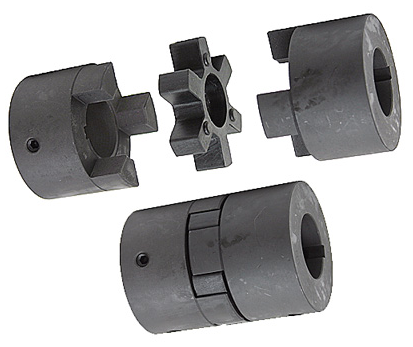
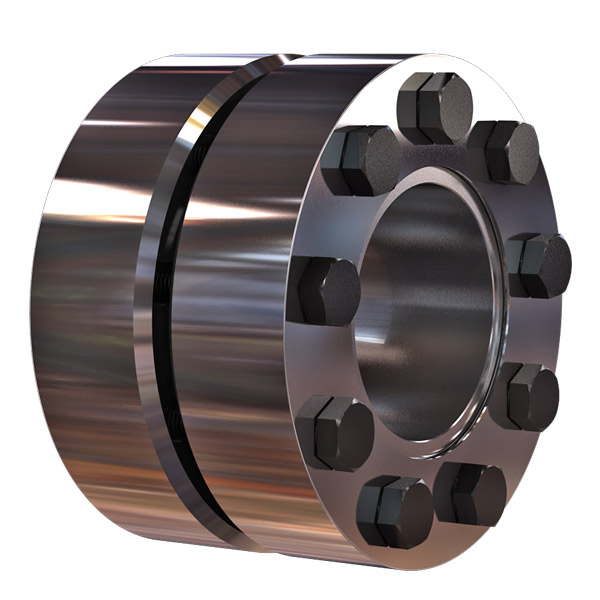
Product Description
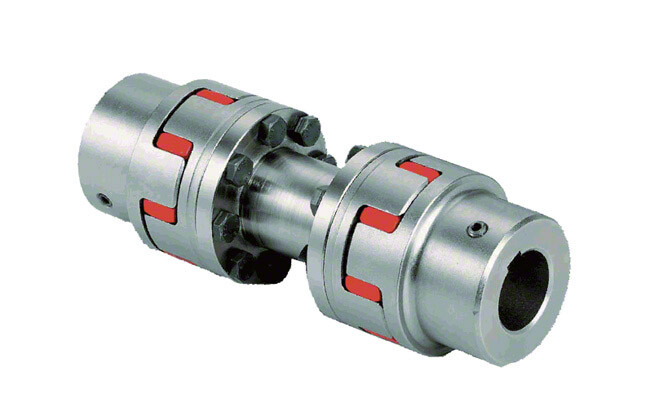
Original Excavator Parts Coupling CF-a Series Rubber Flexible Torsionally Steel Universal Shaft Coupling for Centafle
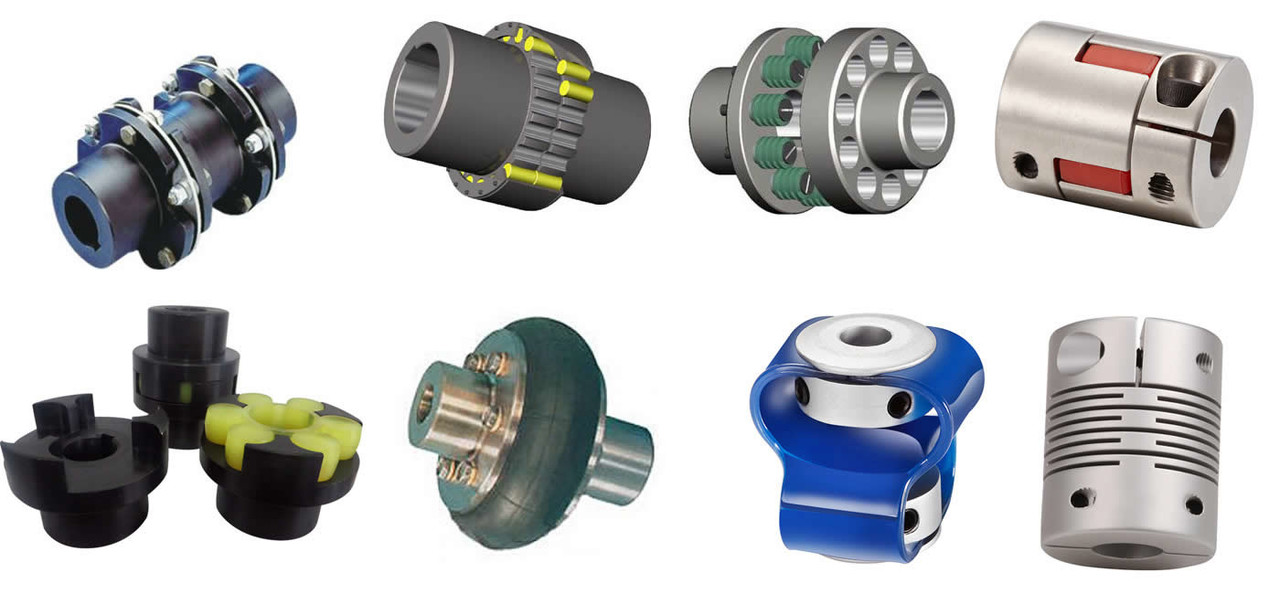
Product Display:
| Model | Outer Diameter(mm) | Inner Diameter(mm) | Hight(mm) | Diameter from Hole to Hole(mm) | Weight(kg) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4A/4AS | 103 | 53 | 28 | 68 | 0.18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8A/8AS | 134 | 71 | 32 | 88 | 0.26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16A/16AS | 160 | 80 | 41 | 110 | 0.54 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22A/22AS | 165 | 86 | 41 | 128 | 0.66 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25A/25AS | 183 | 102 | 46 | 123 | 0.78 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28A/AS | 0.88 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30A/30AS | 213 | 117 | 57 | 145 | 1.28 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 50A/50AS | 220 | 123 | 57 | 165 | 1.48 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 80A/80As | 225 | 120 | 65 | 167 | 1.92 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 90A/90As | 278 | 148 | 70 | 190 | 3.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 140A/140AS | 285 | 151 | 71 | 215 | 3.42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 250A/250AS | 6.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 284B | 6.34 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4, 4655134, EX3, ZAX460MTH, ZAX480MTH, 4636444, ZX470-3, EX470, ZAX470, ZAX450-3, ZAX450-3F, ZAX5, Atlas Copco,,
AC 385, AC 396, AC415, AC416, AC 455, AC485, AC 486, AC86, AC836, AC976, AC 6-712, 4DNV98 Chinese Brand Excavators: LGK: 6085, 200 CLG 60, 205, 220, 906, 907, 908, 920, 925, 936, CLG906C, CLG922LG YC50-8, YC60-8, YC60-8, YC135-8, YC230, YC230-8, YC230LC-8, YC360, YC85, YC50, YC85-7, YC60-7, YC135 SW50, 60, 70, 150 FR85-7, FR65, FR80, FR150-7, ZL 60, 205, 230, 360 SY55, SY60, SY215, SY230, SY210, SY220, SY310 /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
How to Select the Right Shaft Coupling for Specific Torque and Speed RequirementsSelecting the appropriate shaft coupling involves considering the specific torque and speed requirements of the application. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the right coupling: 1. Determine Torque and Speed:Identify the torque and speed requirements of the application. Torque is the rotational force required to transmit power between the shafts, usually measured in Nm (Newton-meters) or lb-ft (pound-feet). Speed refers to the rotational speed of the shafts, typically measured in RPM (revolutions per minute). 2. Calculate Torque Capacity:Check the torque capacity of various shaft couplings. Manufacturers provide torque ratings for each coupling type and size. Ensure that the selected coupling has a torque capacity that exceeds the application’s torque requirements. 3. Consider Misalignment:If the application involves significant shaft misalignment due to thermal expansion, vibration, or other factors, consider flexible couplings with good misalignment compensation capabilities. Elastomeric or beam couplings are popular choices for such applications. 4. Assess Operating Speed:For high-speed applications, choose couplings with high rotational speed ratings to avoid resonance issues and potential coupling failure. High-speed couplings may have specialized designs, such as disk or diaphragm couplings. 5. Evaluate Environmental Conditions:If the coupling will operate in harsh environments with exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures, select couplings made from corrosion-resistant materials or with protective coatings. 6. Check Torsional Stiffness:In applications requiring precision motion control, consider couplings with high torsional stiffness to minimize torsional backlash and maintain accurate positioning. Bellows or Oldham couplings are examples of couplings with low torsional backlash. 7. Size and Space Constraints:Ensure that the selected coupling fits within the available space and aligns with the shaft dimensions. Be mindful of any installation limitations, especially in confined spaces or applications with limited radial clearance. 8. Consult Manufacturer’s Data:Refer to the manufacturer’s catalogs and technical data sheets for detailed information on each coupling’s torque and speed ratings, misalignment capabilities, materials, and other relevant specifications. 9. Consider Cost and Maintenance:Compare the costs and maintenance requirements of different couplings. While some couplings may have higher upfront costs, they could offer longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in the long run. By following these steps and considering the specific torque and speed requirements of your application, you can select the right shaft coupling that will ensure efficient power transmission and reliable performance for your mechanical system. “` Real-World Examples of Shaft Coupling Applications in Different IndustriesShaft couplings play a crucial role in various industries by connecting rotating shafts and transmitting torque between them. Here are some real-world examples of shaft coupling applications in different industries: 1. Manufacturing Industry:In manufacturing plants, shaft couplings are used in various equipment such as conveyor systems, pumps, compressors, and mixers. For example, in a conveyor system, shaft couplings connect the motor shaft to the conveyor belt, allowing efficient material handling and transportation. 2. Oil and Gas Industry:The oil and gas industry utilizes shaft couplings in applications like drilling rigs, pumps, and generators. In drilling rigs, couplings connect the motor to the drill shaft, enabling the drilling process. 3. Marine Industry:In the marine industry, shaft couplings are found in propulsion systems, water pumps, and winches. They connect the ship’s engine to the propeller shaft, providing the necessary torque for propulsion. 4. Power Generation:Power plants use shaft couplings in turbines, generators, and cooling systems. For instance, in a steam turbine, couplings connect the turbine to the electrical generator, allowing the conversion of steam energy into electrical power. 5. Aerospace Industry:Aerospace applications use shaft couplings in aircraft engines, landing gear systems, and auxiliary power units. Couplings enable power transmission between different components of the aircraft systems. 6. Automotive Industry:In vehicles, shaft couplings are present in the drivetrain, steering systems, and transmission. For example, in a car’s transmission system, couplings connect the engine to the gearbox, enabling smooth gear changes and power transmission to the wheels. 7. Mining Industry:The mining industry relies on shaft couplings in heavy-duty machinery such as crushers, conveyor belts, and pumps. Couplings connect motors to various mining equipment, facilitating material extraction and transportation. 8. Agriculture:Agricultural machinery like tractors and harvesters use shaft couplings to connect the engine to implements such as plows, harvesters, and irrigation pumps. These examples demonstrate the wide-ranging applications of shaft couplings across industries. In each case, the specific coupling type is chosen based on factors such as torque requirements, misalignment compensation, environmental conditions, and load characteristics to ensure reliable and efficient operation. “` Diagnosing and Fixing Common Issues with Shaft CouplingsRegular inspection and maintenance of shaft couplings are essential to detect and address common issues that may arise during operation. Here are steps to diagnose and fix some common coupling problems: 1. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:If you notice unusual noise or excessive vibration during equipment operation, it may indicate misalignment, wear, or damage in the coupling. Check for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks or deformations, and inspect the coupling for proper alignment. Diagnosis:Use a vibration analysis tool to measure the vibration levels and identify the frequency of the abnormal vibrations. This can help pinpoint the source of the problem. Fix:If misalignment is the cause, adjust the coupling to achieve proper alignment between the shafts. Replace any damaged or worn coupling components, such as spiders or elastomeric inserts, as needed. 2. Excessive Heat:Feeling excessive heat on the coupling during operation can indicate friction, improper lubrication, or overload conditions. Diagnosis:Inspect the coupling and surrounding components for signs of rubbing, lack of lubrication, or overloading. Fix:Ensure proper lubrication of the coupling, and check for any interference between the coupling and adjacent parts. Address any overloading issues by adjusting the equipment load or using a coupling with a higher torque capacity. 3. Shaft Movement:If you observe axial or radial movement in the connected shafts, it may indicate wear or improper installation of the coupling. Diagnosis:Check the coupling’s set screws, keyways, or other fastening methods to ensure they are secure and not causing the shaft movement. Fix:If the coupling is worn or damaged, replace it with a new one. Ensure proper installation and use appropriate fastening methods to secure the coupling to the shafts. 4. Sheared Shear Pin:In shear pin couplings, a sheared shear pin indicates overloading or shock loads that exceeded the coupling’s torque capacity. Diagnosis:Inspect the shear pin for damage or breakage. Fix:Replace the sheared shear pin with a new one of the correct specifications. Address any overloading issues or adjust the equipment to prevent future shearing. 5. Coupling Wear:Regular wear is normal for couplings, but excessive wear may lead to decreased performance and increased misalignment. Diagnosis:Inspect the coupling components for signs of wear, such as worn elastomeric elements or damaged teeth. Fix:Replace the worn or damaged components with new ones of the appropriate specifications. Remember, regular maintenance and periodic inspection are key to diagnosing issues early and preventing severe problems. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and replacement schedules to ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the shaft coupling. “` China high quality Cast Iron Flexible Jaw Coupling for General Shaft Connection (L035)Product Description
