and stress on the connected machinery. Misaligned shafts can lead to uneven loading and increased wear on bearings and other components. Regularly inspect and maintain the shaft alignment to prevent premature failures.
– Preventing Over-Torquing: Applying excessive torque during the installation of rigid couplings can lead to equipment damage and compromise safety. Follow the manufacturer’s torque specifications and use torque-limiting tools to prevent over-torquing and potential failures.
– Protective Guards: In some applications, rotating machinery with rigid couplings may pose a safety hazard to personnel working nearby. Install appropriate protective guards and covers to prevent accidental contact with rotating shafts, minimizing the risk of injury.
– Regular Maintenance: Implement a routine maintenance schedule to inspect the rigid couplings and associated equipment. Check for signs of wear, fatigue, or cracks. Address any issues promptly to avoid potential catastrophic failures.
– Operational Speed Limits: Be aware of the operational speed limits specified by the manufacturer for the rigid couplings. Exceeding these limits can result in significant stress and fatigue on the coupling, leading to failure.
– Appropriate Coupling Selection: Choose the appropriate type and size of rigid coupling for the specific application. Using an undersized coupling can lead to excessive loads and potential failure, while an oversized coupling may not efficiently transmit torque.
– Temperature Considerations: Rigid couplings can experience temperature variations during operation. Ensure that the material and design of the coupling are suitable for the anticipated temperature range of the application to maintain safety and performance.
– Training and Awareness: Provide proper training to personnel working with rotating machinery equipped with rigid couplings. Ensure they are aware of safety procedures and potential hazards associated with the equipment.
Adhering to these safety considerations will help ensure the safe and reliable operation of rotating machinery equipped with rigid couplings. Regular maintenance, correct installation, and diligent attention to safety guidelines will minimize risks and contribute to a safe working environment.

What Industries Commonly Use Rigid Couplings for Power Transmission?
Rigid couplings are widely used in various industries for power transmission applications that require a solid and reliable connection between rotating shafts. Some of the industries that commonly utilize rigid couplings include:
- Manufacturing: In the manufacturing industry, rigid couplings are employed in a wide range of equipment, such as conveyors, mixers, pumps, compressors, and machine tools. These couplings ensure precise power transmission and alignment, making them ideal for maintaining accuracy in manufacturing processes.
- Material Handling: Material handling equipment, including cranes, hoists, and elevators, often rely on rigid couplings to transfer power between shafts efficiently. Rigid couplings provide a robust connection that can handle the heavy loads and continuous operation common in material handling applications.
- Automotive: The automotive industry employs rigid couplings in various automotive systems, including drive shafts, transmissions, and steering systems. Rigid couplings contribute to the overall performance and reliability of these components, ensuring smooth power transfer and minimizing vibration.
- Mining and Construction: In the mining and construction industries, rugged and durable power transmission components are crucial. Rigid couplings are used in equipment like crushers, mills, and heavy-duty conveyors, where they can withstand the harsh conditions and heavy loads commonly found in these applications.
- Oil and Gas: The oil and gas industry often utilizes rigid couplings in pumps, compressors, and drilling equipment. Rigid couplings offer consistent and dependable power transmission, which is essential for critical operations in this sector.
- Marine: In marine applications, such as ship propulsion systems and marine pumps, rigid couplings are used to transmit power between the ship’s engine and various equipment. They can handle the dynamic forces and vibrations encountered in marine environments.
- Aerospace: In aerospace applications, where precision and reliability are paramount, rigid couplings play a role in power transmission between various aircraft components.
Rigid couplings are chosen in these industries for their ability to maintain shaft alignment, resist misalignment, and provide a backlash-free connection. Their robust construction and simple design make them suitable for high torque and high-speed applications, where precision and efficiency are crucial.

Limitations and Disadvantages of Using Rigid Couplings:
Rigid couplings offer several advantages in providing a strong and direct connection between shafts, but they also have certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered in certain applications:
- No Misalignment Compensation: Rigid couplings are designed to provide a fixed connection with no allowance for misalignment between shafts. As a result, any misalignment, even if slight, can lead to increased stress on connected components and cause premature wear or failure.
- Transmit Shock and Vibration: Rigid couplings do not have any damping or vibration-absorbing properties, which means they can transmit shock and vibration directly from one shaft to another. In high-speed or heavy-duty applications, this can lead to increased wear on bearings and other components.
- No Torque Compensation: Unlike flexible couplings, rigid couplings cannot compensate for torque fluctuations or angular displacement between shafts. This lack of flexibility may not be suitable for systems with varying loads or torque requirements.
- Higher Stress Concentration: Rigid couplings can create higher stress concentration at the points of connection due to their inflexibility. This can be a concern in applications with high torque or when using materials with lower fatigue strength.
- More Challenging Installation: Rigid couplings require precise alignment during installation, which can be more challenging and time-consuming compared to flexible couplings that can tolerate some misalignment.
- Increased Wear: The absence of misalignment compensation and vibration absorption can lead to increased wear on connected components, such as bearings, shafts, and seals.
- Not Suitable for High Misalignment: While some rigid couplings have limited ability to accommodate minor misalignment, they are not suitable for applications with significant misalignment, which could lead to premature failure.
Despite these limitations, rigid couplings are still widely used in many applications where precise alignment and a strong, permanent connection are required. However, in systems with significant misalignment, vibration, or shock loads, flexible couplings may be a more suitable choice to protect the connected components and improve overall system performance and longevity.


editor by CX 2024-03-07
China Standard GF Model Spider Coupling Rigid Type Jaw Shaft Coupling
Product Description
Product Description
|
Product name |
Chain coupling |
|||
|
Material |
Carbon steel material |
|||
|
Structure |
Roller chain+sprocket+cover |
|||
|
Size |
KC3012, KC4012, KC4014, KC4016, KC5014, KC5016, KC5018, KC6018, KC6571, KC6571, KC8018, KC8571, KC8571, KC1571, KC12018, KC12571, KC16018, KC16571, KC20018, KC20571, KC24026 |
|||
|
Other type |
Flexible coupling |
|||
|
Application |
Shaft transmission |
|||
|
Feature |
High performance, light weight, convenient assembly |
|||
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
ZheJiang Haorongshengye Electrical Equipment Co., Ltd.
1. Was founded in 2008
2. Our Principle:
“Credibility Supremacy, and Customer First”
3. Our Promise:
“High quality products, and Excellent Service”
4. Our Value:
“Being Honesty, Doing the Best, and Long-lasting Development”
5. Our Aim:
“Develop to be a leader in the power transmission parts industry in the world”
|
6.Our services: |
1).Competitive price |
|||
|
2).High quality products |
||||
|
3).OEM service or can customized according to your drawings |
||||
|
4).Reply your inquiry in 24 hours |
||||
|
5).Professional technical team 24 hours online service |
||||
|
6).Provide sample service |
||||
Main products
Machines
Exbihition
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Common Industries and Use Cases for Rigid Shaft Couplings
Rigid shaft couplings find applications in various industries where precise and torque-resistant shaft connections are required. Some of the common industries that use rigid shaft couplings include:
- Manufacturing: Rigid shaft couplings are widely used in manufacturing machinery, such as lathes, milling machines, and CNC equipment, to provide rigid and accurate power transmission.
- Robotics: Robots and robotic arms often use rigid shaft couplings to ensure precise motion and synchronization between motors and actuators.
- Aerospace: In aerospace applications, rigid couplings are used in aircraft engines, landing gear systems, and control surfaces.
- Automotive: Rigid couplings are utilized in automotive powertrains and drivetrains to transmit torque efficiently and withstand high loads.
- Marine: Marine propulsion systems and shipboard equipment often employ rigid shaft couplings for reliable torque transmission in challenging environments.
- Packaging: Packaging machinery relies on rigid couplings to achieve accurate and synchronized movements in filling, sealing, and labeling operations.
- Steel and Metal Processing: Rigid shaft couplings are essential in steel mills and metal processing equipment to handle heavy loads and maintain precision.
- Printing and Paper: Printing presses and paper handling machinery use rigid couplings to ensure precise registration and consistent operation.
- Mining and Construction: Mining equipment and construction machinery utilize rigid couplings for robust power transmission in harsh environments.
- Energy and Utilities: In power generation plants and utilities, rigid couplings are employed in pumps, compressors, and turbines.
Rigid shaft couplings are versatile and can be found in numerous other industries where precise and efficient power transmission is critical for smooth operation and high-performance machinery.

