Product Description
Product Description
|
Product name |
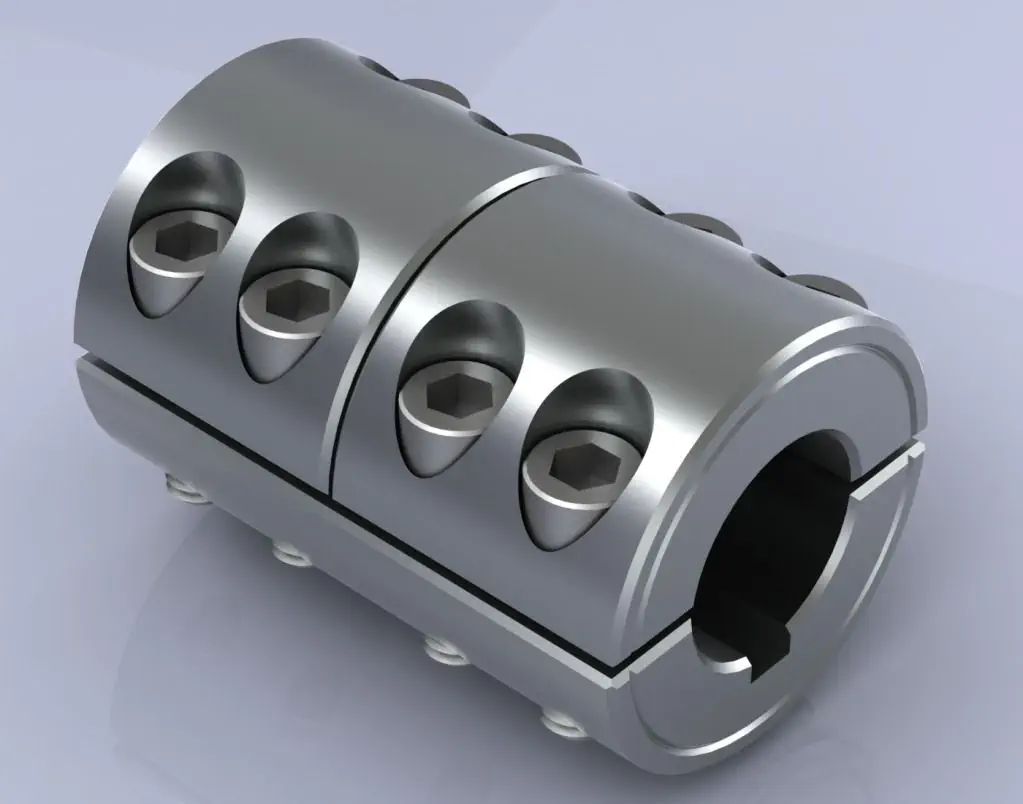
Chain coupling |
|||
|
Material |
Carbon steel material |
|||
|
Structure |
Roller chain+sprocket+cover |
|||
|
Size |
KC3012, KC4012, KC4014, KC4016, KC5014, KC5016, KC5018, KC6018, KC6571, KC6571, KC8018, KC8571, KC8571, KC1571, KC12018, KC12571, KC16018, KC16571, KC20018, KC20571, KC24026 |
|||
|
Other type |
Flexible coupling |
|||
|
Application |
Shaft transmission |
|||
|
Feature |
High performance, light weight, convenient assembly |
|||
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
ZheJiang Haorongshengye Electrical Equipment Co., Ltd.
1. Was founded in 2008
2. Our Principle:
“Credibility Supremacy, and Customer First”
3. Our Promise:
“High quality products, and Excellent Service”
4. Our Value:
“Being Honesty, Doing the Best, and Long-lasting Development”
5. Our Aim:
“Develop to be a leader in the power transmission parts industry in the world”
|
6.Our services: |
1).Competitive price |
|||
|
2).High quality products |
||||
|
3).OEM service or can customized according to your drawings |
||||
|
4).Reply your inquiry in 24 hours |
||||
|
5).Professional technical team 24 hours online service |
||||
|
6).Provide sample service |
||||
Main products
Machines
Exbihition
/* May 10, 2571 16:49:51 */!function(){function d(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Are There Any Safety Considerations When Using Rigid Couplings in Rotating Machinery?
Yes, there are several safety considerations to keep in mind when using rigid couplings in rotating machinery. While rigid couplings offer various advantages, their use in certain applications requires careful attention to safety measures to prevent accidents and equipment damage. Here are some important safety considerations:
– Secure Installation: Proper installation of rigid couplings is crucial to ensure safety. The coupling must be securely mounted and aligned with the shafts to prevent any slippage or disengagement during operation. Use of appropriate mounting hardware, such as high-strength bolts, is essential to maintain the coupling’s integrity under high-speed and high-torque conditions.