JAW coupling, 1. The couplings offer a range of hub and element selection to meet different demands. 2. They can absorb shock and cater for incidental misalignment and damp out small amplitude vibrations. 3. NBR, Urethane, Hytrel elements. 4. Customized requirement is available.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Specific Safety Precautions When Working with Shaft CouplingsWorking with shaft couplings involves handling rotating machinery and mechanical components. To ensure the safety of personnel and prevent accidents, specific safety precautions should be followed during installation, maintenance, and operation: 1. Lockout-Tagout (LOTO):Prior to any work on machinery involving couplings, implement a lockout-tagout procedure to isolate the equipment from its power source. This ensures that the machinery cannot be accidentally energized during maintenance or repair, protecting workers from potential hazards. 2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety goggles, gloves, and appropriate clothing, when working with shaft couplings. PPE helps protect against potential hazards such as flying debris, sharp edges, or contact with moving parts. 3. Proper Training and Supervision:Only trained and authorized personnel should work with shaft couplings. Ensure that workers have the necessary knowledge and experience to handle the equipment safely. Adequate supervision may be required, especially for less-experienced personnel. 4. Inspection and Maintenance:Regularly inspect shaft couplings and associated components for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Address any issues promptly to prevent equipment failure and potential accidents. 5. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:Adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines for installation, operation, and maintenance of the specific coupling model. Improper use or deviation from recommended procedures may compromise safety and void warranties. 6. Avoid Overloading:Do not exceed the torque and speed limits specified by the coupling manufacturer. Overloading a coupling can lead to premature failure and pose safety risks to operators and nearby equipment. 7. Shaft Guards and Enclosures:Install appropriate guards and enclosures to prevent accidental contact with rotating shafts and couplings. These safety measures help reduce the risk of entanglement and injuries. 8. Zero Energy State:Ensure that all stored energy in the equipment, such as compressed air or hydraulic pressure, is released and the equipment is in a zero energy state before starting work. 9. Avoid Loose Clothing and Jewelry:Remove or secure loose clothing, jewelry, and other items that could get caught in moving parts. 10. Maintain a Clean Work Area:Keep the work area clean and free from clutter to avoid tripping hazards and facilitate safe movement around the machinery. By following these safety precautions, personnel can minimize the risks associated with working with shaft couplings and create a safer working environment for everyone involved. “` Do Shaft Couplings Require Regular Maintenance, and if so, What Does it Involve?Yes, shaft couplings do require regular maintenance to ensure their optimal performance, extend their service life, and prevent unexpected failures. The maintenance frequency may vary based on factors such as the coupling type, application, operating conditions, and the manufacturer’s recommendations. Here’s what regular maintenance for shaft couplings typically involves: 1. Visual Inspection:Regularly inspect the coupling for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Check for cracks, corrosion, and worn-out elastomeric elements (if applicable). Look for any abnormal movement or rubbing between the coupling components during operation. 2. Lubrication:If the shaft coupling requires lubrication, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the appropriate lubricant type and frequency. Lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and noise in the coupling. 3. Alignment Check:Monitor shaft alignment periodically. Misalignment can lead to premature coupling failure and damage to connected equipment. Make adjustments as needed to keep the shafts properly aligned. 4. Torque Check:For bolted couplings, periodically check the torque on the bolts to ensure they remain securely fastened. Loose bolts can lead to misalignment and reduce coupling performance. 5. Replace Worn Components:If any coupling components show signs of wear or damage beyond acceptable limits, replace them promptly with genuine replacement parts from the manufacturer. 6. Environmental Considerations:In harsh environments with exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures, take additional measures to protect the coupling, such as applying corrosion-resistant coatings or using special materials. 7. Monitoring Coupling Performance:Implement a monitoring system to track coupling performance and detect any changes or abnormalities early on. This could include temperature monitoring, vibration analysis, or other condition monitoring techniques. 8. Professional Inspection:Periodically have the coupling and connected machinery inspected by qualified professionals to identify any potential issues that may not be apparent during regular inspections. By adhering to a regular maintenance schedule and taking proactive measures to address potential issues, you can ensure that your shaft couplings operate reliably and efficiently throughout their service life, minimizing downtime and improving overall system performance. “` Diagnosing and Fixing Common Issues with Shaft CouplingsRegular inspection and maintenance of shaft couplings are essential to detect and address common issues that may arise during operation. Here are steps to diagnose and fix some common coupling problems: 1. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:If you notice unusual noise or excessive vibration during equipment operation, it may indicate misalignment, wear, or damage in the coupling. Check for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks or deformations, and inspect the coupling for proper alignment. Diagnosis:Use a vibration analysis tool to measure the vibration levels and identify the frequency of the abnormal vibrations. This can help pinpoint the source of the problem. Fix:If misalignment is the cause, adjust the coupling to achieve proper alignment between the shafts. Replace any damaged or worn coupling components, such as spiders or elastomeric inserts, as needed. 2. Excessive Heat:Feeling excessive heat on the coupling during operation can indicate friction, improper lubrication, or overload conditions. Diagnosis:Inspect the coupling and surrounding components for signs of rubbing, lack of lubrication, or overloading. Fix:Ensure proper lubrication of the coupling, and check for any interference between the coupling and adjacent parts. Address any overloading issues by adjusting the equipment load or using a coupling with a higher torque capacity. 3. Shaft Movement:If you observe axial or radial movement in the connected shafts, it may indicate wear or improper installation of the coupling. Diagnosis:Check the coupling’s set screws, keyways, or other fastening methods to ensure they are secure and not causing the shaft movement. Fix:If the coupling is worn or damaged, replace it with a new one. Ensure proper installation and use appropriate fastening methods to secure the coupling to the shafts. 4. Sheared Shear Pin:In shear pin couplings, a sheared shear pin indicates overloading or shock loads that exceeded the coupling’s torque capacity. Diagnosis:Inspect the shear pin for damage or breakage. Fix:Replace the sheared shear pin with a new one of the correct specifications. Address any overloading issues or adjust the equipment to prevent future shearing. 5. Coupling Wear:Regular wear is normal for couplings, but excessive wear may lead to decreased performance and increased misalignment. Diagnosis:Inspect the coupling components for signs of wear, such as worn elastomeric elements or damaged teeth. Fix:Replace the worn or damaged components with new ones of the appropriate specifications. Remember, regular maintenance and periodic inspection are key to diagnosing issues early and preventing severe problems. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and replacement schedules to ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the shaft coupling. “` China best Cast Iron Flexible Jaw Coupling for General Shaft Connection (L035)Product Description