Are there any safety considerations when using rigid shaft couplings in critical applications?
Yes, when using rigid shaft couplings in critical applications, several safety considerations should be taken into account:
- Torsional Stiffness: Rigid couplings have high torsional stiffness, which can lead to increased stresses and potential failures in the connected equipment. Proper analysis of torsional vibrations and stiffness compatibility with the connected components is crucial.
- Shaft Alignment: Inaccurate shaft alignment can lead to additional loads on the coupling and connected machinery. Precision alignment is essential to prevent premature wear, increased stress, and potential breakdowns.
- Overloading: Exceeding the rated torque capacity of the coupling can result in sudden failures and damage to machinery. It’s essential to operate within the coupling’s specified limits to ensure safe operation.
- Maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance are critical to identify signs of wear, fatigue, or misalignment. Neglecting maintenance can lead to unexpected failures and safety hazards.
- Environmental Factors: Harsh environments, extreme temperatures, and corrosive substances can impact the integrity of rigid couplings. Choosing appropriate materials and protective measures can mitigate these effects.
For critical applications, it’s recommended to work closely with experienced engineers, perform thorough risk assessments, and follow industry standards and best practices to ensure the safe and reliable use of rigid shaft couplings.

What is a Rigid Shaft Coupling and How Does It Work in Mechanical Systems?
A rigid shaft coupling is a type of coupling used to connect two shafts together in a mechanical system. As the name suggests, it is designed to provide a rigid and solid connection between the shafts, without any flexibility or misalignment compensation.
The primary function of a rigid shaft coupling is to transmit torque from one shaft to another efficiently and with minimal backlash. It achieves this by directly connecting the two shafts using a rigid mechanical interface.
Rigid shaft couplings typically consist of two halves with flanges that are bolted or clamped together around the shaft ends. The flanges are precision machined to ensure accurate alignment of the shafts. Some common types of rigid shaft couplings include:
- Sleeve Couplings: These are the simplest type of rigid couplings and consist of a cylindrical sleeve with a bore that fits over the shaft ends. The two shafts are aligned and then secured together using screws or pins.
- Clamp or Split Couplings: These couplings have two halves that are split and bolted together around the shafts. The split design allows for easy installation and removal without the need to disassemble other components of the system.
- Flanged Couplings: Flanged couplings have two flanges with precision machined faces that are bolted together, providing a robust connection.
- Tapered Bushing Couplings: These couplings use a tapered bushing to lock the coupling onto the shafts, creating a secure and concentric connection.
Rigid shaft couplings are commonly used in applications where precise alignment is critical, such as in high-speed machinery, precision instruments, and power transmission systems. Since they do not have any flexibility, they are best suited for applications where shaft misalignment is minimal or can be controlled through accurate alignment during installation.
One of the main advantages of rigid shaft couplings is their ability to provide a direct and efficient transfer of torque, making them suitable for high-torque and high-speed applications. Additionally, their simple design and solid connection make them easy to install and maintain.
However, it’s essential to ensure proper alignment during installation to prevent premature wear and stress on the shafts and other components. In cases where misalignment is expected or unavoidable, flexible couplings like beam couplings, bellows couplings, or jaw couplings are more appropriate, as they can compensate for small misalignments and provide some degree of shock absorption.


editor by CX 2024-03-06
China Custom CNC Spider Jaw Coupling Diameter 20 Length 30high Precision Plum Flexible Shaft Couplings
Product Description
Product Description
DO NOT worry about PRICE, we are manufacturer.
DO NOT worry about QUALITY, we have 16 years experience.
DO NOT worry about AFTER-SALES, we are 24 hours online.
Features :
1. The main body is made of high strength aluminum alloy
2. Zero backlash, suitable for forward and reverse rotation
3.Colloid is made of polyurethane, which has good wear resistance
4.Oil resistance and electrical insulation, the middle elasticbody can absorb vibration
5. Compensate radial, angular and axial deviations
6. Removable design for easy installation
7. Tightening method of positioning screw
Suitable for a wide range of devices
CNC lathes Optical inspection equipment
Module slider Servo motor
Company Profile
Certifications
Packaging & Shipping
All products will be well packed with standard export wooden case or
cartons.
Shafts packed with paper tube or plastic bag;
Linear guideways or lead screwswrapped with film or plastic bag;
Guarantee well protected against dampness,moisture, rust and shock.
Our Advantages
FAQ
Q1: Do you have a catalogue? Can you send me the catalogue to have a check of all your products?
A: Yes , We have product catalogue.Please contact us on line or send an Email to sending the catalogue.
Q2: I can’t find the product on your catalogue, can you make this product for me?
A: Our catalogue shows most of our products,but not all.So just let us know what product do you need.
Q3 : Can you make customized products and customized packing?
A: Yes.We made a lot of customized products for our customer before.And we have many moulds for our customers already.About customized packing,we can put your Logo or other info on the packing.There is no problem.Just have to point out that ,it will cause some additional cost.
Q4: Can you provide samples ? Are the samples free ?
A: Yes,we can provide samples.Normally,we provide 1-2pcs free samples for test or quality checking.But you have to pay for the shipping cos.If you need many items, or need more qty for each item,we will charge for the samples.
Any requirements or question,Welcome to “Send” us an e-mail Now!
It’s our great honor to do services for you! You also can get the FREE SAMPLES soon.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Specific Safety Precautions When Working with Shaft Couplings
Working with shaft couplings involves handling rotating machinery and mechanical components. To ensure the safety of personnel and prevent accidents, specific safety precautions should be followed during installation, maintenance, and operation:
1. Lockout-Tagout (LOTO):
Prior to any work on machinery involving couplings, implement a lockout-tagout procedure to isolate the equipment from its power source. This ensures that the machinery cannot be accidentally energized during maintenance or repair, protecting workers from potential hazards.
2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety goggles, gloves, and appropriate clothing, when working with shaft couplings. PPE helps protect against potential hazards such as flying debris, sharp edges, or contact with moving parts.
3. Proper Training and Supervision:
Only trained and authorized personnel should work with shaft couplings. Ensure that workers have the necessary knowledge and experience to handle the equipment safely. Adequate supervision may be required, especially for less-experienced personnel.
4. Inspection and Maintenance:
Regularly inspect shaft couplings and associated components for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Address any issues promptly to prevent equipment failure and potential accidents.
5. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines for installation, operation, and maintenance of the specific coupling model. Improper use or deviation from recommended procedures may compromise safety and void warranties.
6. Avoid Overloading:
Do not exceed the torque and speed limits specified by the coupling manufacturer. Overloading a coupling can lead to premature failure and pose safety risks to operators and nearby equipment.
7. Shaft Guards and Enclosures:
Install appropriate guards and enclosures to prevent accidental contact with rotating shafts and couplings. These safety measures help reduce the risk of entanglement and injuries.
8. Zero Energy State:
Ensure that all stored energy in the equipment, such as compressed air or hydraulic pressure, is released and the equipment is in a zero energy state before starting work.
9. Avoid Loose Clothing and Jewelry:
Remove or secure loose clothing, jewelry, and other items that could get caught in moving parts.
10. Maintain a Clean Work Area:
Keep the work area clean and free from clutter to avoid tripping hazards and facilitate safe movement around the machinery.
By following these safety precautions, personnel can minimize the risks associated with working with shaft couplings and create a safer working environment for everyone involved.
“`
Real-World Examples of Shaft Coupling Applications in Different Industries
Shaft couplings play a crucial role in various industries by connecting rotating shafts and transmitting torque between them. Here are some real-world examples of shaft coupling applications in different industries:
1. Manufacturing Industry:
In manufacturing plants, shaft couplings are used in various equipment such as conveyor systems, pumps, compressors, and mixers. For example, in a conveyor system, shaft couplings connect the motor shaft to the conveyor belt, allowing efficient material handling and transportation.
2. Oil and Gas Industry:
The oil and gas industry utilizes shaft couplings in applications like drilling rigs, pumps, and generators. In drilling rigs, couplings connect the motor to the drill shaft, enabling the drilling process.
3. Marine Industry:
In the marine industry, shaft couplings are found in propulsion systems, water pumps, and winches. They connect the ship’s engine to the propeller shaft, providing the necessary torque for propulsion.
4. Power Generation:
Power plants use shaft couplings in turbines, generators, and cooling systems. For instance, in a steam turbine, couplings connect the turbine to the electrical generator, allowing the conversion of steam energy into electrical power.
5. Aerospace Industry:
Aerospace applications use shaft couplings in aircraft engines, landing gear systems, and auxiliary power units. Couplings enable power transmission between different components of the aircraft systems.
6. Automotive Industry:
In vehicles, shaft couplings are present in the drivetrain, steering systems, and transmission. For example, in a car’s transmission system, couplings connect the engine to the gearbox, enabling smooth gear changes and power transmission to the wheels.
7. Mining Industry:
The mining industry relies on shaft couplings in heavy-duty machinery such as crushers, conveyor belts, and pumps. Couplings connect motors to various mining equipment, facilitating material extraction and transportation.
8. Agriculture:
Agricultural machinery like tractors and harvesters use shaft couplings to connect the engine to implements such as plows, harvesters, and irrigation pumps.
These examples demonstrate the wide-ranging applications of shaft couplings across industries. In each case, the specific coupling type is chosen based on factors such as torque requirements, misalignment compensation, environmental conditions, and load characteristics to ensure reliable and efficient operation.
“`
How Does a Flexible Shaft Coupling Differ from a Rigid Shaft Coupling?
Flexible shaft couplings and rigid shaft couplings are two distinct types of couplings, each designed to serve different purposes in mechanical power transmission. Here are the key differences between the two:
1. Flexibility:
The most significant difference between flexible and rigid shaft couplings is their flexibility. Flexible couplings are designed with elements that can deform or flex to accommodate misalignments between the shafts. This flexibility allows for angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, making them suitable for applications where shafts are not perfectly aligned. In contrast, rigid couplings do not have this flexibility and require precise alignment between the shafts.
2. Misalignment Compensation:
Flexible couplings excel in compensating for misalignments, making them ideal for applications with dynamic conditions or those prone to misalignment due to thermal expansion or vibrations. Rigid couplings, on the other hand, are used in applications where perfect alignment is critical to prevent vibration, wear, and premature failure.
3. Damping Properties:
Flexible couplings, particularly those with elastomeric or flexible elements, offer damping properties, meaning they can absorb and reduce shocks and vibrations. This damping capability helps protect the connected equipment from damage and enhances system reliability. Rigid couplings lack this damping ability and can transmit shocks and vibrations directly between shafts.
4. Torque Transmission:
Both flexible and rigid couplings are capable of transmitting torque from the driving shaft to the driven shaft. However, the torque transmission of flexible couplings can be limited compared to rigid couplings, especially in high-torque applications.
5. Types of Applications:
Flexible couplings find applications in a wide range of industries, especially in situations where misalignment compensation, vibration damping, and shock absorption are essential. They are commonly used in conveyors, pumps, compressors, printing presses, and automation systems. Rigid couplings are used in precision machinery and applications that demand perfect alignment, such as high-speed spindles and certain types of precision equipment.
6. Installation:
Flexible couplings are relatively easier to install due to their ability to accommodate misalignment. On the other hand, rigid couplings require careful alignment during installation to ensure proper functioning and prevent premature wear.
The choice between a flexible and a rigid shaft coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application. If misalignment compensation, damping, and flexibility are critical, a flexible coupling is the preferred choice. If precision alignment and direct torque transmission are essential, a rigid coupling is more suitable.
“`

