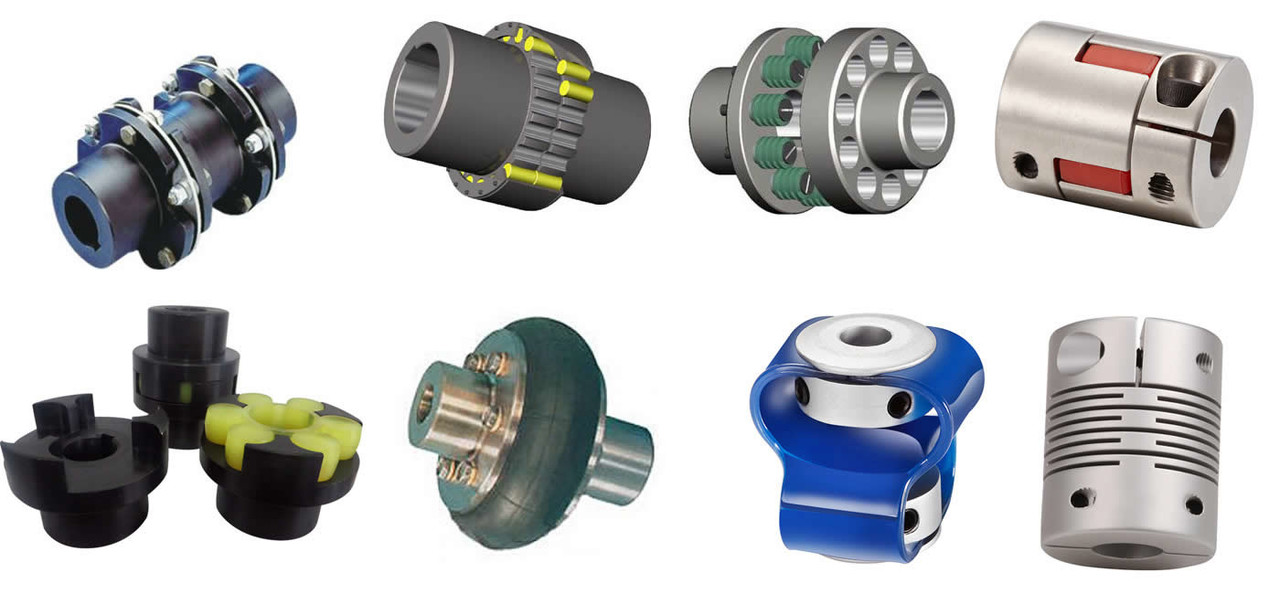
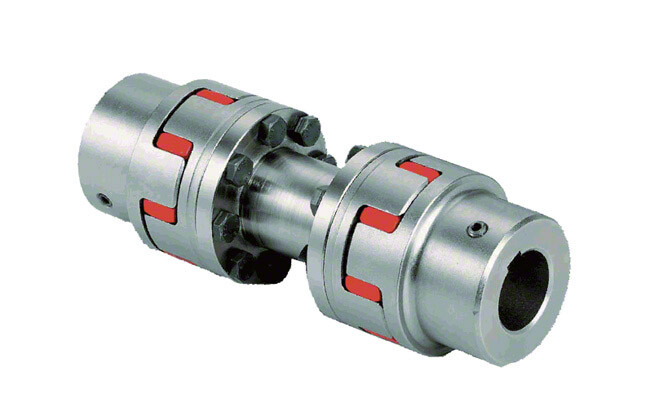
Product Description
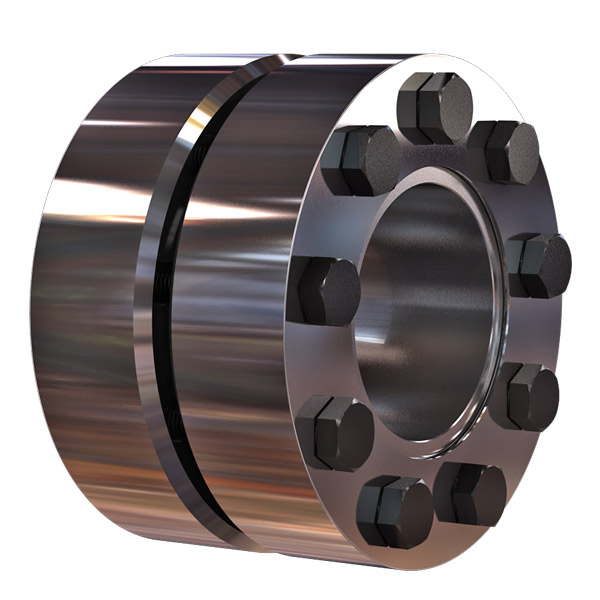
Cardan Coupling SWC Cross Shaft Universal stainless steel coupling
Description:
The SWC-CH long flexible welded universal joint is a Universal joint designed to transmit power between 2 misaligned shafts. It is a flexible coupling, which means it can compensate for misalignment up to 25 degrees. The SWC-CH long bend welded universal coupling is made of 35CrMo material and comes in various sizes to meet the needs of different applications. SWC-CH long bend welded universal couplings are widely used in mechanical applications such as rolling mills, punches, straighteners, crushers, ship transmissions, papermaking equipment, ordinary machinery, water pump equipment, test benches, etc.
Features:
1. Possess the ability to compensate for large angles.
2. The structure is compact and reasonable. The SWC-CH universal coupling is equipped with an integrated fork, making it more reliable in carrying capacity.
3. Carrying capacity. Compared to other types of rotating joint shafts with the same diameter, it provides more torque, limits the turning diameter of mechanical equipment, and has a wider range.
4. High transmission efficiency. Its transmission efficiency is 98-99.8%, suitable for high-power transmission and has energy-saving effect.
5. Smooth carrying, low noise, easy disassembly and maintenance.
Paramters:
Application:
(1) Construction machinery: SWC-CH long flexible welded universal couplings are used in various construction machinery, such as excavators, bulldozers, and cranes. It helps to ensure smooth and efficient operation of the machine, even when the shafts are not fully aligned.
(2) Mining machinery: SWC-CH long flexible welded universal couplings are also used in mining machinery, such as loaders, conveyors, and drilling rigs. It helps to transfer power from the engine to the working components of the machine, even if the shaft is affected by high loads and vibrations.
(3) Agricultural machinery: SWC-CH long flexible welded universal coupling is used for tractors, harvesters, Combine harvester and other agricultural machinery. It helps to ensure smooth and efficient operation of the machine, even when the shafts are not fully aligned.