JAW coupling, 1. The couplings offer a range of hub and element selection to meet different demands. 2. They can absorb shock and cater for incidental misalignment and damp out small amplitude vibrations. 3. NBR, Urethane, Hytrel elements. 4. Customized requirement is available.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Exploring the Use of Elastomeric Materials in Flexible Shaft CouplingsElastomeric materials play a crucial role in the design and function of flexible shaft couplings. These materials, commonly known as elastomers, are rubber-like substances that exhibit high elasticity and flexibility. They are widely used in various types of flexible couplings due to their unique properties and benefits: 1. Damping and Vibration Absorption:Elastomeric materials have excellent damping characteristics, meaning they can absorb and dissipate vibrations and shocks. This property is particularly useful in applications where vibration control is essential to protect sensitive equipment and improve overall system performance. 2. Misalignment Compensation:Flexible shaft couplings with elastomeric elements can accommodate different types of misalignments, including angular, parallel, and radial misalignments. The elasticity of the material allows for limited movement between the shafts while still transmitting torque efficiently. 3. Torsional Flexibility:Elastomers offer torsional flexibility, which allows them to twist and deform under torque loads. This feature helps to minimize torsional stresses and torsional backlash, making them suitable for applications requiring precise motion control. 4. Shock and Impact Resistance:Due to their high resilience, elastomers can withstand sudden shocks and impacts without permanent deformation. This property makes them ideal for use in machinery subjected to varying loads or rapid changes in torque. 5. No Lubrication Requirement:Elastomeric couplings are often maintenance-free because the elastomer material does not require additional lubrication. This reduces maintenance costs and simplifies the overall system upkeep. 6. Electric Isolation:In certain applications, elastomeric materials can provide electrical isolation between the driving and driven components. This can help prevent the transmission of electrical currents or static charges through the coupling. 7. Corrosion Resistance:Many elastomers used in couplings are resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for use in challenging environments where exposure to chemicals or moisture is a concern. 8. Easy Installation:Elastomeric couplings are often designed for ease of installation and replacement. Their flexibility allows for simple and quick assembly onto the shafts without the need for special tools or complex procedures. Given these advantages, elastomeric materials are popular choices for various flexible shaft couplings, including jaw couplings, tire couplings, and spider couplings. However, it is essential to select the right elastomer material based on the specific application requirements, such as temperature range, chemical compatibility, and torque capacity. “` Temperature and Speed Limits for Different Shaft Coupling TypesThe temperature and speed limits of shaft couplings vary depending on the materials and design of the coupling. Manufacturers provide specific guidelines and ratings for each coupling type. Below are general temperature and speed limits for some common shaft coupling types: 1. Elastomeric Couplings:Elastomeric couplings, such as jaw couplings and tire couplings, typically have temperature limits ranging from -40°C to 100°C (-40°F to 212°F). The speed limits for elastomeric couplings are generally up to 5,000 RPM, but some designs may allow higher speeds. 2. Metallic Couplings:Metallic couplings, like gear couplings and disc couplings, can handle a wider temperature range, typically from -50°C to 200°C (-58°F to 392°F). The speed limits for metallic couplings vary based on the size and design, but they can range from 3,000 RPM to over 10,000 RPM. 3. Grid Couplings:Grid couplings have temperature limits similar to metallic couplings, ranging from -50°C to 200°C (-58°F to 392°F). The speed limits for grid couplings are typically in the range of 3,000 to 5,000 RPM. 4. Oldham Couplings:Oldham couplings usually have temperature limits from -30°C to 100°C (-22°F to 212°F) and speed limits ranging from 1,000 to 5,000 RPM. 5. Beam Couplings:Beam couplings generally have temperature limits from -40°C to 120°C (-40°F to 248°F) and speed limits between 5,000 to 10,000 RPM. 6. Fluid Couplings:Fluid couplings are suitable for a wide range of temperatures, often from -50°C to 300°C (-58°F to 572°F). The speed limits depend on the size and design of the fluid coupling but can extend to several thousand RPM. It’s important to note that these are general guidelines, and the actual temperature and speed limits may vary based on the specific coupling manufacturer, material quality, and application requirements. Always refer to the manufacturer’s documentation and technical specifications for accurate and up-to-date temperature and speed limits for a particular shaft coupling model. “` How Does a Flexible Shaft Coupling Differ from a Rigid Shaft Coupling?Flexible shaft couplings and rigid shaft couplings are two distinct types of couplings, each designed to serve different purposes in mechanical power transmission. Here are the key differences between the two: 1. Flexibility:The most significant difference between flexible and rigid shaft couplings is their flexibility. Flexible couplings are designed with elements that can deform or flex to accommodate misalignments between the shafts. This flexibility allows for angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, making them suitable for applications where shafts are not perfectly aligned. In contrast, rigid couplings do not have this flexibility and require precise alignment between the shafts. 2. Misalignment Compensation:Flexible couplings excel in compensating for misalignments, making them ideal for applications with dynamic conditions or those prone to misalignment due to thermal expansion or vibrations. Rigid couplings, on the other hand, are used in applications where perfect alignment is critical to prevent vibration, wear, and premature failure. 3. Damping Properties:Flexible couplings, particularly those with elastomeric or flexible elements, offer damping properties, meaning they can absorb and reduce shocks and vibrations. This damping capability helps protect the connected equipment from damage and enhances system reliability. Rigid couplings lack this damping ability and can transmit shocks and vibrations directly between shafts. 4. Torque Transmission:Both flexible and rigid couplings are capable of transmitting torque from the driving shaft to the driven shaft. However, the torque transmission of flexible couplings can be limited compared to rigid couplings, especially in high-torque applications. 5. Types of Applications:Flexible couplings find applications in a wide range of industries, especially in situations where misalignment compensation, vibration damping, and shock absorption are essential. They are commonly used in conveyors, pumps, compressors, printing presses, and automation systems. Rigid couplings are used in precision machinery and applications that demand perfect alignment, such as high-speed spindles and certain types of precision equipment. 6. Installation:Flexible couplings are relatively easier to install due to their ability to accommodate misalignment. On the other hand, rigid couplings require careful alignment during installation to ensure proper functioning and prevent premature wear. The choice between a flexible and a rigid shaft coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application. If misalignment compensation, damping, and flexibility are critical, a flexible coupling is the preferred choice. If precision alignment and direct torque transmission are essential, a rigid coupling is more suitable. “` China wholesaler Support Customer Customized Sizes Flexible Coupling Shaft Coupling for CNCProduct Description
About Us UP GOLD Automation Technology Co., LTD., independent brand, NYZ and UP. The main products are linear guide rail, slider, ball screw, linear optical shaft, linear bearing, machine tool spindle special P4 high precision bearings and accessories, with advanced production equipment and testing instruments to ensure the accuracy of each product. Precision products will provide higher value to the equipment. The company promises to sell each product, warranty period of 24 months, 24 hours after-sales service. Provide professional OEM cooperation model. At the same time, the company agents international first-line brands HIWIN, TBI, NSK,THK. Sufficient resources to ensure every customer needs.