editor by CX 2024-03-06
China Standard Carved Exquisitely Stainless Steel Rigid Internal Thread NPT Full Coupling
Product Description
Product Details
| Product Name | Female Thread Full Coupling |
| Material | Stainless steel: 201,TP304,TP316, TP304L, TP316L, 304L, 316L, TP321, TP310S, 904L etc. Carbon steel: A105, Q234, Q235, X52, F60,F70, Y60, Y70 etc. Duplex steel: 2205(S31803), S32205, 2507(S2750), S3276 etc. Other special: C70600, 254MO |
| Connection | Male, Female |
| Size | 1/8″, 1/4″, 3/8″, 1/2″, 3/4″, 1″, 1-1/4″, 1-1/2″, 2-1/2″, 3″, 4 ” etc |
| Standard | ASME, ANSI, MSS-SP, GB etc |
| Application | Pipe lines connection of water, steam, air, gas, oil etc |
| Technics | Forged, Casting |
Our Advantages
01. Customization
Get a perfect, custom pipe coupling
02. Advanced Technique
Mature and advanced equipment and professional test engineers ensure high quality products
03. Excellent Quality
Real material with uniform wall thickness
Smooth surface
Strong tensile strength
Corrosion resistance
Long-term use
Appilcation
Transportation
About Us
Founded in 2571, our company, HangZhou Dejia Special Steel Co., Ltd is specialized in producing various products such as elbows, tees, reducers, caps, flanges and valves. We can produce products according to National standard, American standard etc. It’s our feature that we can produce products of any size ad per customers’ special demands.
Our company CHINAMFG on honesty, continuity and transparency with our clients. We would like to cooperate with global customers and make the good protection project in world market.
Why choose our company? We features scientific and rational design, advanced production process, quality manufacturing materials, comprehensive security protection and first-class after-sales service.
FAQ
Q: What are your main products?
A: We specialize in producing a wide range of valves, elbows, flanges, Tee, Cross, gaskets etc.
Q: How long is your delivery time?
A:Usually it’s 15-30 days all the best or it’s more than 30 days according to the quantity.
Q: Do you provide samples? Free or charge?
A:Yes, we’d like to offer you samples but you have to cough up dough for shipping.
Q: How do you guarantee the quality of your products?
A: Before mass production, a few products made by our engineers for conduct tests. All products must be checked before shipping.
Q: How about your service?
A: Xihu (West Lake) Dis.g to the concept of ” Service Supremacy”, we have pre-sale service, on-purchase service and after-sales service.
Q: About packing?
A: Depending on the properties of the product, choose its appropriate packaging to protect the item from damage and allow you to purchase at ease.
Q: About color difference?
A: All products are shot in real objects, and there will be a slight degree of color difference between the real thing and the picture due to the shooting light, the color value bias of the display, and the individual’s understanding of color. Colour is subject to the goods received.
Q: What size can your company produce?
A: We have all the common sizes on the market. In addition, we can also customize according to your needs, whether its size or material.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can Rigid Couplings Handle Misalignment Between Shafts?
Rigid couplings are not designed to handle misalignment between shafts. Unlike flexible couplings that can accommodate slight misalignment through their bending or elastic properties, rigid couplings are intended to provide a fixed and immovable connection between two shafts. As a result, any misalignment between the shafts can lead to increased stress and uneven loading on connected components.
It is essential to ensure precise alignment when using rigid couplings to avoid premature wear and failure of the system. The shafts must be perfectly aligned in both the axial and angular directions before installing the rigid coupling. Proper alignment helps distribute the load evenly and reduces stress concentration on specific areas, such as bearings and keyways.
If a system requires some level of misalignment compensation due to factors like thermal expansion or slight shaft deflection, a flexible coupling should be considered instead. Flexible couplings can tolerate small degrees of angular and axial misalignment while still transmitting torque efficiently and protecting the connected equipment from excessive stress and wear.
In summary, rigid couplings are best suited for applications where precise shaft alignment can be achieved and maintained, while flexible couplings are more appropriate for systems with potential misalignment or other dynamic factors that require some degree of flexibility.

Can Rigid Couplings Be Used in Applications with Varying Operating Temperatures?
Rigid couplings are versatile mechanical components that can be used in a wide range of applications, including those with varying operating temperatures. However, the selection of the appropriate material for the rigid coupling is crucial to ensure its reliable performance under different temperature conditions.
Material Selection: The choice of material for the rigid coupling depends on the specific operating temperature range of the application. Common materials used in manufacturing rigid couplings include steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, among others. Each material has its own temperature limitations:
– Steel: Rigid couplings made from steel are suitable for applications with moderate to high temperatures. Steel couplings can handle temperatures ranging from -40°C to around 300°C, depending on the specific grade of steel used.
– Stainless Steel: Stainless steel rigid couplings offer higher corrosion resistance and can be used in applications with more demanding temperature environments. They can withstand temperatures from -80°C to approximately 400°C.
– Aluminum: Aluminum rigid couplings are commonly used in applications with lower temperature requirements, typically ranging from -50°C to around 120°C.
Thermal Expansion: When selecting a rigid coupling for an application with varying temperatures, it is essential to consider thermal expansion. Different materials have different coefficients of thermal expansion, meaning they expand and contract at different rates as the temperature changes. If the operating temperature fluctuates significantly, the thermal expansion of the rigid coupling and the connected components must be carefully accounted for to avoid issues with misalignment or binding.
Extreme Temperature Environments: For applications with extremely high or low temperatures beyond the capabilities of traditional materials, specialized high-temperature alloys or composites may be required. These materials can withstand more extreme temperature conditions but may come with higher costs.
Lubrication: The choice of lubrication can also play a role in the suitability of rigid couplings for varying temperature applications. In high-temperature environments, consideration should be given to using high-temperature lubricants that can maintain their effectiveness and viscosity at elevated temperatures.
In conclusion, rigid couplings can indeed be used in applications with varying operating temperatures, but careful material selection, consideration of thermal expansion, and appropriate lubrication are essential to ensure reliable and efficient performance under changing temperature conditions.