– Shaft Alignment: Accurate shaft alignment is necessary to avoid excessive forces and stress on the connected machinery. Misaligned shafts can lead to uneven loading and increased wear on bearings and other components. Regularly inspect and maintain the shaft alignment to prevent premature failures.
– Preventing Over-Torquing: Applying excessive torque during the installation of rigid couplings can lead to equipment damage and compromise safety. Follow the manufacturer’s torque specifications and use torque-limiting tools to prevent over-torquing and potential failures.
– Protective Guards: In some applications, rotating machinery with rigid couplings may pose a safety hazard to personnel working nearby. Install appropriate protective guards and covers to prevent accidental contact with rotating shafts, minimizing the risk of injury.
– Regular Maintenance: Implement a routine maintenance schedule to inspect the rigid couplings and associated equipment. Check for signs of wear, fatigue, or cracks. Address any issues promptly to avoid potential catastrophic failures.
– Operational Speed Limits: Be aware of the operational speed limits specified by the manufacturer for the rigid couplings. Exceeding these limits can result in significant stress and fatigue on the coupling, leading to failure.
– Appropriate Coupling Selection: Choose the appropriate type and size of rigid coupling for the specific application. Using an undersized coupling can lead to excessive loads and potential failure, while an oversized coupling may not efficiently transmit torque.
– Temperature Considerations: Rigid couplings can experience temperature variations during operation. Ensure that the material and design of the coupling are suitable for the anticipated temperature range of the application to maintain safety and performance.
– Training and Awareness: Provide proper training to personnel working with rotating machinery equipped with rigid couplings. Ensure they are aware of safety procedures and potential hazards associated with the equipment.
Adhering to these safety considerations will help ensure the safe and reliable operation of rotating machinery equipped with rigid couplings. Regular maintenance, correct installation, and diligent attention to safety guidelines will minimize risks and contribute to a safe working environment.

What Industries Commonly Use Rigid Couplings for Power Transmission?
Rigid couplings are widely used in various industries for power transmission applications that require a solid and reliable connection between rotating shafts. Some of the industries that commonly utilize rigid couplings include:
- Manufacturing: In the manufacturing industry, rigid couplings are employed in a wide range of equipment, such as conveyors, mixers, pumps, compressors, and machine tools. These couplings ensure precise power transmission and alignment, making them ideal for maintaining accuracy in manufacturing processes.
- Material Handling: Material handling equipment, including cranes, hoists, and elevators, often rely on rigid couplings to transfer power between shafts efficiently. Rigid couplings provide a robust connection that can handle the heavy loads and continuous operation common in material handling applications.
- Automotive: The automotive industry employs rigid couplings in various automotive systems, including drive shafts, transmissions, and steering systems. Rigid couplings contribute to the overall performance and reliability of these components, ensuring smooth power transfer and minimizing vibration.
- Mining and Construction: In the mining and construction industries, rugged and durable power transmission components are crucial. Rigid couplings are used in equipment like crushers, mills, and heavy-duty conveyors, where they can withstand the harsh conditions and heavy loads commonly found in these applications.
- Oil and Gas: The oil and gas industry often utilizes rigid couplings in pumps, compressors, and drilling equipment. Rigid couplings offer consistent and dependable power transmission, which is essential for critical operations in this sector.
- Marine: In marine applications, such as ship propulsion systems and marine pumps, rigid couplings are used to transmit power between the ship’s engine and various equipment. They can handle the dynamic forces and vibrations encountered in marine environments.
- Aerospace: In aerospace applications, where precision and reliability are paramount, rigid couplings play a role in power transmission between various aircraft components.
Rigid couplings are chosen in these industries for their ability to maintain shaft alignment, resist misalignment, and provide a backlash-free connection. Their robust construction and simple design make them suitable for high torque and high-speed applications, where precision and efficiency are crucial.

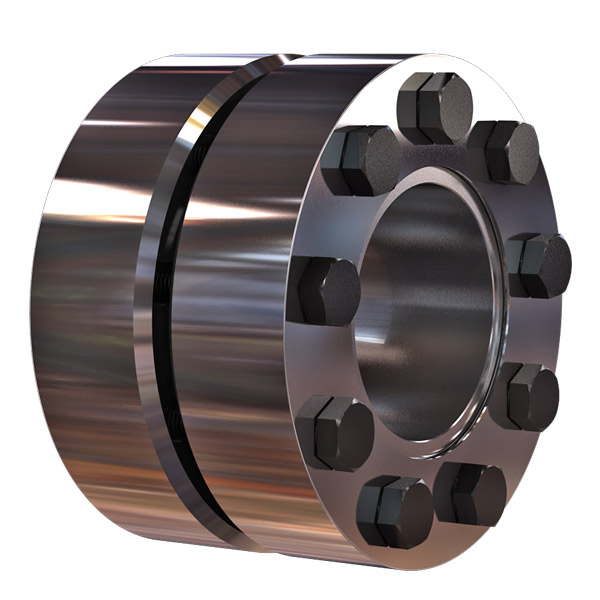
What is a Rigid Coupling and How Does it Work?