Our Advantages *Two-year warranty, replace instead of repair. Product Description Couplings are the most commonly used connecting components in shaft transmission of mechanical products. Its function is to connect 2 axes to rotate together to transmit torque and motion, compensate for the relative displacement of the 2 connected axes, and improve the transmission dynamics of the system. Its application range covers many fields of the national economy, and it is a universal basic component with many varieties and large usage. With the advancement of science and technology and the development of production, the types of mechanical products are increasing day by day, and the requirements for their performance are also increasing. In order to adapt to the needs of various working conditions, couplings with various characteristics are required to achieve the expected use effects.
Customer Comment
Packaging and Logistics Commercial packaging Plastic bag + individual packing+ Carton+ Pallet Mode of transportation
FAQ Q: What is the producing process? /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
How to Select the Right Shaft Coupling for Specific Torque and Speed RequirementsSelecting the appropriate shaft coupling involves considering the specific torque and speed requirements of the application. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the right coupling: 1. Determine Torque and Speed:Identify the torque and speed requirements of the application. Torque is the rotational force required to transmit power between the shafts, usually measured in Nm (Newton-meters) or lb-ft (pound-feet). Speed refers to the rotational speed of the shafts, typically measured in RPM (revolutions per minute). 2. Calculate Torque Capacity:Check the torque capacity of various shaft couplings. Manufacturers provide torque ratings for each coupling type and size. Ensure that the selected coupling has a torque capacity that exceeds the application’s torque requirements. 3. Consider Misalignment:If the application involves significant shaft misalignment due to thermal expansion, vibration, or other factors, consider flexible couplings with good misalignment compensation capabilities. Elastomeric or beam couplings are popular choices for such applications. 4. Assess Operating Speed:For high-speed applications, choose couplings with high rotational speed ratings to avoid resonance issues and potential coupling failure. High-speed couplings may have specialized designs, such as disk or diaphragm couplings. 5. Evaluate Environmental Conditions:If the coupling will operate in harsh environments with exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures, select couplings made from corrosion-resistant materials or with protective coatings. 6. Check Torsional Stiffness:In applications requiring precision motion control, consider couplings with high torsional stiffness to minimize torsional backlash and maintain accurate positioning. Bellows or Oldham couplings are examples of couplings with low torsional backlash. 7. Size and Space Constraints:Ensure that the selected coupling fits within the available space and aligns with the shaft dimensions. Be mindful of any installation limitations, especially in confined spaces or applications with limited radial clearance. 8. Consult Manufacturer’s Data:Refer to the manufacturer’s catalogs and technical data sheets for detailed information on each coupling’s torque and speed ratings, misalignment capabilities, materials, and other relevant specifications. 9. Consider Cost and Maintenance:Compare the costs and maintenance requirements of different couplings. While some couplings may have higher upfront costs, they could offer longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in the long run. By following these steps and considering the specific torque and speed requirements of your application, you can select the right shaft coupling that will ensure efficient power transmission and reliable performance for your mechanical system. “` Comparing Shaft Couplings with Other Types of Couplings in PerformanceShaft couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, and their performance characteristics vary depending on the coupling type. Let’s compare shaft couplings with other common types of couplings: 1. Shaft Couplings:Shaft couplings come in various designs, including flexible and rigid couplings. They are widely used in a broad range of applications due to their ability to transmit torque and accommodate misalignments between rotating shafts. Flexible shaft couplings, with elastomeric or metallic elements, offer good misalignment compensation and damping characteristics. Rigid couplings, on the other hand, provide precise torque transmission and are ideal for applications where shafts are well-aligned. 2. Gear Couplings:Gear couplings are robust and designed for heavy-duty applications. They consist of two external gear hubs with internal gear teeth that mesh together. Gear couplings can handle high torque, high-speed, and angular misalignment. They are often used in demanding industries such as steel, mining, and paper manufacturing. 3. Grid Couplings:Grid couplings feature a flexible grid element between the two halves of the coupling. They provide excellent shock absorption and misalignment compensation. Grid couplings are commonly used in pumps, compressors, and other industrial machinery. 4. Disc Couplings:Disc couplings utilize flexible metallic discs to transmit torque and compensate for misalignment. They offer high torsional stiffness, making them suitable for applications requiring precise motion control, such as robotics and CNC machines. 5. Jaw Couplings:Jaw couplings consist of two hubs with elastomeric spider inserts. They are easy to install, have good misalignment capabilities, and offer electrical isolation between shafts. Jaw couplings are widely used in light to medium-duty applications. 6. Oldham Couplings:Oldham couplings have three discs—two outer discs with slots and a central disc with a tongue that fits into the slots. They provide excellent angular misalignment compensation while maintaining constant velocity between shafts. Oldham couplings are commonly used in printing machines and conveyors. 7. Beam Couplings:Beam couplings are made from a single piece of flexible material with spiral cuts. They offer good misalignment compensation and torsional flexibility, making them suitable for precision equipment like encoders and servo motors. The choice of coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application, including torque, speed, misalignment compensation, environmental conditions, and space limitations. Each coupling type has its strengths and limitations, and selecting the right coupling is crucial to ensure optimal performance and reliability in the mechanical system. “` How Does a Flexible Shaft Coupling Differ from a Rigid Shaft Coupling?Flexible shaft couplings and rigid shaft couplings are two distinct types of couplings, each designed to serve different purposes in mechanical power transmission. Here are the key differences between the two: 1. Flexibility:The most significant difference between flexible and rigid shaft couplings is their flexibility. Flexible couplings are designed with elements that can deform or flex to accommodate misalignments between the shafts. This flexibility allows for angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, making them suitable for applications where shafts are not perfectly aligned. In contrast, rigid couplings do not have this flexibility and require precise alignment between the shafts. 2. Misalignment Compensation:Flexible couplings excel in compensating for misalignments, making them ideal for applications with dynamic conditions or those prone to misalignment due to thermal expansion or vibrations. Rigid couplings, on the other hand, are used in applications where perfect alignment is critical to prevent vibration, wear, and premature failure. 3. Damping Properties:Flexible couplings, particularly those with elastomeric or flexible elements, offer damping properties, meaning they can absorb and reduce shocks and vibrations. This damping capability helps protect the connected equipment from damage and enhances system reliability. Rigid couplings lack this damping ability and can transmit shocks and vibrations directly between shafts. 4. Torque Transmission:Both flexible and rigid couplings are capable of transmitting torque from the driving shaft to the driven shaft. However, the torque transmission of flexible couplings can be limited compared to rigid couplings, especially in high-torque applications. 5. Types of Applications:Flexible couplings find applications in a wide range of industries, especially in situations where misalignment compensation, vibration damping, and shock absorption are essential. They are commonly used in conveyors, pumps, compressors, printing presses, and automation systems. Rigid couplings are used in precision machinery and applications that demand perfect alignment, such as high-speed spindles and certain types of precision equipment. 6. Installation:Flexible couplings are relatively easier to install due to their ability to accommodate misalignment. On the other hand, rigid couplings require careful alignment during installation to ensure proper functioning and prevent premature wear. The choice between a flexible and a rigid shaft coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application. If misalignment compensation, damping, and flexibility are critical, a flexible coupling is the preferred choice. If precision alignment and direct torque transmission are essential, a rigid coupling is more suitable. “` China Best Sales Double Pack Disc Coupling for Pumps Flexible Single Diaphragm Coupling Disc Couplings Torsionally Rigid Double Disc PacksProduct Description
Product Description