Limitations and Disadvantages of Using Rigid Couplings:
Rigid couplings offer several advantages in providing a strong and direct connection between shafts, but they also have certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered in certain applications:
- No Misalignment Compensation: Rigid couplings are designed to provide a fixed connection with no allowance for misalignment between shafts. As a result, any misalignment, even if slight, can lead to increased stress on connected components and cause premature wear or failure.
- Transmit Shock and Vibration: Rigid couplings do not have any damping or vibration-absorbing properties, which means they can transmit shock and vibration directly from one shaft to another. In high-speed or heavy-duty applications, this can lead to increased wear on bearings and other components.
- No Torque Compensation: Unlike flexible couplings, rigid couplings cannot compensate for torque fluctuations or angular displacement between shafts. This lack of flexibility may not be suitable for systems with varying loads or torque requirements.
- Higher Stress Concentration: Rigid couplings can create higher stress concentration at the points of connection due to their inflexibility. This can be a concern in applications with high torque or when using materials with lower fatigue strength.
- More Challenging Installation: Rigid couplings require precise alignment during installation, which can be more challenging and time-consuming compared to flexible couplings that can tolerate some misalignment.
- Increased Wear: The absence of misalignment compensation and vibration absorption can lead to increased wear on connected components, such as bearings, shafts, and seals.
- Not Suitable for High Misalignment: While some rigid couplings have limited ability to accommodate minor misalignment, they are not suitable for applications with significant misalignment, which could lead to premature failure.
Despite these limitations, rigid couplings are still widely used in many applications where precise alignment and a strong, permanent connection are required. However, in systems with significant misalignment, vibration, or shock loads, flexible couplings may be a more suitable choice to protect the connected components and improve overall system performance and longevity.


editor by CX 2024-03-06
China Hot selling High Rigid Shaft Stainless Steel Bellow Flexible Coupling for Motors Spring
Product Description
| Item No. | φD | L | L1 | L2 | M | Tighten the strength(N.m) |
| SG7-6-40- | 40 | 55 | 19 | 24 | M3 | 3 |
| SG7-6-55- | 55 | 65 | 22 | 31 | M4 | 6 |
| SG7-6-65- | 65 | 76 | 27 | 37 | M5 | 8 |
| SG7-6-82- | 82 | 88 | 32 | 41 | M6 | 10 |
| SG7-6-90- | 90 | 88 | 32 | 41 | M6 | 12 |
11111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111
1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111112111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111
| Item No. | Rated torque | Maximum Torque | Max Speed | Inertia Moment | N.m rad | RRO | Tilting Tolerance | End-play | Weight:(g) |
| SG7-6-40- | 13N.m | 26N.m | 8000prm | 9×10-5kg.m² | 15×103N.m/rad | 0.15mm | 2c | 1mm | 231 |
| SG7-6-55- | 28N.m | 56N.m | 6000prm | 2.9×10-4kg.m² | 28×103N.m/rad | 0.2mm | 2c | 1.5mm | 485 |
| SG7-6-65- | 60N.m | 120N.m | 5000prm | 4.6×10-4kg.m² | 55×103N.m/rad | 0.25mm | 2c | 1.5mm | 787 |
| SG7-6-82- | 150N.m | 300N.m | 4500prm | 1.1×10-3kg.m² | 110×103N.m/rad | 0.28mm | 2c | 1.5mm | 1512 |
| SG7-6-90- | 200N.m | 400N.m | 4000prm | 2×10-3kg.m² | 140×103N.m/rad | 0.3mm | 2c | 1.5mm | 1800 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

How to Properly Install a Rigid Shaft Coupling for Optimal Performance and Reliability
Proper installation of a rigid shaft coupling is essential to ensure optimal performance and reliability in mechanical systems. Here are the steps to follow for a successful installation:
- Shaft Preparation: Ensure that the shafts to be connected are clean, smooth, and free from any burrs or contaminants that could affect the coupling’s performance.
- Alignment: Align the two shafts accurately to minimize misalignment during installation. The alignment process is critical as any misalignment can lead to premature wear and reduced coupling efficiency.
- Fitment: Choose the appropriate size of the rigid shaft coupling that matches the shaft diameters. Carefully slide the coupling onto one shaft at a time.
- Fastening: For one-piece rigid couplings, ensure that the coupling is fitted snugly onto both shafts. For two-piece couplings, bolt the two halves together securely around the shafts.
- Tightening: Use the recommended torque value and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to tighten the coupling bolts properly. Over-tightening can cause distortion, while under-tightening can lead to slippage and reduced torque transmission.
- Inspection: After installation, inspect the coupling to ensure that it is centered and aligned correctly. Check for any signs of misalignment or interference during rotation.
- Lubrication: Some rigid couplings may require lubrication at the friction points to reduce wear and friction. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and types.
- Load Testing: Perform load testing on the system to verify the coupling’s performance and check for any unusual vibrations or noises during operation.
- Regular Maintenance: Include the rigid coupling in your regular maintenance schedule. Periodically check for signs of wear, misalignment, or damage, and replace the coupling if necessary.
By following these installation steps and best practices, you can ensure that the rigid shaft coupling operates optimally, providing reliable torque transmission and contributing to the overall efficiency and longevity of the mechanical system.

How do rigid shaft couplings compare to flexible couplings in terms of torque transmission and misalignment handling?
Rigid shaft couplings and flexible couplings differ in their ability to handle torque transmission and misalignment. Here’s a comparison of these aspects:
- Torque Transmission: Rigid shaft couplings offer excellent torque transmission due to their solid construction. They efficiently transmit high torque loads without significant power loss. Flexible couplings, on the other hand, may have some inherent power loss due to their flexibility.
- Misalignment Handling: Flexible couplings excel in compensating for misalignment between shafts. They can accommodate angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, reducing stress on connected equipment. Rigid couplings are limited in their misalignment compensation, primarily handling minimal misalignments. Significant misalignment can lead to increased wear and premature failure.
The choice between rigid and flexible couplings depends on the specific requirements of the application. If precise torque transmission and minimal misalignment are priorities, rigid couplings may be suitable. However, if misalignment compensation and vibration dampening are crucial, flexible couplings are a better option.

What is a Rigid Shaft Coupling and How Does It Work in Mechanical Systems?
A rigid shaft coupling is a type of coupling used to connect two shafts together in a mechanical system. As the name suggests, it is designed to provide a rigid and solid connection between the shafts, without any flexibility or misalignment compensation.
The primary function of a rigid shaft coupling is to transmit torque from one shaft to another efficiently and with minimal backlash. It achieves this by directly connecting the two shafts using a rigid mechanical interface.
Rigid shaft couplings typically consist of two halves with flanges that are bolted or clamped together around the shaft ends. The flanges are precision machined to ensure accurate alignment of the shafts. Some common types of rigid shaft couplings include:
- Sleeve Couplings: These are the simplest type of rigid couplings and consist of a cylindrical sleeve with a bore that fits over the shaft ends. The two shafts are aligned and then secured together using screws or pins.
- Clamp or Split Couplings: These couplings have two halves that are split and bolted together around the shafts. The split design allows for easy installation and removal without the need to disassemble other components of the system.
- Flanged Couplings: Flanged couplings have two flanges with precision machined faces that are bolted together, providing a robust connection.
- Tapered Bushing Couplings: These couplings use a tapered bushing to lock the coupling onto the shafts, creating a secure and concentric connection.
Rigid shaft couplings are commonly used in applications where precise alignment is critical, such as in high-speed machinery, precision instruments, and power transmission systems. Since they do not have any flexibility, they are best suited for applications where shaft misalignment is minimal or can be controlled through accurate alignment during installation.
One of the main advantages of rigid shaft couplings is their ability to provide a direct and efficient transfer of torque, making them suitable for high-torque and high-speed applications. Additionally, their simple design and solid connection make them easy to install and maintain.
However, it’s essential to ensure proper alignment during installation to prevent premature wear and stress on the shafts and other components. In cases where misalignment is expected or unavoidable, flexible couplings like beam couplings, bellows couplings, or jaw couplings are more appropriate, as they can compensate for small misalignments and provide some degree of shock absorption.