(4) Marine machinery: SWC-CH long flexible welded universal coupling is used for marine machinery such as ships. It helps to transfer power from the engine to the propeller, even if the shaft is affected by high loads and vibrations.
(5) Power generation equipment: SWC-CH long flexible welded universal coupling is used for power generation equipment, such as turbines and generators. It helps to transfer power from the prime mover to the generator, even if the shafts are not fully aligned.
Packing & shipping:
1 Prevent from damage.
2. As customers’ requirements, in perfect condition.
3. Delivery : As per contract delivery on time
4. Shipping : As per client request. We can accept CIF, Door to Door etc. or client authorized agent we supply all the necessary assistant.
FAQ:
Q 1: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We are a professional manufacturer specializing in manufacturing various series of couplings.
Q 2:Can you do OEM?
Yes, we can. We can do OEM & ODM for all the customers with customized artworks in PDF or AI format.
Q 3:How long is your delivery time?
Generally, it is 20-30 days if the goods are not in stock. It is according to quantity.
Q 4: How long is your warranty?
A: Our Warranty is 12 months under normal circumstances.
Q 5: Do you have inspection procedures for coupling?
A:100% self-inspection before packing.
Q 6: Can I have a visit to your factory before the order?
A: Sure, welcome to visit our factory.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Understanding the Torque and Misalignment Capabilities of Shaft Couplings
Shaft couplings play a critical role in transmitting torque and accommodating misalignment between rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. Understanding their torque and misalignment capabilities is essential for selecting the right coupling for a specific application. Here’s an overview:
Torque Transmission:
The torque capacity of a shaft coupling refers to its ability to transmit rotational force from one shaft to another. It is typically specified in torque units, such as Nm (Newton-meters) or lb-ft (pound-feet). The coupling’s torque capacity depends on its design, size, and material.