1. The allowable compensation quantity listed in the table refers to the relative offset of 2 axes formed by the comprehensive factors such as vibration, shock, deformation and temperature change caused by manufacturing error, installation error and working load change under working condition. The maximum opening value is a circular hole or a tapered hole with a keyway. Main applications: DWZ disc eddy current brake is mainly used as load in loading dynamometer equipment. it is experimental apparatus which can measure the dynamic mechanical properties, especially in dynamic loading test whose power value is small or tiny, also can be treated as suction power devices of other dynamic devices. DW series disc eddy current dynamometer is, is that add device for measuring torque and rotational speed on DWZ series disc eddy current brake, it is experimental apparatus which can measure the dynamic mechnical properties, especial in dynamic loading test whose power value is small or tiny. CW eddy current brake as a load is mainly used to measure the mechanical characteristics of inspection equipment, it and other control instrument (including loading apparatus, torque speed sensor and torque power acquisition instrument etc.) can be composed of eddy current dynamometer can be used for performance testing of the internal combustion engine, motor, gas turbine, automobile and its dynamic mechanical components, compared with other power measuring device, the CW series power measuring device has the advantages of reliability, high stability and practicability.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Can Rigid Couplings Accommodate High Torque and High-Speed Applications?Yes, rigid couplings are well-suited for high torque and high-speed applications. Their design and construction allow them to efficiently transmit large amounts of torque and handle high rotational speeds without compromising performance or introducing backlash. Rigid couplings are typically made from robust materials, such as steel or aluminum, which provide high strength and stiffness. This allows them to withstand substantial torque loads without deformation or failure. Additionally, rigid couplings do not have flexible elements, such as elastomers or springs, which can be a limiting factor in high-torque applications. The absence of flexible elements also means that rigid couplings have minimal backlash. Backlash is the clearance between mating teeth in a coupling and can cause position inaccuracies, especially in high-precision systems. Since rigid couplings have a solid, one-piece design, they offer precise and immediate torque transmission, making them suitable for applications requiring high accuracy and repeatability. Furthermore, the solid construction of rigid couplings allows them to handle high rotational speeds. They do not exhibit the bending or torsional flexibility seen in some other coupling types, which can be limiting factors in high-speed applications. As a result, rigid couplings are commonly used in various high-speed machinery, such as power transmission systems, motors, pumps, and industrial equipment. However, it is essential to ensure proper alignment and installation when using rigid couplings in high-torque and high-speed applications. Any misalignment between the shafts can lead to increased stresses and premature failure. Regular maintenance, including shaft alignment checks, can help ensure optimal performance and longevity in such demanding applications. In summary, rigid couplings are an excellent choice for high torque and high-speed applications due to their robust design, minimal backlash, and ability to provide precise torque transmission. When correctly installed and maintained, rigid couplings can reliably handle the demands of various industrial and mechanical systems.
Use of Rigid Couplings for Motor-to-Shaft and Shaft-to-Shaft ConnectionsYes, rigid couplings can be used for both motor-to-shaft and shaft-to-shaft connections in mechanical systems. Rigid couplings are designed to provide a solid and non-flexible connection between two shafts. This characteristic makes them versatile for various applications, including motor-to-shaft and shaft-to-shaft connections. 1. Motor-to-Shaft Connections: In motor-to-shaft connections, a rigid coupling is used to connect the output shaft of an electric motor to the driven shaft of a machine or equipment. This ensures direct power transmission without any flexibility. Motor-to-shaft connections are common in applications where the motor’s rotational motion needs to be transferred to the driven equipment with high precision and efficiency. 2. Shaft-to-Shaft Connections: In shaft-to-shaft connections, a rigid coupling joins two shafts directly, providing a solid and immovable link between them. This is beneficial in applications where precise alignment and torque transmission are essential, such as in precision motion control systems or heavy-duty industrial machinery. Rigid couplings are available in various designs, such as one-piece, two-piece, and split types, to accommodate different shaft arrangements. The type of rigid coupling used depends on the specific application and the shaft sizes to be connected. Advantages of Using Rigid Couplings: – Zero backlash ensures accurate motion transfer and positioning. – Efficient power transmission without loss due to flexibility. – Minimal maintenance requirements due to their simple design. – High torque capacity suitable for heavy-duty applications. – Tolerance to misalignment (within design limits) enhances versatility. – Provides system stiffness, reducing the risk of resonance and vibration-related issues. – Suitable for high-speed applications. – Versatility for various industrial applications. Whether it’s connecting a motor to a driven shaft or joining two shafts together, rigid couplings offer reliability, precision, and efficiency, making them a popular choice in numerous mechanical systems.
Advantages of Using Rigid Couplings in Mechanical Systems:Rigid couplings offer several advantages when used in mechanical systems. These advantages make them a preferred choice in certain applications where precise alignment and high torque transmission are essential. Here are the key advantages of using rigid couplings:
Rigid couplings are commonly used in various industries and applications, including high-precision machinery, robotics, automation systems, precision motion control, and machine tools. They are especially beneficial in scenarios where misalignment needs to be minimized or avoided altogether. It’s important to note that while rigid couplings offer these advantages, they are not suitable for applications where shaft misalignment or shock absorption is required. In such cases, flexible couplings or other specialized coupling types may be more appropriate.
China Good quality CNC Aluminum Elastic Rubber Spider Jaw Shaft Coupler GF14*22 20*25 25*30 40*50 Shaft Flexible Coupling Ball Screw Plum CouplingProduct Description
Product Description Coupling Deatails Name: High precision plum blossom
Product Parameters Detailed Photos /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Understanding the Torque and Misalignment Capabilities of Shaft CouplingsShaft couplings play a critical role in transmitting torque and accommodating misalignment between rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. Understanding their torque and misalignment capabilities is essential for selecting the right coupling for a specific application. Here’s an overview: Torque Transmission:The torque capacity of a shaft coupling refers to its ability to transmit rotational force from one shaft to another. It is typically specified in torque units, such as Nm (Newton-meters) or lb-ft (pound-feet). The coupling’s torque capacity depends on its design, size, and material. When selecting a coupling, it’s crucial to ensure that its torque capacity meets or exceeds the torque requirements of the application. Overloading a coupling beyond its torque capacity can lead to premature failure or damage to the coupling and connected equipment. Misalignment Compensation:Shaft misalignment can occur due to various factors, including thermal expansion, manufacturing tolerances, or foundation settling. Misalignment puts additional stress on the coupling and connected components, potentially leading to increased wear and reduced efficiency. Shaft couplings are designed to compensate for different types of misalignment:
The coupling’s misalignment capabilities are specified in terms of angular and axial misalignment values, usually in degrees or millimeters. Different coupling designs can accommodate varying degrees of misalignment, and the choice depends on the specific application and operating conditions. Flexible Couplings:Flexible couplings, such as elastomeric or jaw couplings, offer good misalignment compensation. They can handle a combination of angular, parallel, and axial misalignments. However, their torque capacity may be limited compared to rigid couplings. Rigid Couplings:Rigid couplings, such as clamp or sleeve couplings, have high torque transmission capabilities but offer minimal misalignment compensation. They are best suited for applications where shafts are well-aligned and precise torque transmission is critical. Torsional Stiffness:Another factor to consider is the coupling’s torsional stiffness, which determines how much torsional deflection or twist occurs under load. Some applications, like precision systems, may require couplings with high torsional stiffness to maintain accurate positioning and avoid torsional backlash. By understanding the torque and misalignment capabilities of shaft couplings, engineers can make informed decisions when selecting a coupling to ensure efficient power transmission and reliable performance in their mechanical systems. “` Do Shaft Couplings Require Regular Maintenance, and if so, What Does it Involve?Yes, shaft couplings do require regular maintenance to ensure their optimal performance, extend their service life, and prevent unexpected failures. The maintenance frequency may vary based on factors such as the coupling type, application, operating conditions, and the manufacturer’s recommendations. Here’s what regular maintenance for shaft couplings typically involves: 1. Visual Inspection:Regularly inspect the coupling for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Check for cracks, corrosion, and worn-out elastomeric elements (if applicable). Look for any abnormal movement or rubbing between the coupling components during operation. 2. Lubrication:If the shaft coupling requires lubrication, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the appropriate lubricant type and frequency. Lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and noise in the coupling. 3. Alignment Check:Monitor shaft alignment periodically. Misalignment can lead to premature coupling failure and damage to connected equipment. Make adjustments as needed to keep the shafts properly aligned. 4. Torque Check:For bolted couplings, periodically check the torque on the bolts to ensure they remain securely fastened. Loose bolts can lead to misalignment and reduce coupling performance. 5. Replace Worn Components:If any coupling components show signs of wear or damage beyond acceptable limits, replace them promptly with genuine replacement parts from the manufacturer. 6. Environmental Considerations:In harsh environments with exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures, take additional measures to protect the coupling, such as applying corrosion-resistant coatings or using special materials. 7. Monitoring Coupling Performance:Implement a monitoring system to track coupling performance and detect any changes or abnormalities early on. This could include temperature monitoring, vibration analysis, or other condition monitoring techniques. 