editor by CX 2024-03-05
China high quality Swp-C Short Cardan Shaft Coupling Flexible Coupling Cross Quick Coupling Universal Joint Coupling Flexible Coupling
Product Description
SWP-C Short Universal Joint Coupling Without Flex Type
Description:
The SWP-C short non bending universal joint coupling is a universal joint designed specifically for short distance applications that do not require length compensation. It is a non flexible coupling, which means it does not allow any movement between the 2 connected shafts. This makes it very suitable for applications where accuracy is important, such as machine tools. The SWP-C short flexible universal joint coupling consists of 3 magnetic yokes, which are connected by 2 cross joints. The yoke is made of high-strength steel, and the cross joint is made of high-quality bearings. This material combination ensures that the coupling is sturdy and durable, and can withstand the high loads and stresses often encountered in industrial applications. SWP-C short type flexible universal joint couplings are available in various sizes to adapt to different shaft diameters. It also offers multiple options, such as different yoke styles and different types of bearings. This makes it possible to find perfect coupling for any application.
SWP-C short type flexible universal coupling application:
The following are some applications where SWP-C short type flexible universal joint couplings can be used:
(1) Machine tool: SWP-C short flexible universal joint coupling can be used to connect the motor to the spindle, ensuring that the spindle rotates at precise speed. This is crucial for applications where accuracy is crucial, such as in CNC machining.
(2) Conveyor: SWP-C short type flexible universal joint coupling can be used to connect the drive shaft to the conveyor belt, ensuring that the conveyor belt moves at a constant speed. This is important for applications where conveyor belts need to move at a consistent rate, such as in food processing or packaging.
(3) Elevator: SWP-C short type flexible universal joint coupling can be used to connect the motor to the elevator cable, ensuring smooth and safe operation of the elevator. This is crucial for passenger safety and the smooth operation of the elevator.
(4) Crane: SWP-C short type flexible universal joint coupling can be used to connect the crane to the boom, ensuring smooth and safe lifting of the load. This is important for the safety of both the operator and the load.
(5) Wind turbine: SWP-C short type flexible universal joint coupling can be used to connect the generator to the turbine shaft, ensuring that the generator generates electricity at a constant rate. This is crucial for the effective operation of wind turbines.
The SWP-C short non bending universal joint coupling is a universal and reliable coupling that can be used in various applications. If you are looking for a coupling that can handle high loads and stresses, and provide accurate and stable power transmission, then SWP-C coupling is a good choice.
Packing & shipping:
1 Prevent from damage.
2. As customers’ requirements, in perfect condition.
3. Delivery : As per contract delivery on time
4. Shipping : As per client request. We can accept CIF, Door to Door etc. or client authorized agent we supply all the necessary assistant.
FAQ:
Q 1: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We are a professional manufacturer specializing in manufacturing various series of couplings.
Q 2:Can you do OEM?
Yes, we can. We can do OEM & ODM for all the customers with customized artworks in PDF or AI format.
Q 3:How long is your delivery time?
Generally, it is 20-30 days if the goods are not in stock. It is according to quantity.
Q 4: How long is your warranty?
A: Our Warranty is 12 months under normal circumstances.
Q 5: Do you have inspection procedures for coupling?
A:100% self-inspection before packing.
Q 6: Can I have a visit to your factory before the order?
A: Sure, welcome to visit our factory. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can Shaft Couplings Compensate for Angular, Parallel, and Axial Misalignments?
Yes, shaft couplings are designed to compensate for different types of misalignments between rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. They can handle the following types of misalignments:
- Angular Misalignment: This occurs when the shafts are not parallel and have an angle between them. Flexible couplings, such as elastomeric, beam, or Oldham couplings, can accommodate angular misalignments by allowing slight angular movement between the shafts while transmitting torque.
- Parallel Misalignment: This happens when the shafts are not collinear, resulting in axial displacement. Flexible couplings with lateral flexibility, like elastomeric or bellows couplings, can handle parallel misalignment by allowing limited lateral movement between the shafts.
- Radial Misalignment: Radial misalignment occurs when the shafts have lateral displacement but remain parallel. Flexible couplings, such as jaw or grid couplings, can absorb radial misalignment by permitting some lateral deflection while transmitting torque.
It is essential to note that while shaft couplings can compensate for misalignments to some extent, they do have their limits. The magnitude of misalignment they can handle depends on the type and design of the coupling. Exceeding the specified misalignment capabilities of a coupling can lead to premature wear, reduced efficiency, and possible coupling failure.
Therefore, when selecting a shaft coupling for an application, it is crucial to consider the expected misalignment and choose a coupling that can accommodate the anticipated misalignment range. Additionally, maintaining proper alignment through regular maintenance and periodic inspections is essential to ensure the coupling’s optimal performance and extend its service life.
“`
Explaining the Concept of Backlash and How It Affects Shaft Coupling Performance
Backlash is the angular movement or play between the mating components of a mechanical system when the direction of motion is reversed. In the context of shaft couplings, backlash refers to the free rotational movement between the connected shafts before the coupling transmits torque from one shaft to the other.
Backlash occurs in certain coupling designs that have features allowing relative movement between the coupling’s mating parts. Common coupling types that may exhibit some degree of backlash include elastomeric couplings (such as jaw couplings), gear couplings, and Oldham couplings.
How Backlash Affects Shaft Coupling Performance:
1. Loss of Precision: In applications requiring precise motion control, backlash can lead to inaccuracies and reduced positional accuracy. For example, in CNC machines or robotics, any rotational play due to backlash can result in positioning errors and decreased machining or movement precision.
2. Reversal Impact: When a reversing load is applied to a coupling, the presence of backlash can lead to a brief period of rotational play before the coupling re-engages, causing a momentary jolt or impact. This impact can lead to increased stress on the coupling and connected components, potentially reducing their lifespan.
3. Dynamic Response: Backlash can affect the dynamic response of the mechanical system. In systems requiring rapid acceleration or deceleration, the initial play due to backlash may create a delay in torque transmission, affecting the system’s responsiveness.
4. Noise and Vibration: Backlash can cause noise and vibration in the system, leading to increased wear and potential fatigue failure of components.
5. Misalignment Compensation: In some flexible coupling designs, a certain amount of backlash is intentionally incorporated to allow for misalignment compensation. While this is a beneficial feature, excessive backlash can compromise the coupling’s performance.
Minimizing Backlash:
Manufacturers often design couplings with specific features to minimize backlash. For instance, some gear couplings employ crowned gear teeth to reduce clearance, while elastomeric couplings may have preloaded elastomeric elements. Precision couplings like zero-backlash or torsionally rigid couplings are engineered to eliminate or minimize backlash for applications requiring high accuracy and responsiveness.
When selecting a coupling, it’s essential to consider the application’s specific requirements regarding precision, speed, reversing loads, and misalignment compensation, as these factors will determine the acceptable level of backlash for optimal performance.
“`
What is a Shaft Coupling and Its Role in Mechanical Power Transmission?
A shaft coupling is a mechanical device used to connect two shafts together at their ends, allowing for the transmission of mechanical power from one shaft to another. It serves as an essential component in various machinery and industrial applications where rotational motion needs to be transmitted between two shafts that are not perfectly aligned or are separated by a distance.
The role of a shaft coupling in mechanical power transmission includes the following:
1. Power Transmission:
The primary function of a shaft coupling is to transmit power from a driving shaft to a driven shaft. When the driving shaft rotates, the coupling transfers the rotational motion to the driven shaft, enabling the driven equipment to perform its intended function.
2. Misalignment Compensation:
In real-world applications, it is often challenging to achieve perfect alignment between two shafts due to manufacturing tolerances or dynamic conditions. Shaft couplings are designed to accommodate different types of misalignment, such as angular, parallel, and axial misalignment, allowing the equipment to function smoothly even when the shafts are not perfectly aligned.
3. Vibration Damping:
Shaft couplings can help dampen vibrations and shocks caused by uneven loads or sudden changes in the operating conditions. This vibration damping feature protects the connected components from damage and contributes to the overall system’s reliability.
4. Overload Protection:
In some cases, a shaft coupling can act as a safety device by providing overload protection. When the connected machinery experiences excessive torque or shock loads, certain types of couplings can disengage or shear to prevent damage to the equipment.
5. Torque and Speed Conversion:
Shaft couplings can be designed to provide torque and speed conversion between the driving and driven shafts. This allows for adaptation to different operating conditions and varying torque requirements in the connected machinery.
6. Flexible Connection:
Shaft couplings with flexible elements, such as elastomeric inserts or flexible discs, provide a flexible connection that can absorb shocks and misalignments. This flexibility helps reduce stress on the connected equipment and extends its lifespan.
Overall, shaft couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, enabling the efficient transfer of rotational motion between shafts while accommodating misalignments and providing protection against overloads and vibrations. The selection of the appropriate coupling type and design depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the type of misalignment, torque capacity, and operating conditions.
“`