A rigid coupling is a type of mechanical coupling used to connect two shafts together at their ends to transmit torque and rotational motion without any flexibility or misalignment accommodation. Unlike flexible couplings, rigid couplings do not allow for angular, parallel, or axial misalignment between the shafts. The main purpose of a rigid coupling is to provide a strong and solid connection between two shafts, ensuring precise and synchronous power transmission between them.
Structure and Design:
Rigid couplings are typically made from durable materials such as steel, stainless steel, or aluminum, which can withstand high torque and load applications. The coupling consists of two halves, each with a cylindrical bore that fits tightly onto the respective shafts. The two halves are then fastened together using bolts or set screws to ensure a secure and rigid connection.
Working Principle:
The working principle of a rigid coupling is straightforward. When the two shafts are aligned precisely and the coupling is securely fastened, any torque applied to one shaft gets directly transferred to the other shaft. The rigid coupling essentially makes the two shafts act as one continuous shaft, allowing for synchronous rotation without any relative movement or play between them.
Applications:
Rigid couplings are commonly used in applications where precise alignment and torque transmission are essential. Some common applications of rigid couplings include:
- High-precision machinery and equipment
- Robotics and automation systems
- Precision motion control systems
- Machine tools
- Shaft-driven pumps and compressors
Advantages:
The key advantages of using rigid couplings include:
- High Torque Transmission: Rigid couplings can handle high torque and power transmission without any loss due to flexibility.
- Precision: They provide accurate and synchronous rotation between the shafts, making them suitable for precise applications.
- Simple Design: Rigid couplings have a simple design with minimal moving parts, making them easy to install and maintain.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to some other coupling types, rigid couplings are generally more cost-effective.
Limitations:
Despite their advantages, rigid couplings have certain limitations:
- No Misalignment Compensation: Rigid couplings cannot accommodate any misalignment between the shafts, making precise alignment during installation crucial.
- Transmits Vibrations: Since rigid couplings do not dampen vibrations, they can transmit vibrations and shocks from one shaft to the other.
- Stress Concentration: In some applications, rigid couplings can create stress concentration at the ends of the shafts.
In summary, rigid couplings are ideal for applications that require precise alignment and high torque transmission. They offer a robust and straightforward solution for connecting shafts and ensuring synchronous power transmission without any flexibility or misalignment accommodation.
<img src="https://img.hzpt.com/img/coupling/coupling-l1.webp" alt="China factory GB Rigid Coupling Encoder Special Aluminium Alloy Rigid Shaft Coupling “><img src="https://img.hzpt.com/img/coupling/coupling-l2.webp" alt="China factory GB Rigid Coupling Encoder Special Aluminium Alloy Rigid Shaft Coupling “>
editor by LMC 2024-09-09
China best GB Rigid Coupling Encoder Special Aluminium Alloy Rigid Shaft Coupling
Product Description
Product Description
|
Product name |
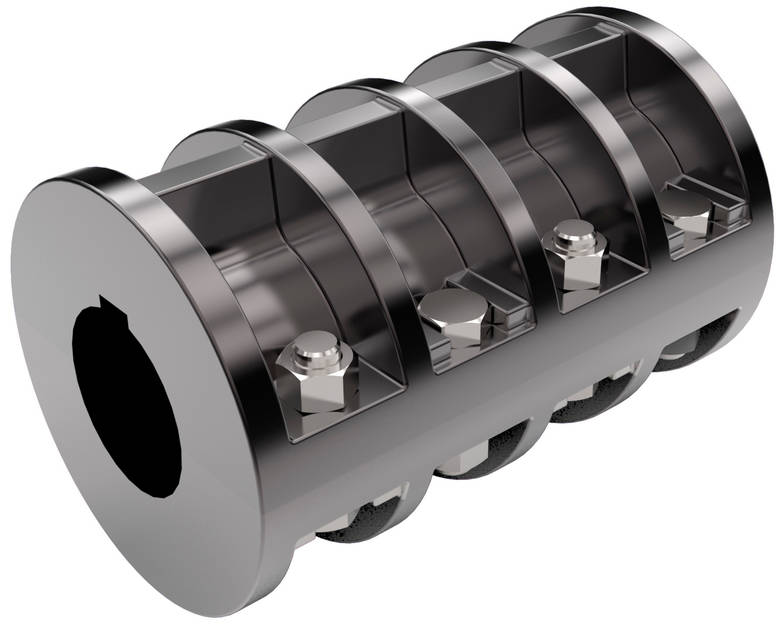
Chain coupling |
|||
|
Material |
Carbon steel material |
|||
|
Structure |
Roller chain+sprocket+cover |
|||
|
Size |
KC3012, KC4012, KC4014, KC4016, KC5014, KC5016, KC5018, KC6018, KC6571, KC6571, KC8018, KC8571, KC8571, KC1571, KC12018, KC12571, KC16018, KC16571, KC20018, KC20571, KC24026 |
|||
|
Other type |
Flexible coupling |
|||
|
Application |
Shaft transmission |
|||
|
Feature |
High performance, light weight, convenient assembly |
|||
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
ZheJiang Haorongshengye Electrical Equipment Co., Ltd.