8. Professional Inspection:Periodically have the coupling and connected machinery inspected by qualified professionals to identify any potential issues that may not be apparent during regular inspections. By adhering to a regular maintenance schedule and taking proactive measures to address potential issues, you can ensure that your shaft couplings operate reliably and efficiently throughout their service life, minimizing downtime and improving overall system performance. “` Diagnosing and Fixing Common Issues with Shaft CouplingsRegular inspection and maintenance of shaft couplings are essential to detect and address common issues that may arise during operation. Here are steps to diagnose and fix some common coupling problems: 1. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:If you notice unusual noise or excessive vibration during equipment operation, it may indicate misalignment, wear, or damage in the coupling. Check for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks or deformations, and inspect the coupling for proper alignment. Diagnosis:Use a vibration analysis tool to measure the vibration levels and identify the frequency of the abnormal vibrations. This can help pinpoint the source of the problem. Fix:If misalignment is the cause, adjust the coupling to achieve proper alignment between the shafts. Replace any damaged or worn coupling components, such as spiders or elastomeric inserts, as needed. 2. Excessive Heat:Feeling excessive heat on the coupling during operation can indicate friction, improper lubrication, or overload conditions. Diagnosis:Inspect the coupling and surrounding components for signs of rubbing, lack of lubrication, or overloading. Fix:Ensure proper lubrication of the coupling, and check for any interference between the coupling and adjacent parts. Address any overloading issues by adjusting the equipment load or using a coupling with a higher torque capacity. 3. Shaft Movement:If you observe axial or radial movement in the connected shafts, it may indicate wear or improper installation of the coupling. Diagnosis:Check the coupling’s set screws, keyways, or other fastening methods to ensure they are secure and not causing the shaft movement. Fix:If the coupling is worn or damaged, replace it with a new one. Ensure proper installation and use appropriate fastening methods to secure the coupling to the shafts. 4. Sheared Shear Pin:In shear pin couplings, a sheared shear pin indicates overloading or shock loads that exceeded the coupling’s torque capacity. Diagnosis:Inspect the shear pin for damage or breakage. Fix:Replace the sheared shear pin with a new one of the correct specifications. Address any overloading issues or adjust the equipment to prevent future shearing. 5. Coupling Wear:Regular wear is normal for couplings, but excessive wear may lead to decreased performance and increased misalignment. Diagnosis:Inspect the coupling components for signs of wear, such as worn elastomeric elements or damaged teeth. Fix:Replace the worn or damaged components with new ones of the appropriate specifications. Remember, regular maintenance and periodic inspection are key to diagnosing issues early and preventing severe problems. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and replacement schedules to ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the shaft coupling. “` China OEM Double Pack Disc Coupling for Pumps Flexible Single Diaphragm Coupling Disc Couplings Torsionally Rigid Double Disc Packs SellingProduct Description
Product Description
1. The allowable compensation quantity listed in the table refers to the relative offset of 2 axes formed by the comprehensive factors such as vibration, shock, deformation and temperature change caused by manufacturing error, installation error and working load change under working condition. The maximum opening value is a circular hole or a tapered hole with a keyway. Main applications: DWZ disc eddy current brake is mainly used as load in loading dynamometer equipment. it is experimental apparatus which can measure the dynamic mechanical properties, especially in dynamic loading test whose power value is small or tiny, also can be treated as suction power devices of other dynamic devices. DW series disc eddy current dynamometer is, is that add device for measuring torque and rotational speed on DWZ series disc eddy current brake, it is experimental apparatus which can measure the dynamic mechnical properties, especial in dynamic loading test whose power value is small or tiny. CW eddy current brake as a load is mainly used to measure the mechanical characteristics of inspection equipment, it and other control instrument (including loading apparatus, torque speed sensor and torque power acquisition instrument etc.) can be composed of eddy current dynamometer can be used for performance testing of the internal combustion engine, motor, gas turbine, automobile and its dynamic mechanical components, compared with other power measuring device, the CW series power measuring device has the advantages of reliability, high stability and practicability.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Can Rigid Couplings Accommodate High Torque and High-Speed Applications?Yes, rigid couplings are well-suited for high torque and high-speed applications. Their design and construction allow them to efficiently transmit large amounts of torque and handle high rotational speeds without compromising performance or introducing backlash. Rigid couplings are typically made from robust materials, such as steel or aluminum, which provide high strength and stiffness. This allows them to withstand substantial torque loads without deformation or failure. Additionally, rigid couplings do not have flexible elements, such as elastomers or springs, which can be a limiting factor in high-torque applications. The absence of flexible elements also means that rigid couplings have minimal backlash. Backlash is the clearance between mating teeth in a coupling and can cause position inaccuracies, especially in high-precision systems. Since rigid couplings have a solid, one-piece design, they offer precise and immediate torque transmission, making them suitable for applications requiring high accuracy and repeatability. Furthermore, the solid construction of rigid couplings allows them to handle high rotational speeds. They do not exhibit the bending or torsional flexibility seen in some other coupling types, which can be limiting factors in high-speed applications. As a result, rigid couplings are commonly used in various high-speed machinery, such as power transmission systems, motors, pumps, and industrial equipment. However, it is essential to ensure proper alignment and installation when using rigid couplings in high-torque and high-speed applications. Any misalignment between the shafts can lead to increased stresses and premature failure. Regular maintenance, including shaft alignment checks, can help ensure optimal performance and longevity in such demanding applications. In summary, rigid couplings are an excellent choice for high torque and high-speed applications due to their robust design, minimal backlash, and ability to provide precise torque transmission. When correctly installed and maintained, rigid couplings can reliably handle the demands of various industrial and mechanical systems.
Can Rigid Couplings Be Used in Applications with Varying Operating Temperatures?Rigid couplings are versatile mechanical components that can be used in a wide range of applications, including those with varying operating temperatures. However, the selection of the appropriate material for the rigid coupling is crucial to ensure its reliable performance under different temperature conditions. Material Selection: The choice of material for the rigid coupling depends on the specific operating temperature range of the application. Common materials used in manufacturing rigid couplings include steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, among others. Each material has its own temperature limitations: – Steel: Rigid couplings made from steel are suitable for applications with moderate to high temperatures. Steel couplings can handle temperatures ranging from -40°C to around 300°C, depending on the specific grade of steel used. – Stainless Steel: Stainless steel rigid couplings offer higher corrosion resistance and can be used in applications with more demanding temperature environments. They can withstand temperatures from -80°C to approximately 400°C. – Aluminum: Aluminum rigid couplings are commonly used in applications with lower temperature requirements, typically ranging from -50°C to around 120°C. Thermal Expansion: When selecting a rigid coupling for an application with varying temperatures, it is essential to consider thermal expansion. Different materials have different coefficients of thermal expansion, meaning they expand and contract at different rates as the temperature changes. If the operating temperature fluctuates significantly, the thermal expansion of the rigid coupling and the connected components must be carefully accounted for to avoid issues with misalignment or binding. Extreme Temperature Environments: For applications with extremely high or low temperatures beyond the capabilities of traditional materials, specialized high-temperature alloys or composites may be required. These materials can withstand more extreme temperature conditions but may come with higher costs. Lubrication: The choice of lubrication can also play a role in the suitability of rigid couplings for varying temperature applications. In high-temperature environments, consideration should be given to using high-temperature lubricants that can maintain their effectiveness and viscosity at elevated temperatures. In conclusion, rigid couplings can indeed be used in applications with varying operating temperatures, but careful material selection, consideration of thermal expansion, and appropriate lubrication are essential to ensure reliable and efficient performance under changing temperature conditions.
Advantages of Using Rigid Couplings in Mechanical Systems:Rigid couplings offer several advantages when used in mechanical systems. These advantages make them a preferred choice in certain applications where precise alignment and high torque transmission are essential. Here are the key advantages of using rigid couplings:
Rigid couplings are commonly used in various industries and applications, including high-precision machinery, robotics, automation systems, precision motion control, and machine tools. They are especially beneficial in scenarios where misalignment needs to be minimized or avoided altogether. It’s important to note that while rigid couplings offer these advantages, they are not suitable for applications where shaft misalignment or shock absorption is required. In such cases, flexible couplings or other specialized coupling types may be more appropriate.