editor by CX 2024-03-05
China Good quality Kc Type Spline Shaft Couplings Roller Chain Coupling Rigid Shaft Coupling
Product Description
KC Type Spline Shaft Couplings Roller Chain Coupling Rigid Shaft Coupling
Product Description
Chain coupling: It comprises 2 sprockets, 1 double-row chain, and a yellow shell.
The chain coupling comprises a double-row roller chain and a pair of connecting sprockets. The connection and disassembly functions are completed through the joint of the chain. Our own factory with quality assurance produces the sprocket. Our couplings are characterized by compact structure, sturdiness, durability, safety, and easy installation.
Detailed Photos
Product Parameters
| SIZE | BORE | Pilot | A | d | O | L | I | S | B | C | BOLT | TORQUE ARM(Nm) | SPEED(rpm) | (kg.cm2) | WEIGHT |
| (kg) | |||||||||||||||
| 3012 | 12-16 | 12 | 69 | 25 | 45 | 64.8 | 29.8 | 5.2 | 63 | 10.2 | 6M | 190 | 5000 | 3.7 | 0.4 |
| 4012 | 12-22 | 12 | 77 | 33 | 62 | 79.4 | 36 | 7.4 | 72 | 14.4 | 6M | 249 | 4800 | 5.5 | 0.8 |
| 4014 | 12-28 | 12 | 84 | 43 | 69 | 79.4 | 36 | 7.4 | 75 | 14.4 | 6M | 329 | 4800 | 9.7 | 1.1 |
| 4016 | 14-32 | 14 | 92 | 48 | 77 | 87.4 | 40 | 7.4 | 75 | 14.4 | 6M | 429 | 4800 | 14.4 | 1.4 |
| 5014 | 15-35 | 14 | 101 | 53 | 86 | 99.7 | 45 | 9.7 | 85 | 18.1 | 8M | 620 | 3600 | 28 | 2.2 |
| 5016 | 16-40 | 16 | 111 | 60 | 93 | 99.7 | 45 | 9.7 | 85 | 18.1 | 8M | 791 | 3600 | 37 | 2.7 |
| 5018 | 16-45 | 16 | 122 | 70 | 106 | 99.7 | 45 | 9.7 | 85 | 18.1 | 8M | 979 | 3000 | 56.3 | 3.8 |
| 6018 | 20-56 | 20 | 142 | 85 | 127 | 123.5 | 56 | 11.5 | 105 | 22.8 | 10M | 1810 | 2500 | 137.3 | 6.2 |
| 6571 | 20-60 | 20 | 158 | 98 | 139 | 123.5 | 56 | 11.5 | 105 | 22.8 | 10M | 2210 | 2500 | 210.2 | 7.8 |
| 6571 | 20-71 | 20 | 168 | 110 | 151 | 123.5 | 56 | 11.5 | 117 | 22.8 | 10M | 2610 | 2500 | 295 | 10.4 |
| 8018 | 20-80 | 20 | 190 | 110 | 169 | 141.2 | 63 | 15.2 | 129 | 29.3 | 12M | 3920 | 2000 | 520 | 12.7 |
| 8571 | 20-90 | 20 | 210 | 121 | 185 | 145.2 | 65 | 15.2 | 137 | 29.3 | 12M | 4800 | 2000 | 812.4 | 16 |
| 8571 | 20-100 | 20 | 226 | 140 | 202 | 157.2 | 71 | 15.2 | 137 | 29.3 | 12M | 5640 | 1800 | 1110 | 20.2 |
| 1571 | 25-110 | 25 | 281 | 160 | 233 | 178.8 | 80 | 18.8 | 153 | 35.8 | 12M | 8400 | 1800 | 2440 | 33 |
| 12018 | 35-125 | 35 | 307 | 170 | 256 | 202.7 | 90 | 22.7 | 181 | 45.4 | 12M | 12700 | 1500 | 3940 | 47 |
| 12571 | 35-140 | 35 | 357 | 210 | 304 | 222.7 | 100 | 22.7 | 181 | 45.5 | 12M | 18300 | 1250 | 7810 | 72 |
| 16018 | 63-160 | 35 | 375 | 228 | 340 | 254.1 | 112 | 30.1 | 240 | 58.5 | 16M | 26400 | 1100 | 14530 | 108 |
| 16571 | 80-200 | 70 | 440 | 279 | 405 | 310.1 | 140 | 30.1 | 245 | 58.5 | 16M | 37100 | 1000 | 32220 | 187 |
| 20018 | 82-205 | 75 | 465 | 289 | 425 | 437.5 | 200 | 37.5 | 285 | 71.6 | 20M | 54100 | 800 | 50980 | 286 |
| 20571 | 100-255 | 90 | 545 | 263 | 506 | 477.5 | 220 | 37.5 | 300 | 71.6 | 20M | 77800 | 600 | 111100 | 440 |
| 24571 | 120-310 | 110 | 650 | 448 | 607 | 650 | 302.5 | 45 | 340 | 87.8 | 20M | 137000 | 600 | 310000 | 869 |
| 24026 | 150-360 | 140 | 745 | 526 | 704 | 700 | 327.5 | 45 | 350 | 87.8 | 20M | 186000 | 500 | 598500 | 1260 |
Related Products
Company Profile
FAQ
Q: Can you make the coupling with customization?
A: Yes, we can customize per your request.
Q: Do you provide samples?
A: Yes. The sample is available for testing.
Q: What is your MOQ?
A: It is 10pcs for the beginning of our business.
Q: What’s your lead time?
A: Standard products need 5-30days, a bit longer for customized products.
Q: Do you provide technical support?
A: Yes. Our company has a design and development team, and we can provide technical support if you
need.
Q: How to ship to us?
A: It is available by air, sea, or by train.
Q: How to pay the money?
A: T/T and L/C are preferred, with different currencies, including USD, EUR, RMB, etc.
Q: How can I know if the product is suitable for me?
A: >1ST confirm drawing and specification >2nd test sample >3rd start mass production.
Q: Can I come to your company to visit?
A: Yes, you are welcome to visit us at any time.
Q: How shall we contact you?
A: You can send an inquiry directly, and we will respond within 24 hours. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

How to Properly Install a Rigid Shaft Coupling for Optimal Performance and Reliability
Proper installation of a rigid shaft coupling is essential to ensure optimal performance and reliability in mechanical systems. Here are the steps to follow for a successful installation:
- Shaft Preparation: Ensure that the shafts to be connected are clean, smooth, and free from any burrs or contaminants that could affect the coupling’s performance.
- Alignment: Align the two shafts accurately to minimize misalignment during installation. The alignment process is critical as any misalignment can lead to premature wear and reduced coupling efficiency.
- Fitment: Choose the appropriate size of the rigid shaft coupling that matches the shaft diameters. Carefully slide the coupling onto one shaft at a time.
- Fastening: For one-piece rigid couplings, ensure that the coupling is fitted snugly onto both shafts. For two-piece couplings, bolt the two halves together securely around the shafts.
- Tightening: Use the recommended torque value and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to tighten the coupling bolts properly. Over-tightening can cause distortion, while under-tightening can lead to slippage and reduced torque transmission.
- Inspection: After installation, inspect the coupling to ensure that it is centered and aligned correctly. Check for any signs of misalignment or interference during rotation.
- Lubrication: Some rigid couplings may require lubrication at the friction points to reduce wear and friction. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and types.
- Load Testing: Perform load testing on the system to verify the coupling’s performance and check for any unusual vibrations or noises during operation.
- Regular Maintenance: Include the rigid coupling in your regular maintenance schedule. Periodically check for signs of wear, misalignment, or damage, and replace the coupling if necessary.
By following these installation steps and best practices, you can ensure that the rigid shaft coupling operates optimally, providing reliable torque transmission and contributing to the overall efficiency and longevity of the mechanical system.

Can rigid shaft couplings be used for shafts with different rotational speeds and directions?
Rigid shaft couplings are typically designed for applications where the connected shafts have the same rotational speed and direction. They are not well-suited for scenarios involving significant speed differences or reverse rotation between shafts. The limitations arise from the coupling’s rigid construction, which does not allow for the compensation of speed differentials or changes in direction.
When shafts have different rotational speeds or need to rotate in opposite directions, it can result in uneven loading, increased wear, vibrations, and even coupling failure. Rigid couplings lack the flexibility required to accommodate the variations in speed and direction, which can lead to undesirable consequences in the system.
If your application involves shafts with varying speeds or reverse rotation, it’s recommended to explore flexible coupling options. Flexible couplings, such as gear couplings, elastomeric couplings, or universal joints, are designed to handle these situations by providing a degree of angular and radial flexibility. These couplings can help distribute the loads more evenly, reduce vibrations, and compensate for speed differences, ultimately contributing to smoother and more reliable operation.
It’s essential to accurately assess the requirements of your application and choose the appropriate coupling type based on the specific operational conditions. If there are varying speeds or reverse rotation involved, opting for flexible couplings designed for such scenarios will help ensure the longevity, efficiency, and performance of your machinery.