1. Was founded in 2008
2. Our Principle:
“Credibility Supremacy, and Customer First”
3. Our Promise:
“High quality products, and Excellent Service”
4. Our Value:
“Being Honesty, Doing the Best, and Long-lasting Development”
5. Our Aim:
“Develop to be a leader in the power transmission parts industry in the world”
|
6.Our services: |
1).Competitive price |
|||
|
2).High quality products |
||||
|
3).OEM service or can customized according to your drawings |
||||
|
4).Reply your inquiry in 24 hours |
||||
|
5).Professional technical team 24 hours online service |
||||
|
6).Provide sample service |
||||
Main products
Machines
Exbihition
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can Rigid Shaft Couplings Accommodate Different Shaft Sizes and Handle High Torque Loads?
Yes, rigid shaft couplings are designed to accommodate different shaft sizes and are capable of handling high torque loads. One of the key advantages of rigid couplings is their ability to provide a solid and strong connection between two shafts.
Rigid shaft couplings come in various designs, such as one-piece and two-piece configurations. The one-piece couplings have a solid construction with no moving parts and are ideal for applications where precise alignment and torque transmission are essential.
The two-piece rigid couplings consist of two halves that are bolted together around the shafts, creating a tight and secure connection. These couplings allow for easier installation and removal without the need to move the connected shafts. They are commonly used in applications where frequent maintenance is required.
The design of rigid shaft couplings enables them to handle high torque loads efficiently. The solid and rigid construction allows for the direct transfer of torque from one shaft to another, minimizing power loss and ensuring precise torque transmission.
Moreover, rigid couplings can accommodate different shaft sizes by offering various bore diameters and keyway options. This adaptability allows users to connect shafts of different diameters without the need for additional modifications or couplings.
However, it is crucial to select the appropriate size and type of rigid coupling based on the specific application’s torque requirements and shaft sizes. Properly sized rigid couplings will ensure reliable and efficient power transmission while preventing issues such as misalignment, vibration, and premature wear.

What are the maintenance requirements for rigid shaft couplings to extend their lifespan?
Rigid shaft couplings are mechanical components used to connect two shafts and transmit torque between them. While rigid couplings are known for their durability and minimal maintenance needs, proper care and maintenance can further extend their lifespan and ensure optimal performance. Here are key maintenance considerations:
- Lubrication: Some rigid couplings, especially those with moving parts like set screws, may require periodic lubrication to reduce friction and wear. Use appropriate lubricants as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the coupling for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Look for cracks, dents, or any other abnormalities that could affect its performance. Address any issues promptly.
- Tightening Fasteners: If the rigid coupling is secured using fasteners such as set screws or bolts, ensure they are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications. Loose fasteners can lead to misalignment and reduced coupling effectiveness.
- Alignment Check: Periodically check the alignment of the connected shafts. Misalignment can lead to increased stress on the coupling and premature wear. Realign the shafts if necessary.
- Coupling Integrity: Make sure the coupling is securely fastened and properly seated on both shafts. Any looseness or improper fitting can lead to vibrations and wear.
- Cleanliness: Keep the coupling and surrounding area clean from dirt, debris, and contaminants. Foreign particles can lead to increased wear and reduced performance.
- Environmental Factors: Consider the operating environment. If the coupling is exposed to harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures or corrosive substances, take appropriate measures to protect the coupling’s surfaces and materials.
- Replacement of Worn Parts: If any components of the coupling show significant wear or damage, consider replacing them as per the manufacturer’s recommendations. This can prevent further issues and maintain coupling integrity.
- Manufacturer Guidelines: Always follow the maintenance recommendations provided by the coupling manufacturer. They can provide specific guidelines based on the coupling’s design and materials.
Proper maintenance practices not only extend the lifespan of rigid shaft couplings but also contribute to the overall reliability and efficiency of the connected machinery. Regular inspections and maintenance can help identify potential issues early, preventing costly downtime and repairs.
It’s important to note that maintenance requirements can vary based on the specific design and material of the rigid coupling. Consulting the manufacturer’s documentation and seeking professional advice can help establish a suitable maintenance schedule tailored to the coupling’s characteristics and the application’s demands.

What are the Materials Commonly Used to Manufacture Rigid Shaft Couplings, and How Do They Impact Performance?