China wholesaler Stainless Steel Coupling Gear Rigid Roller Chain Fluid Tyre Grid Jaw Spider HRC Nm Motor Flange Gear Pump Rubber Spline Shaft Flexible Universal Joint CouplingProduct Description
Stainless Steel Coupling Gear Rigid Roller Chain Fluid Tyre Grid Jaw Spider HRC Nm Motor Flange Gear Pump Rubber Spline Shaft Flexible Universal Joint Coupling Product Description Main products Couplings can be divided into rigid couplings and flexible couplings. Coupling performance 1) Mobility. The movability of the coupling refers to the ability to compensate the relative displacement of 2 rotating components. Factors such as manufacturing and installation errors between connected components, temperature changes during operation and deformation under load all put CHINAMFG requirements for mobility. The movable performance compensates or alleviates the additional load between shafts, bearings, couplings and other components caused by the relative displacement between rotating components. How to select the appropriate coupling type The following items should be considered when selecting the coupling type. If you cannot determine the type, you can contact our professional engineer Related products
Company Profile
Our Equipments Main production equipment:
Machining equipments
Our Factory Company Profile /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Is It Possible to Replace a Shaft Coupling Without Professional Assistance?Yes, it is possible to replace a shaft coupling without professional assistance, especially if you have some mechanical knowledge and the necessary tools. However, the ease of replacement can vary depending on the type of coupling and the complexity of the equipment. Here are some general steps to guide you through the process: 1. Safety First:Before starting any work, ensure that the equipment is turned off and disconnected from the power source. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to protect yourself from potential hazards. 2. Assess the Coupling Type:Different types of couplings may have specific installation and removal methods. Identify the type of coupling you need to replace, and consult the manufacturer’s documentation or online resources for guidance. 3. Gather Tools and Materials:Collect the necessary tools, such as wrenches, sockets, and a puller (if required), to safely remove the old coupling. Have the new coupling ready for installation, ensuring it matches the specifications of the old one. 4. Disassembly:If your coupling is a split or clamp-style coupling, you may be able to replace it without fully disassembling the connected equipment. Otherwise, you may need to remove other components to access the coupling. 5. Remove Fasteners:Loosen and remove any fasteners, such as set screws, that secure the old coupling to the shafts. Take care not to damage the shafts during this process. 6. Extraction:If the old coupling is tightly fitted on the shafts, you may need to use a coupling puller or other appropriate extraction tools to safely remove it. 7. Clean and Inspect:After removing the old coupling, clean the shaft ends and inspect them for any signs of damage or wear. Also, check for any misalignment issues that may have contributed to the old coupling’s failure. 8. Install New Coupling:Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installing the new coupling. Apply appropriate lubrication and ensure the coupling is correctly aligned with the shafts. 9. Fasten Securely:Tighten the fasteners to the manufacturer’s recommended torque values to securely attach the new coupling to the shafts. 10. Test Run:After installation, perform a test run of the equipment to ensure the new coupling operates smoothly and without issues. While it is possible to replace a shaft coupling without professional assistance, keep in mind that some couplings and equipment may require specialized knowledge and tools for safe and proper replacement. If you are uncertain about the process or encounter any difficulties, it is advisable to seek help from a qualified professional or technician to avoid potential damage to the equipment or injury to yourself. “` How to Identify Signs of Wear or Failure in a Shaft CouplingRegular inspection and monitoring are essential to identify signs of wear or potential failure in a shaft coupling. Detecting issues early can help prevent costly downtime and equipment damage. Here are common signs to look for: 1. Visible Damage:Inspect the coupling for visible signs of damage, such as cracks, chips, or deformation. These can indicate mechanical stress or overload. 2. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:Unusual noise or excessive vibration during operation may indicate misalignment, worn-out components, or a coupling nearing its failure point. 3. Increased Temperature:If the coupling becomes noticeably hotter during operation than usual, it could be a sign of friction or misalignment issues. 4. Shaft Misalignment:Check for misalignment between the shafts connected by the coupling. Misalignment can lead to increased stress on the coupling and its components. 5. Excessive Backlash:If the coupling exhibits too much free play or rotational play before torque transmission, it might indicate wear or fatigue in the coupling’s components. 6. Lubrication Issues:Inspect the coupling for lubrication leaks or insufficient lubrication, which can lead to increased friction and wear. 7. Elastomeric Element Deterioration:If the coupling uses elastomeric elements (e.g., rubber or polyurethane), check for signs of deterioration, such as cracking, softening, or deformation. 8. Bolts and Fasteners:Examine the bolts and fasteners connecting the coupling components. Loose or damaged bolts can lead to misalignment and coupling failure. 9. Age and Service Life:Consider the age and service life of the coupling. If it has been in use for a long time or exceeds the manufacturer’s recommended service life, it may be more susceptible to wear and failure. 10. Abnormal Performance:Monitor the overall performance of the connected equipment. Any abnormal behavior, such as reduced power transmission or erratic operation, could be indicative of coupling issues. If any of these signs are observed, it’s crucial to take immediate action. Depending on the severity of the issue, this may involve replacing worn components, realigning the shafts, or replacing the entire coupling. Regular maintenance and periodic inspections are key to identifying these signs early and ensuring the coupling operates optimally and safely. “` What is a Shaft Coupling and Its Role in Mechanical Power Transmission?A shaft coupling is a mechanical device used to connect two shafts together at their ends, allowing for the transmission of mechanical power from one shaft to another. It serves as an essential component in various machinery and industrial applications where rotational motion needs to be transmitted between two shafts that are not perfectly aligned or are separated by a distance. The role of a shaft coupling in mechanical power transmission includes the following: 1. Power Transmission:The primary function of a shaft coupling is to transmit power from a driving shaft to a driven shaft. When the driving shaft rotates, the coupling transfers the rotational motion to the driven shaft, enabling the driven equipment to perform its intended function. 2. Misalignment Compensation:In real-world applications, it is often challenging to achieve perfect alignment between two shafts due to manufacturing tolerances or dynamic conditions. Shaft couplings are designed to accommodate different types of misalignment, such as angular, parallel, and axial misalignment, allowing the equipment to function smoothly even when the shafts are not perfectly aligned. 3. Vibration Damping:Shaft couplings can help dampen vibrations and shocks caused by uneven loads or sudden changes in the operating conditions. This vibration damping feature protects the connected components from damage and contributes to the overall system’s reliability. 4. Overload Protection:In some cases, a shaft coupling can act as a safety device by providing overload protection. When the connected machinery experiences excessive torque or shock loads, certain types of couplings can disengage or shear to prevent damage to the equipment. 5. Torque and Speed Conversion:Shaft couplings can be designed to provide torque and speed conversion between the driving and driven shafts. This allows for adaptation to different operating conditions and varying torque requirements in the connected machinery. 6. Flexible Connection:Shaft couplings with flexible elements, such as elastomeric inserts or flexible discs, provide a flexible connection that can absorb shocks and misalignments. This flexibility helps reduce stress on the connected equipment and extends its lifespan. Overall, shaft couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, enabling the efficient transfer of rotational motion between shafts while accommodating misalignments and providing protection against overloads and vibrations. The selection of the appropriate coupling type and design depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the type of misalignment, torque capacity, and operating conditions. “` China Best Sales Machinery Part Roller Chain Coupling Aluminum Case with Sprockets Shaft Flexible Coupling KC6018Product Description
FAQ
Q:Is your company a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We have our own factory. Q:How long does the lead time take? Q: Can I order shaft bore couplings that are not listed in the catalog?)(Additional machining service for coupling shaft hole Q: How to handle when the received parts are of poor quality? Q: Why choose XingHe Precision Transmission ?