What is a Rigid Shaft Coupling and How Does It Work in Mechanical Systems?
A rigid shaft coupling is a type of coupling used to connect two shafts together in a mechanical system. As the name suggests, it is designed to provide a rigid and solid connection between the shafts, without any flexibility or misalignment compensation.
The primary function of a rigid shaft coupling is to transmit torque from one shaft to another efficiently and with minimal backlash. It achieves this by directly connecting the two shafts using a rigid mechanical interface.
Rigid shaft couplings typically consist of two halves with flanges that are bolted or clamped together around the shaft ends. The flanges are precision machined to ensure accurate alignment of the shafts. Some common types of rigid shaft couplings include:
- Sleeve Couplings: These are the simplest type of rigid couplings and consist of a cylindrical sleeve with a bore that fits over the shaft ends. The two shafts are aligned and then secured together using screws or pins.
- Clamp or Split Couplings: These couplings have two halves that are split and bolted together around the shafts. The split design allows for easy installation and removal without the need to disassemble other components of the system.
- Flanged Couplings: Flanged couplings have two flanges with precision machined faces that are bolted together, providing a robust connection.
- Tapered Bushing Couplings: These couplings use a tapered bushing to lock the coupling onto the shafts, creating a secure and concentric connection.
Rigid shaft couplings are commonly used in applications where precise alignment is critical, such as in high-speed machinery, precision instruments, and power transmission systems. Since they do not have any flexibility, they are best suited for applications where shaft misalignment is minimal or can be controlled through accurate alignment during installation.
One of the main advantages of rigid shaft couplings is their ability to provide a direct and efficient transfer of torque, making them suitable for high-torque and high-speed applications. Additionally, their simple design and solid connection make them easy to install and maintain.
However, it’s essential to ensure proper alignment during installation to prevent premature wear and stress on the shafts and other components. In cases where misalignment is expected or unavoidable, flexible couplings like beam couplings, bellows couplings, or jaw couplings are more appropriate, as they can compensate for small misalignments and provide some degree of shock absorption.


editor by CX 2024-03-04
China best Wd Type Heavy-Duty Cross Shaft Universal Coupling for Industrial Vehicle and Rig
Product Description
Product Description
Product Parameters
| product | Wd Type Cross Shaft Universal Coupling for Industrial Vehicle |
| material | stainless steel , iron , aluminum ,bronze ,carbon steel ,brass etc . |
| size | ISO standard ,customer requirements |
| kind | expansion sleeve Z1/Z2/Z3/Z4/Z5/Z6/Z7/Z8/Z9/Z10/Z11/Z12/Z13/Z14/Z18/Z19 |
| BORE | Finished bore, Pilot Bore, Special request |
| surface treatment | Carburizing and Quenching,Tempering ,Tooth suface high quenching Hardening,Tempering |
| Processing Method | Molding, Shaving, Hobbing, Drilling, Tapping, Reaming, Manual Chamfering, Grinding etc |
| Heat Treatment | Quenching & Tempering, Carburizing & Quenching, High-frequency Hardening, Carbonitriding…… |
| Package | Wooden Case/Container and pallet, or made-to-order |
| Certificate | ISO9001 ,SGS |
| Machining Process | Gear Hobbing, Gear Milling, Gear Shaping, Gear Broaching, Gear Shaving, Gear Grinding and Gear Lapping |
| Applications | Toy, Automotive, instrument, electrical equipment, household appliances, furniture, mechanical equipment,daily living equipment, electronic sports equipment, , sanitation machinery, market/ hotel equipment supplies, etc. |
| Testing Equipment | Rockwell hardness tester 500RA, Double mesh instrument HD-200B & 3102,Gear measurement center instrument CNC3906T and other High precision detection equipments |
workshop & equipment
Production process
Certifications
Our Advantages
1 . Prioritized Quality
2 .Integrity-based Management
3 .Service Orientation
4 .150+ advanced equipment
5 .10000+ square meter factory area
6 .200+ outstanding employees
7 .90% employees have more than 10 year- working experience in our factory
8 .36 technical staff
9 .certificate ISO 9001 , SGS
10 . Customization support
11 .Excellent after-sales service
shipping
sample orders delivery time:
10-15 working days as usual
15-20 working days in busy season
large order leading time :
20-30 working days as usual
30-40 working days in busy season
FAQ
1. why should you buy products from us not from other suppliers?
We are a 32 year-experience manufacturer on making the gear, specializing in manufacturing varieties of gears, such as helical gear ,bevel gear ,spur gear and grinding gear, gear shaft, timing pulley, rack, , timing pulley and other transmission parts . There are 150+ advanced equipment ,200+ excellent employees ,and 36 technical staff . what’s more ,we have got ISO9001 and SGS certificate .
2 .Do you accept small order?
If your order bearings are our standard size, we accept even 1pcs.
3 .How long is the delivery?
A: Small orders usually takes 10-15 working days,big order usually 20-35 days, depending on orders quantity and whether are standard size.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can Shaft Couplings Compensate for Angular, Parallel, and Axial Misalignments?
Yes, shaft couplings are designed to compensate for different types of misalignments between rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. They can handle the following types of misalignments:
- Angular Misalignment: This occurs when the shafts are not parallel and have an angle between them. Flexible couplings, such as elastomeric, beam, or Oldham couplings, can accommodate angular misalignments by allowing slight angular movement between the shafts while transmitting torque.
- Parallel Misalignment: This happens when the shafts are not collinear, resulting in axial displacement. Flexible couplings with lateral flexibility, like elastomeric or bellows couplings, can handle parallel misalignment by allowing limited lateral movement between the shafts.
- Radial Misalignment: Radial misalignment occurs when the shafts have lateral displacement but remain parallel. Flexible couplings, such as jaw or grid couplings, can absorb radial misalignment by permitting some lateral deflection while transmitting torque.
It is essential to note that while shaft couplings can compensate for misalignments to some extent, they do have their limits. The magnitude of misalignment they can handle depends on the type and design of the coupling. Exceeding the specified misalignment capabilities of a coupling can lead to premature wear, reduced efficiency, and possible coupling failure.
Therefore, when selecting a shaft coupling for an application, it is crucial to consider the expected misalignment and choose a coupling that can accommodate the anticipated misalignment range. Additionally, maintaining proper alignment through regular maintenance and periodic inspections is essential to ensure the coupling’s optimal performance and extend its service life.
“`
Can Shaft Couplings Handle Reversing Loads and Shock Loads Effectively?
Yes, shaft couplings are designed to handle both reversing loads and shock loads effectively, but the capability depends on the specific type of coupling and its design.
Reversing Loads:
Many shaft couplings, such as elastomeric couplings, gear couplings, and grid couplings, can handle reversing loads without any issue. Reversing loads occur when the direction of the torque changes periodically, causing the shafts to rotate in opposite directions. The flexibility of elastomeric couplings and the sturdy design of gear and grid couplings allow them to accommodate these reversing loads while maintaining reliable torque transmission.
Shock Loads:
Shock loads are sudden and high-magnitude forces that occur during start-up, sudden stops, or impact events. Shaft couplings with shock-absorbing features, such as elastomeric couplings and grid couplings, excel at handling shock loads. The elastomeric material in elastomeric couplings and the grid element in grid couplings act as shock absorbers, reducing the impact on the connected equipment and minimizing the risk of damage to the coupling itself.
It’s essential to select the appropriate coupling type based on the specific application’s requirements, including the magnitude and frequency of reversing loads and shock loads. Some couplings may have limitations on the amount of shock load they can handle, so it’s crucial to refer to the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines for proper coupling selection.
In heavy-duty applications with high reversing loads and shock loads, it may be necessary to consider specialized couplings designed explicitly for such conditions, like disc couplings or fluid couplings, which can offer even better performance in handling these challenging load conditions.
“`
What is a Shaft Coupling and Its Role in Mechanical Power Transmission?
A shaft coupling is a mechanical device used to connect two shafts together at their ends, allowing for the transmission of mechanical power from one shaft to another. It serves as an essential component in various machinery and industrial applications where rotational motion needs to be transmitted between two shafts that are not perfectly aligned or are separated by a distance.
The role of a shaft coupling in mechanical power transmission includes the following:
1. Power Transmission:
The primary function of a shaft coupling is to transmit power from a driving shaft to a driven shaft. When the driving shaft rotates, the coupling transfers the rotational motion to the driven shaft, enabling the driven equipment to perform its intended function.
2. Misalignment Compensation:
In real-world applications, it is often challenging to achieve perfect alignment between two shafts due to manufacturing tolerances or dynamic conditions. Shaft couplings are designed to accommodate different types of misalignment, such as angular, parallel, and axial misalignment, allowing the equipment to function smoothly even when the shafts are not perfectly aligned.
3. Vibration Damping:
Shaft couplings can help dampen vibrations and shocks caused by uneven loads or sudden changes in the operating conditions. This vibration damping feature protects the connected components from damage and contributes to the overall system’s reliability.
4. Overload Protection:
In some cases, a shaft coupling can act as a safety device by providing overload protection. When the connected machinery experiences excessive torque or shock loads, certain types of couplings can disengage or shear to prevent damage to the equipment.
5. Torque and Speed Conversion:
Shaft couplings can be designed to provide torque and speed conversion between the driving and driven shafts. This allows for adaptation to different operating conditions and varying torque requirements in the connected machinery.
6. Flexible Connection:
Shaft couplings with flexible elements, such as elastomeric inserts or flexible discs, provide a flexible connection that can absorb shocks and misalignments. This flexibility helps reduce stress on the connected equipment and extends its lifespan.
Overall, shaft couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, enabling the efficient transfer of rotational motion between shafts while accommodating misalignments and providing protection against overloads and vibrations. The selection of the appropriate coupling type and design depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the type of misalignment, torque capacity, and operating conditions.
“`