Rigid shaft couplings are typically made from a variety of materials, and the choice of material can significantly impact the performance of the coupling in specific applications. Some common materials used in manufacturing rigid shaft couplings include:
- Steel: Steel is one of the most commonly used materials for rigid shaft couplings. It offers excellent strength and durability, making it suitable for high-torque and heavy-duty applications. Steel couplings can withstand significant stresses and provide reliable torque transmission.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel couplings offer the same benefits as regular steel couplings but with the added advantage of corrosion resistance. They are commonly used in applications where the coupling may be exposed to harsh environments or moisture.
- Aluminum: Aluminum couplings are lightweight and have good corrosion resistance. They are often used in applications where weight reduction is essential, such as in aerospace and automotive industries.
- Brass: Brass couplings are known for their excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. They are commonly used in applications where electrical conductivity is required.
- Cast Iron: Cast iron couplings are robust and offer good resistance to wear and tear. They are commonly used in industrial machinery and equipment.
The choice of material depends on various factors, including the application’s operating conditions, such as torque requirements, temperature, and environmental conditions. For example, in high-torque applications, steel or stainless steel couplings are often preferred due to their high strength. On the other hand, aluminum couplings are favored in applications where weight reduction is critical.
It is essential to consider the specific needs of the application and the coupling’s material properties to ensure optimal performance, longevity, and reliability of the rigid shaft coupling.


editor by CX 2024-04-04
China Custom GB Rigid Coupling Encoder Special Aluminium Alloy Rigid Shaft Coupling
Product Description
Product Description
|
Product name |
Chain coupling |
|||
|
Material |
Carbon steel material |
|||
|
Structure |
Roller chain+sprocket+cover |
|||
|
Size |
KC3012, KC4012, KC4014, KC4016, KC5014, KC5016, KC5018, KC6018, KC6571, KC6571, KC8018, KC8571, KC8571, KC1571, KC12018, KC12571, KC16018, KC16571, KC20018, KC20571, KC24026 |
|||
|
Other type |
Flexible coupling |
|||
|
Application |
Shaft transmission |
|||
|
Feature |
High performance, light weight, convenient assembly |
|||
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
ZheJiang Haorongshengye Electrical Equipment Co., Ltd.
1. Was founded in 2008
2. Our Principle:
“Credibility Supremacy, and Customer First”
3. Our Promise:
“High quality products, and Excellent Service”
4. Our Value:
“Being Honesty, Doing the Best, and Long-lasting Development”
5. Our Aim:
“Develop to be a leader in the power transmission parts industry in the world”
|
6.Our services: |
1).Competitive price |
|||
|
2).High quality products |
||||
|
3).OEM service or can customized according to your drawings |
||||
|
4).Reply your inquiry in 24 hours |
||||
|
5).Professional technical team 24 hours online service |
||||
|
6).Provide sample service |
||||
Main products
Machines
Exbihition
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Common Industries and Use Cases for Rigid Shaft Couplings
Rigid shaft couplings find applications in various industries where precise and torque-resistant shaft connections are required. Some of the common industries that use rigid shaft couplings include:
- Manufacturing: Rigid shaft couplings are widely used in manufacturing machinery, such as lathes, milling machines, and CNC equipment, to provide rigid and accurate power transmission.
- Robotics: Robots and robotic arms often use rigid shaft couplings to ensure precise motion and synchronization between motors and actuators.
- Aerospace: In aerospace applications, rigid couplings are used in aircraft engines, landing gear systems, and control surfaces.
- Automotive: Rigid couplings are utilized in automotive powertrains and drivetrains to transmit torque efficiently and withstand high loads.
- Marine: Marine propulsion systems and shipboard equipment often employ rigid shaft couplings for reliable torque transmission in challenging environments.
- Packaging: Packaging machinery relies on rigid couplings to achieve accurate and synchronized movements in filling, sealing, and labeling operations.
- Steel and Metal Processing: Rigid shaft couplings are essential in steel mills and metal processing equipment to handle heavy loads and maintain precision.
- Printing and Paper: Printing presses and paper handling machinery use rigid couplings to ensure precise registration and consistent operation.
- Mining and Construction: Mining equipment and construction machinery utilize rigid couplings for robust power transmission in harsh environments.
- Energy and Utilities: In power generation plants and utilities, rigid couplings are employed in pumps, compressors, and turbines.
Rigid shaft couplings are versatile and can be found in numerous other industries where precise and efficient power transmission is critical for smooth operation and high-performance machinery.

How do rigid shaft couplings contribute to the overall efficiency of rotating machinery?
Rigid shaft couplings play a crucial role in enhancing the overall efficiency and performance of rotating machinery by ensuring precise torque transmission, accurate shaft alignment, and reduced power losses. Their contribution to efficiency can be understood through the following points:
- Accurate Torque Transmission: Rigid couplings provide a direct and efficient connection between two shafts, allowing torque to be transmitted without significant losses. Unlike flexible couplings that can absorb some energy through flexibility, rigid couplings minimize energy dissipation, leading to efficient power transfer.