When selecting a coupling, it’s crucial to ensure that its torque capacity meets or exceeds the torque requirements of the application. Overloading a coupling beyond its torque capacity can lead to premature failure or damage to the coupling and connected equipment.
Misalignment Compensation:
Shaft misalignment can occur due to various factors, including thermal expansion, manufacturing tolerances, or foundation settling. Misalignment puts additional stress on the coupling and connected components, potentially leading to increased wear and reduced efficiency.
Shaft couplings are designed to compensate for different types of misalignment:
- Angular Misalignment: Occurs when the shafts are not parallel and have an angle between them.
- Parallel Misalignment: Occurs when the shafts are not collinear, resulting in axial displacement.
- Radial Misalignment: Occurs when the shafts have lateral displacement but remain parallel.
The coupling’s misalignment capabilities are specified in terms of angular and axial misalignment values, usually in degrees or millimeters. Different coupling designs can accommodate varying degrees of misalignment, and the choice depends on the specific application and operating conditions.
Flexible Couplings:
Flexible couplings, such as elastomeric or jaw couplings, offer good misalignment compensation. They can handle a combination of angular, parallel, and axial misalignments. However, their torque capacity may be limited compared to rigid couplings.
Rigid Couplings:
Rigid couplings, such as clamp or sleeve couplings, have high torque transmission capabilities but offer minimal misalignment compensation. They are best suited for applications where shafts are well-aligned and precise torque transmission is critical.
Torsional Stiffness:
Another factor to consider is the coupling’s torsional stiffness, which determines how much torsional deflection or twist occurs under load. Some applications, like precision systems, may require couplings with high torsional stiffness to maintain accurate positioning and avoid torsional backlash.
By understanding the torque and misalignment capabilities of shaft couplings, engineers can make informed decisions when selecting a coupling to ensure efficient power transmission and reliable performance in their mechanical systems.
“`
Comparing Shaft Couplings with Other Types of Couplings in Performance
Shaft couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, and their performance characteristics vary depending on the coupling type. Let’s compare shaft couplings with other common types of couplings:
1. Shaft Couplings:
Shaft couplings come in various designs, including flexible and rigid couplings. They are widely used in a broad range of applications due to their ability to transmit torque and accommodate misalignments between rotating shafts. Flexible shaft couplings, with elastomeric or metallic elements, offer good misalignment compensation and damping characteristics. Rigid couplings, on the other hand, provide precise torque transmission and are ideal for applications where shafts are well-aligned.
2. Gear Couplings:
Gear couplings are robust and designed for heavy-duty applications. They consist of two external gear hubs with internal gear teeth that mesh together. Gear couplings can handle high torque, high-speed, and angular misalignment. They are often used in demanding industries such as steel, mining, and paper manufacturing.
3. Grid Couplings:
Grid couplings feature a flexible grid element between the two halves of the coupling. They provide excellent shock absorption and misalignment compensation. Grid couplings are commonly used in pumps, compressors, and other industrial machinery.
4. Disc Couplings:
Disc couplings utilize flexible metallic discs to transmit torque and compensate for misalignment. They offer high torsional stiffness, making them suitable for applications requiring precise motion control, such as robotics and CNC machines.
5. Jaw Couplings:
Jaw couplings consist of two hubs with elastomeric spider inserts. They are easy to install, have good misalignment capabilities, and offer electrical isolation between shafts. Jaw couplings are widely used in light to medium-duty applications.
6. Oldham Couplings:
Oldham couplings have three discs—two outer discs with slots and a central disc with a tongue that fits into the slots. They provide excellent angular misalignment compensation while maintaining constant velocity between shafts. Oldham couplings are commonly used in printing machines and conveyors.
7. Beam Couplings:
Beam couplings are made from a single piece of flexible material with spiral cuts. They offer good misalignment compensation and torsional flexibility, making them suitable for precision equipment like encoders and servo motors.