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Exploring the Use of Elastomeric Materials in Flexible Shaft CouplingsElastomeric materials play a crucial role in the design and function of flexible shaft couplings. These materials, commonly known as elastomers, are rubber-like substances that exhibit high elasticity and flexibility. They are widely used in various types of flexible couplings due to their unique properties and benefits: 1. Damping and Vibration Absorption:Elastomeric materials have excellent damping characteristics, meaning they can absorb and dissipate vibrations and shocks. This property is particularly useful in applications where vibration control is essential to protect sensitive equipment and improve overall system performance. 2. Misalignment Compensation:Flexible shaft couplings with elastomeric elements can accommodate different types of misalignments, including angular, parallel, and radial misalignments. The elasticity of the material allows for limited movement between the shafts while still transmitting torque efficiently. 3. Torsional Flexibility:Elastomers offer torsional flexibility, which allows them to twist and deform under torque loads. This feature helps to minimize torsional stresses and torsional backlash, making them suitable for applications requiring precise motion control. 4. Shock and Impact Resistance:Due to their high resilience, elastomers can withstand sudden shocks and impacts without permanent deformation. This property makes them ideal for use in machinery subjected to varying loads or rapid changes in torque. 5. No Lubrication Requirement:Elastomeric couplings are often maintenance-free because the elastomer material does not require additional lubrication. This reduces maintenance costs and simplifies the overall system upkeep. 6. Electric Isolation:In certain applications, elastomeric materials can provide electrical isolation between the driving and driven components. This can help prevent the transmission of electrical currents or static charges through the coupling. 7. Corrosion Resistance:Many elastomers used in couplings are resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for use in challenging environments where exposure to chemicals or moisture is a concern. 8. Easy Installation:Elastomeric couplings are often designed for ease of installation and replacement. Their flexibility allows for simple and quick assembly onto the shafts without the need for special tools or complex procedures. Given these advantages, elastomeric materials are popular choices for various flexible shaft couplings, including jaw couplings, tire couplings, and spider couplings. However, it is essential to select the right elastomer material based on the specific application requirements, such as temperature range, chemical compatibility, and torque capacity. “` Temperature and Speed Limits for Different Shaft Coupling TypesThe temperature and speed limits of shaft couplings vary depending on the materials and design of the coupling. Manufacturers provide specific guidelines and ratings for each coupling type. Below are general temperature and speed limits for some common shaft coupling types: 1. Elastomeric Couplings:Elastomeric couplings, such as jaw couplings and tire couplings, typically have temperature limits ranging from -40°C to 100°C (-40°F to 212°F). The speed limits for elastomeric couplings are generally up to 5,000 RPM, but some designs may allow higher speeds. 2. Metallic Couplings:Metallic couplings, like gear couplings and disc couplings, can handle a wider temperature range, typically from -50°C to 200°C (-58°F to 392°F). The speed limits for metallic couplings vary based on the size and design, but they can range from 3,000 RPM to over 10,000 RPM. 3. Grid Couplings:Grid couplings have temperature limits similar to metallic couplings, ranging from -50°C to 200°C (-58°F to 392°F). The speed limits for grid couplings are typically in the range of 3,000 to 5,000 RPM. 4. Oldham Couplings:Oldham couplings usually have temperature limits from -30°C to 100°C (-22°F to 212°F) and speed limits ranging from 1,000 to 5,000 RPM. 5. Beam Couplings:Beam couplings generally have temperature limits from -40°C to 120°C (-40°F to 248°F) and speed limits between 5,000 to 10,000 RPM. 6. Fluid Couplings:Fluid couplings are suitable for a wide range of temperatures, often from -50°C to 300°C (-58°F to 572°F). The speed limits depend on the size and design of the fluid coupling but can extend to several thousand RPM. It’s important to note that these are general guidelines, and the actual temperature and speed limits may vary based on the specific coupling manufacturer, material quality, and application requirements. Always refer to the manufacturer’s documentation and technical specifications for accurate and up-to-date temperature and speed limits for a particular shaft coupling model. “` Diagnosing and Fixing Common Issues with Shaft CouplingsRegular inspection and maintenance of shaft couplings are essential to detect and address common issues that may arise during operation. Here are steps to diagnose and fix some common coupling problems: 1. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:If you notice unusual noise or excessive vibration during equipment operation, it may indicate misalignment, wear, or damage in the coupling. Check for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks or deformations, and inspect the coupling for proper alignment. Diagnosis:Use a vibration analysis tool to measure the vibration levels and identify the frequency of the abnormal vibrations. This can help pinpoint the source of the problem. Fix:If misalignment is the cause, adjust the coupling to achieve proper alignment between the shafts. Replace any damaged or worn coupling components, such as spiders or elastomeric inserts, as needed. 2. Excessive Heat:Feeling excessive heat on the coupling during operation can indicate friction, improper lubrication, or overload conditions. Diagnosis:Inspect the coupling and surrounding components for signs of rubbing, lack of lubrication, or overloading. Fix:Ensure proper lubrication of the coupling, and check for any interference between the coupling and adjacent parts. Address any overloading issues by adjusting the equipment load or using a coupling with a higher torque capacity. 3. Shaft Movement:If you observe axial or radial movement in the connected shafts, it may indicate wear or improper installation of the coupling. Diagnosis:Check the coupling’s set screws, keyways, or other fastening methods to ensure they are secure and not causing the shaft movement. Fix:If the coupling is worn or damaged, replace it with a new one. Ensure proper installation and use appropriate fastening methods to secure the coupling to the shafts. 4. Sheared Shear Pin:In shear pin couplings, a sheared shear pin indicates overloading or shock loads that exceeded the coupling’s torque capacity. Diagnosis:Inspect the shear pin for damage or breakage. Fix:Replace the sheared shear pin with a new one of the correct specifications. Address any overloading issues or adjust the equipment to prevent future shearing. 5. Coupling Wear:Regular wear is normal for couplings, but excessive wear may lead to decreased performance and increased misalignment. Diagnosis:Inspect the coupling components for signs of wear, such as worn elastomeric elements or damaged teeth. Fix:Replace the worn or damaged components with new ones of the appropriate specifications. Remember, regular maintenance and periodic inspection are key to diagnosing issues early and preventing severe problems. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and replacement schedules to ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the shaft coupling. “` China best Stainless Steel Coupling Gear Rigid Roller Chain Fluid Tyre Grid Jaw Spider HRC Nm Motor Flange Gear Pump Rubber Spline Shaft Flexible Universal Joint CouplingProduct Description
Stainless Steel Coupling Gear Rigid Roller Chain Fluid Tyre Grid Jaw Spider HRC Nm Motor Flange Gear Pump Rubber Spline Shaft Flexible Universal Joint Coupling Product Description Main products Couplings can be divided into rigid couplings and flexible couplings. Coupling performance 1) Mobility. The movability of the coupling refers to the ability to compensate the relative displacement of 2 rotating components. Factors such as manufacturing and installation errors between connected components, temperature changes during operation and deformation under load all put CHINAMFG requirements for mobility. The movable performance compensates or alleviates the additional load between shafts, bearings, couplings and other components caused by the relative displacement between rotating components. How to select the appropriate coupling type The following items should be considered when selecting the coupling type. If you cannot determine the type, you can contact our professional engineer Related products
Company Profile
Our Equipments Main production equipment:
Machining equipments
Our Factory Company Profile /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Can rigid shaft couplings operate in high-temperature or corrosive environments?Rigid shaft couplings can be designed and manufactured using materials that are suitable for high-temperature or corrosive environments. Common materials used for such applications include stainless steel, nickel alloys, and other corrosion-resistant materials. These materials can withstand elevated temperatures and resist the effects of corrosive substances. When selecting a rigid shaft coupling for high-temperature or corrosive environments, it is essential to consider factors such as the operating temperature range, the specific corrosive substances present, and the overall environmental conditions. Additionally, proper lubrication and maintenance are crucial to ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of rigid couplings in these demanding environments. It is essential to consult with coupling manufacturers or suppliers who specialize in providing solutions for high-temperature or corrosive applications. They can help identify the appropriate materials and designs that will meet the specific requirements of the intended environment.
How do rigid shaft couplings compare to flexible couplings in terms of torque transmission and misalignment handling?Rigid shaft couplings and flexible couplings differ in their ability to handle torque transmission and misalignment. Here’s a comparison of these aspects:
The choice between rigid and flexible couplings depends on the specific requirements of the application. If precise torque transmission and minimal misalignment are priorities, rigid couplings may be suitable. However, if misalignment compensation and vibration dampening are crucial, flexible couplings are a better option.
Are There Different Types of Rigid Shaft Couplings Available, and What Are Their Specific Applications?Yes, there are different types of rigid shaft couplings available, each with its own specific applications. Some common types of rigid shaft couplings include:
The choice of rigid shaft coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application. Factors such as torque transmission, shaft size, alignment precision, ease of installation, and maintenance needs play a crucial role in selecting the appropriate coupling type. Rigid shaft couplings are widely used in various industries, including manufacturing, power generation, robotics, aerospace, and automotive. They are often employed in applications such as pumps, compressors, conveyors, and high-precision machinery. It is essential to consider the specific demands of the application and consult with coupling manufacturers or experts to determine the most suitable rigid coupling type for optimal performance and reliability.
|