- Minimized Misalignment: Proper alignment of shafts is essential for efficient operation. Rigid couplings maintain accurate shaft alignment, reducing friction, wear, and energy losses that can occur due to misaligned shafts.
- Reduced Vibrations: By preventing misalignment and maintaining shaft stability, rigid couplings help minimize vibrations. Reduced vibrations lead to smoother operation, less wear and tear, and a decrease in energy losses associated with friction and oscillations.
- Consistent Performance: Rigid couplings ensure consistent and reliable torque transmission throughout the machinery’s operation. This stability helps maintain optimal operating conditions and prevents sudden disruptions or fluctuations in performance.
- Enhanced System Integrity: A stable and secure connection between shafts provided by rigid couplings reduces the risk of equipment failures and breakdowns. This enhances the machinery’s overall reliability and uptime, contributing to improved efficiency.
- Minimized Power Losses: With their rigid construction, these couplings have minimal flexibility, reducing power losses associated with elastic deformation. As a result, more of the input power is effectively utilized for productive work.
- Reduced Maintenance Needs: Rigid couplings, when properly installed and maintained, experience fewer wear-related issues compared to flexible couplings. This translates to reduced downtime and maintenance requirements, further enhancing machinery efficiency.
Efficient rotating machinery is critical for various industries, as it leads to cost savings, improved productivity, and extended equipment lifespan. Rigid shaft couplings contribute significantly to achieving these goals by ensuring reliable torque transmission, stable operation, and minimized energy losses.
It’s important to note that while rigid couplings offer advantages in terms of efficiency, they might not be suitable for applications requiring flexibility to accommodate misalignment or shock absorption. Engineers should carefully consider the specific requirements of their machinery and select couplings that best align with the desired balance of efficiency, flexibility, and other operational needs.

Can Rigid Shaft Couplings Handle Misalignment Between Shafts Effectively?
Rigid shaft couplings are not designed to accommodate misalignment between shafts effectively. Unlike flexible couplings, which can bend or flex to some degree to compensate for misalignment, rigid couplings are inflexible and require precise alignment for proper operation.
When using rigid shaft couplings, it is crucial to ensure that the two shafts being connected are aligned with high accuracy. Misalignment between the shafts can lead to various issues, including:
- Vibrations: Misalignment can cause vibrations and increase stress on the coupling and connected machinery, leading to premature wear and reduced performance.
- Increased Stress: Misalignment results in additional stress on the shafts and coupling, which may lead to fatigue failure over time.
- Reduced Efficiency: Misalignment can result in power loss and reduced overall system efficiency.
- Noise: Misalignment may generate noise during operation, leading to potential discomfort for operators and additional wear on components.
To ensure the effective functioning of rigid shaft couplings, it is crucial to align the shafts accurately during installation. The alignment process typically involves using precision tools and techniques to achieve the desired alignment tolerances.
For applications where misalignment is expected or unavoidable, flexible couplings such as beam couplings or jaw couplings may be more suitable as they can accommodate slight misalignments and reduce the transmission of shock and vibration between shafts.
Overall, rigid shaft couplings are best suited for applications where precise shaft alignment is feasible and necessary for optimal performance. Proper alignment and regular maintenance are essential to maximize the life and efficiency of rigid couplings in mechanical systems.


editor by CX 2024-04-04
China supplier Helical Drive Flexible Coupling for Encoder Shaft Coupling Dimensions
Product Description
Helical Drive Flexible Coupling For Encoder Shaft Coupling Dimensions
Product Description
Coupling refers to a device that connects 2 shafts or shafts and rotating parts, rotates together during the transmission of motion and power, and does not disengage under normal conditions. Sometimes it is also usedas a safety device to prevent the connected parts from bearing excessive load, which plays the role of overload protection.
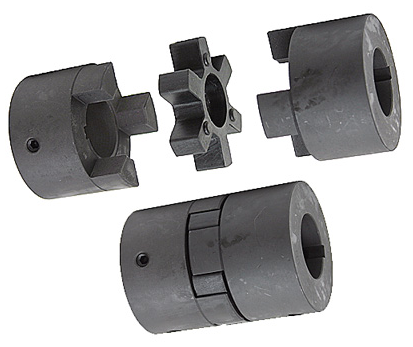
Couplings can be divided into rigid couplings and flexible couplings. Rigid couplings do not have buffering property and the ability to compensate the relative displacement of 2 axes. It is required that the 2 axes be strictly aligned. However, such couplings are simple in structure, low in manufacturing cost, convenient in assembly and disassembly, and maintenance, which can ensure that the 2 axes are relatively neutral, have large transmission torque, and are widely used. Commonly used are flange coupling, sleeve coupling and jacket coupling.