editor by CX 2024-03-04
China supplier Rigid Conduit Coupling 4″ UL Listed
Product Description
Rigid Conduit Coupling 4″
| Standard: BS4568 20MM TO 50MM BS31: 3/4″ TO 2″ | Surface Treatment: Hot dip galvanized(bsi), Electro Galvanized |
| Length: 35mm long standard length | Thread Type: BS4568 BS31 |
GI couplers are small and in-expensive parts which are very handy and easy to use. GI couplers are mainly used for commercial, industrial and utility usage which is durable and effective in underground, encased and exposed applications. It enables you to join/connect-1 part to another such as GI flexible conduits to conduits, conduits to fitting and sometimes even fittings to fittings which helps in protecting the wires under the ground or under the walls of the premises and eventually increase the life of cables and wires.
Specifications
| Attribute | Value |
| Brand | axwill or ranlic |
| Nominal Size | 20mm to 50 mm |
| Finish | Galvanised hot dip |
| Fitting Type | Coupler |
| Standards Met | BS EN 5 |
| Material | Steel |
Submersible GI (Galvanized Iron) & Seamless (CNC Thread) Socket that is widely used in pipelines and submersible pumps. Under the directions of our adroit professionals, the offered socket is precisely manufactured using quality assured raw material and ultra-modern technology in line with set industry standards. In addition, our provided socket is highly praised among our clients owing to its long service life. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can Rigid Couplings Be Used in Both Horizontal and Vertical Shaft Arrangements?
Yes, rigid couplings can be used in both horizontal and vertical shaft arrangements. Rigid couplings are designed to provide a solid, non-flexible connection between two shafts, making them suitable for various types of shaft orientations.
Horizontal Shaft Arrangements: In horizontal shaft arrangements, the two shafts are positioned parallel to the ground or at a slight incline. Rigid couplings are commonly used in horizontal setups as they efficiently transmit torque and maintain precise alignment between the shafts. The horizontal orientation allows gravity to aid in keeping the coupling elements securely in place.
Vertical Shaft Arrangements: In vertical shaft arrangements, the two shafts are positioned vertically, with one shaft above the other. This type of setup is often found in applications such as pumps, compressors, and some gearboxes. Rigid couplings can also be used in vertical shaft arrangements, but additional considerations must be taken into account:
- Keyless Design: To accommodate the vertical orientation, some rigid couplings have a keyless design. Traditional keyed couplings may experience issues with keyway shear due to the force of gravity on the key, especially in overhung load situations.
- Set Screw Tightening: When installing rigid couplings in vertical shaft arrangements, set screws must be tightened securely to prevent any axial movement during operation. Locking compound can also be used to provide additional security.
- Thrust Load Considerations: Vertical shaft arrangements may generate thrust loads due to the weight of the equipment and components. Rigid couplings should be chosen or designed to handle these thrust loads to prevent axial displacement of the shafts.
It’s essential to select a rigid coupling that is suitable for the specific shaft orientation and operating conditions. Proper installation and alignment are critical for both horizontal and vertical shaft arrangements to ensure the rigid coupling’s optimal performance and reliability.

Factors to Consider When Choosing a Rigid Coupling for a Specific System
Choosing the right rigid coupling for a specific system is crucial to ensure proper functionality and reliable performance. Several factors should be considered when making this decision:
1. Shaft Size and Compatibility: The most fundamental factor is ensuring that the rigid coupling is compatible with the shaft sizes of the connected components. The coupling should have the appropriate bore size and keyway dimensions to fit securely onto the shafts.
2. Operating Torque: Consider the torque requirements of the application. The rigid coupling should have a torque rating that exceeds the maximum torque expected during operation to prevent failures and ensure safety.
3. Speed: Determine the rotational speed (RPM) of the connected shafts. Rigid couplings have maximum RPM limits, and the selected coupling should be capable of handling the system’s operating speed.
4. Misalignment Tolerance: Assess the potential misalignment between the shafts. Rigid couplings provide no flexibility, so the system must have minimal misalignment to prevent excessive forces on the components.
5. Temperature and Environment: Consider the operating temperature range and the environment where the coupling will be used. Ensure the chosen material can withstand the temperature and any corrosive or harsh conditions present.
6. Space Limitations: Evaluate the available space for the coupling. Rigid couplings have a compact design, but ensure that there is enough clearance for installation and maintenance.
7. Backlash and Torsional Stiffness: In some precision systems, backlash must be minimized to maintain accurate positioning. Additionally, the torsional stiffness of the coupling can impact system response and stability.
8. Keyway or Keyless Design: Decide between a coupling with a keyway or a keyless design based on the specific application requirements and ease of installation.
9. Material Selection: Consider the material properties of the rigid coupling. Common materials include steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, each with its own advantages and limitations.
10. Maintenance: Determine the maintenance requirements of the coupling. Some couplings may need periodic lubrication or inspections, while others may be maintenance-free.
11. Cost: While cost should not be the sole consideration, it is essential to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of the coupling, taking into account its performance and longevity.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the most suitable rigid coupling for your specific system, ensuring optimal performance, and longevity of your mechanical setup.

Limitations and Disadvantages of Using Rigid Couplings:
Rigid couplings offer several advantages in providing a strong and direct connection between shafts, but they also have certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered in certain applications:
- No Misalignment Compensation: Rigid couplings are designed to provide a fixed connection with no allowance for misalignment between shafts. As a result, any misalignment, even if slight, can lead to increased stress on connected components and cause premature wear or failure.
- Transmit Shock and Vibration: Rigid couplings do not have any damping or vibration-absorbing properties, which means they can transmit shock and vibration directly from one shaft to another. In high-speed or heavy-duty applications, this can lead to increased wear on bearings and other components.
- No Torque Compensation: Unlike flexible couplings, rigid couplings cannot compensate for torque fluctuations or angular displacement between shafts. This lack of flexibility may not be suitable for systems with varying loads or torque requirements.
- Higher Stress Concentration: Rigid couplings can create higher stress concentration at the points of connection due to their inflexibility. This can be a concern in applications with high torque or when using materials with lower fatigue strength.
- More Challenging Installation: Rigid couplings require precise alignment during installation, which can be more challenging and time-consuming compared to flexible couplings that can tolerate some misalignment.
- Increased Wear: The absence of misalignment compensation and vibration absorption can lead to increased wear on connected components, such as bearings, shafts, and seals.
- Not Suitable for High Misalignment: While some rigid couplings have limited ability to accommodate minor misalignment, they are not suitable for applications with significant misalignment, which could lead to premature failure.
Despite these limitations, rigid couplings are still widely used in many applications where precise alignment and a strong, permanent connection are required. However, in systems with significant misalignment, vibration, or shock loads, flexible couplings may be a more suitable choice to protect the connected components and improve overall system performance and longevity.


editor by CX 2024-03-04