Flexible coupling can also be divided into flexible coupling without elastic element and flexible coupling with elastic element. The former type only has the ability to compensate the relative displacement of 2 axes, but cannot cushion and reduce vibration. Common types include slider coupling, gear coupling, universal coupling and chain coupling; The latter type contains elastic elements. In addition to the ability to compensate the relative displacement
of 2 axes, it also has the functions of buffering and vibration reduction.
Our leading mainly including universal couplings, drum gear couplings, elastic couplings etc.
Main production equipments:
Large lathe, surface grinder, milling machine, spline milling machine, horizontal broaching machine, gear hobbing machine, shaper, slotting machine, bench drilling machine, radial drilling machine, boring machine, band sawing machine, horizontal lathe, end milling machine, crankshaft grinder, CNC milling machine, etc.
Coupling performance
1) Mobility. The movability of the coupling refers to the ability to compensate the relative displacement of 2 rotating components. Factors such as manufacturing and installation errors between connected components, temperature changes during operation and deformation under load all put CHINAMFG requirements for mobility. The movable performance compensates or alleviates the additional load between shafts, bearings, couplings and other components caused by the relative displacement between rotating components.
(2) Buffering. For the occasions where the load is often started or the working load changes, the coupling shall be equipped with elastic elements that play the role of cushioning and vibration reduction to protect the prime mover and the working machine from little or no damage.
(3) Safe, reliable, with sufficient strength and service life.
(4) Simple structure, easy to assemble, disassemble and maintain.
Inspection equipment:
Dynamic balance tester, high-speed intelligent carbon and sulfur analyzer, Blochon optical hardness tester, Leeb hardness tester, magnetic yoke flaw detector etc.
It is widely used in metallurgical steel rolling, wind power, hydropower, mining, engineering machinery, petrochemical, lifting, paper making, rubber, rail transit, shipbuilding and marine engineering and other industries.
How to select the appropriate coupling type
The following items should be considered when selecting the coupling type.
1. The size and nature of the required transmission torque, the requirements for buffering and damping functions, and whether resonance may occur.
2. The relative displacement of the axes of the 2 shafts is caused by manufacturing and assembly errors, shaft load and thermal expansion deformation, and relative movement between components.
3. Permissible overall dimensions and installation methods, and necessary operating space for assembly, adjustment and maintenance. For large couplings, they should be able to be disassembled without axial movement of the shaft.
In addition, the working environment, service life, lubrication, sealing, economy and other conditions should also be considered, and a suitable coupling type should be selected by referring to the characteristics of various couplings.
If you cannot determine the type, you can contact our professional engineer.
FAQ
| Q: What is the payment method? A: We accept TT (Bank Transfer), Western Union, L/C. 1. For total amount under US$500, 100% in advance. 2. For total amount above US$500, 30% in advance, the rest before shipment. |
| Q: What is your MOQ? A: MOQ depends on our client’s needs, besides,we welcome trial order before mass-production. |
| Q: What is the production cycle? A: It varies a lot depending on product dimension,technical requirements and quantity. We always try to meet customers’ requirement by adjusting our workshop schedule. |
| Q: What kind of payment terms do you accept? A: T/T, western union, etc. |
| Q: Is it possible to know how is my product going on without visiting your company? A: We will offer a detailed products schedule and send weekly reports with digital pictures and videos which show the machining progress. |
| Q: If you make poor quality goods,will you refund our fund? A: We make products according to drawings or samples strictly until them reach your 100% satisfaction. And actually we wont take a chance to do poor quality products.We are proud of keeping the spirit of good quality. |
If there’s anything we can help, please feel free to contact with us.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can Shaft Couplings Compensate for Angular, Parallel, and Axial Misalignments?
Yes, shaft couplings are designed to compensate for different types of misalignments between rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. They can handle the following types of misalignments:
- Angular Misalignment: This occurs when the shafts are not parallel and have an angle between them. Flexible couplings, such as elastomeric, beam, or Oldham couplings, can accommodate angular misalignments by allowing slight angular movement between the shafts while transmitting torque.
- Parallel Misalignment: This happens when the shafts are not collinear, resulting in axial displacement. Flexible couplings with lateral flexibility, like elastomeric or bellows couplings, can handle parallel misalignment by allowing limited lateral movement between the shafts.
- Radial Misalignment: Radial misalignment occurs when the shafts have lateral displacement but remain parallel. Flexible couplings, such as jaw or grid couplings, can absorb radial misalignment by permitting some lateral deflection while transmitting torque.
It is essential to note that while shaft couplings can compensate for misalignments to some extent, they do have their limits. The magnitude of misalignment they can handle depends on the type and design of the coupling. Exceeding the specified misalignment capabilities of a coupling can lead to premature wear, reduced efficiency, and possible coupling failure.
Therefore, when selecting a shaft coupling for an application, it is crucial to consider the expected misalignment and choose a coupling that can accommodate the anticipated misalignment range. Additionally, maintaining proper alignment through regular maintenance and periodic inspections is essential to ensure the coupling’s optimal performance and extend its service life.
“`
Comparing Shaft Couplings with Other Types of Couplings in Performance
Shaft couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, and their performance characteristics vary depending on the coupling type. Let’s compare shaft couplings with other common types of couplings:
1. Shaft Couplings:
Shaft couplings come in various designs, including flexible and rigid couplings. They are widely used in a broad range of applications due to their ability to transmit torque and accommodate misalignments between rotating shafts. Flexible shaft couplings, with elastomeric or metallic elements, offer good misalignment compensation and damping characteristics. Rigid couplings, on the other hand, provide precise torque transmission and are ideal for applications where shafts are well-aligned.
2. Gear Couplings:
Gear couplings are robust and designed for heavy-duty applications. They consist of two external gear hubs with internal gear teeth that mesh together. Gear couplings can handle high torque, high-speed, and angular misalignment. They are often used in demanding industries such as steel, mining, and paper manufacturing.
3. Grid Couplings:
Grid couplings feature a flexible grid element between the two halves of the coupling. They provide excellent shock absorption and misalignment compensation. Grid couplings are commonly used in pumps, compressors, and other industrial machinery.
4. Disc Couplings:
Disc couplings utilize flexible metallic discs to transmit torque and compensate for misalignment. They offer high torsional stiffness, making them suitable for applications requiring precise motion control, such as robotics and CNC machines.
5. Jaw Couplings:
Jaw couplings consist of two hubs with elastomeric spider inserts. They are easy to install, have good misalignment capabilities, and offer electrical isolation between shafts. Jaw couplings are widely used in light to medium-duty applications.
6. Oldham Couplings:
Oldham couplings have three discs—two outer discs with slots and a central disc with a tongue that fits into the slots. They provide excellent angular misalignment compensation while maintaining constant velocity between shafts. Oldham couplings are commonly used in printing machines and conveyors.
7. Beam Couplings:
Beam couplings are made from a single piece of flexible material with spiral cuts. They offer good misalignment compensation and torsional flexibility, making them suitable for precision equipment like encoders and servo motors.
The choice of coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application, including torque, speed, misalignment compensation, environmental conditions, and space limitations. Each coupling type has its strengths and limitations, and selecting the right coupling is crucial to ensure optimal performance and reliability in the mechanical system.
“`
Diagnosing and Fixing Common Issues with Shaft Couplings
Regular inspection and maintenance of shaft couplings are essential to detect and address common issues that may arise during operation. Here are steps to diagnose and fix some common coupling problems:
1. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:
If you notice unusual noise or excessive vibration during equipment operation, it may indicate misalignment, wear, or damage in the coupling. Check for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks or deformations, and inspect the coupling for proper alignment.
Diagnosis:
Use a vibration analysis tool to measure the vibration levels and identify the frequency of the abnormal vibrations. This can help pinpoint the source of the problem.
Fix:
If misalignment is the cause, adjust the coupling to achieve proper alignment between the shafts. Replace any damaged or worn coupling components, such as spiders or elastomeric inserts, as needed.
2. Excessive Heat:
Feeling excessive heat on the coupling during operation can indicate friction, improper lubrication, or overload conditions.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the coupling and surrounding components for signs of rubbing, lack of lubrication, or overloading.
Fix:
Ensure proper lubrication of the coupling, and check for any interference between the coupling and adjacent parts. Address any overloading issues by adjusting the equipment load or using a coupling with a higher torque capacity.
3. Shaft Movement:
If you observe axial or radial movement in the connected shafts, it may indicate wear or improper installation of the coupling.
Diagnosis:
Check the coupling’s set screws, keyways, or other fastening methods to ensure they are secure and not causing the shaft movement.
Fix:
If the coupling is worn or damaged, replace it with a new one. Ensure proper installation and use appropriate fastening methods to secure the coupling to the shafts.
4. Sheared Shear Pin:
In shear pin couplings, a sheared shear pin indicates overloading or shock loads that exceeded the coupling’s torque capacity.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the shear pin for damage or breakage.
Fix:
Replace the sheared shear pin with a new one of the correct specifications. Address any overloading issues or adjust the equipment to prevent future shearing.
5. Coupling Wear:
Regular wear is normal for couplings, but excessive wear may lead to decreased performance and increased misalignment.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the coupling components for signs of wear, such as worn elastomeric elements or damaged teeth.
Fix:
Replace the worn or damaged components with new ones of the appropriate specifications.
Remember, regular maintenance and periodic inspection are key to diagnosing issues early and preventing severe problems. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and replacement schedules to ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the shaft coupling.
“`

editor by CX 2024-03-10