The choice of coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application, including torque, speed, misalignment compensation, environmental conditions, and space limitations. Each coupling type has its strengths and limitations, and selecting the right coupling is crucial to ensure optimal performance and reliability in the mechanical system.
“`
Best Practices for Installing a Shaft Coupling for Optimal Performance
Proper installation of a shaft coupling is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and preventing premature wear or failure. Follow these best practices to install a shaft coupling correctly:
1. Shaft Alignment:
Ensure that both the driving and driven shafts are properly aligned before installing the coupling. Misalignment can lead to increased stress on the coupling and other connected components, reducing efficiency and causing premature wear. Use alignment tools, such as dial indicators or laser alignment systems, to achieve accurate shaft alignment.
2. Cleanliness:
Before installation, clean the shaft ends and the coupling bore thoroughly. Remove any dirt, debris, or residue that could interfere with the coupling’s fit or cause misalignment.
3. Lubrication:
Apply the recommended lubricant to the coupling’s contact surfaces, such as the bore and shaft ends. Proper lubrication ensures smooth installation and reduces friction during operation.
4. Correct Fit:
Ensure that the coupling is the correct size and type for the application. Use couplings with the appropriate torque and speed ratings to match the equipment’s requirements.
5. Fastening:
Use the recommended fastening methods, such as set screws or keyways, to securely attach the coupling to the shafts. Make sure the fasteners are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications to prevent loosening during operation.
6. Spacer or Adapter:
If required, use a spacer or adapter to properly position the coupling on the shafts and maintain the desired distance between the driving and driven components.
7. Avoid Shaft Damage:
Be careful during installation to avoid damaging the shaft ends, especially when using set screws or other fastening methods. Shaft damage can lead to stress concentrations and eventual failure.
8. Check Runout:
After installation, check the coupling’s runout using a dial indicator to ensure that it rotates smoothly and without wobbling. Excessive runout can indicate misalignment or improper fit.
9. Periodic Inspection:
Regularly inspect the coupling and its components for signs of wear, misalignment, or damage. Perform routine maintenance as recommended by the manufacturer to prevent issues from worsening over time.
10. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Always follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions and guidelines. Different types of couplings may have specific installation requirements that need to be adhered to for optimal performance and safety.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your shaft coupling is installed correctly, maximizing its efficiency and reliability in your mechanical power transmission system.
“`

editor by CX 2024-02-01
China OEM CNC Customizable Forged Steel Flexible Jaw Tooth Shaft Gear Couplings
Product Description
|
Material |
20CrMn5,20CrMnTi,40Cr,Powder deposit,45#steel,42CrMo,Stainless steel and so on as per your requests. |
|||
|
Custom |
OEM/ODM |
|||
|
Lead Time |
Sample: 20-30 days after deposit received, Batch goods: 30-45days after samples have been approved. Die opening product:7-15days after samples have been approved.It takes 45-60 days to open the mold. |
|||
|
Processing |
Forging,Machining,Hobbing,Milling,Shaving,Grinding teeth, inserting teeth, shot blasting, Grinding,Heat treatment…… |
|||
|
Heat Treatment |
Intermediate frequency, high frequency, tempering, desalinating, carburizing…… |
|||
|
Main Machines |
CNC gear hobbing machine, CNC gear cutting machine, CNC lathe, CNC gear shaving machine, CNC gear milling machine, CNC gear grinding machine, CNC Grinding Machine…. |
|||
CHINAMFG has been engaged in manufacturing of forgings, castings, heat treatment and CNC machining parts since 1999.
The products materials have passed EN15714-3.1 certification, covering various grades of: low carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, ductile iron, aluminum alloy, copper alloy, titanium alloy.
The main processes are: free forging, die forging, rolling ring, high pressure casting, centrifugal casting, normalizing, quenching and tempering, solution treatment, aging treatment, carbonitriding, turning, milling, drilling, grinding, hobbing, high frequency quenching, galvanizing, chrome plating, anodizing, powder spraying and other processes.
Rings and plates dimensions: Max 3000mm, shafts length: Max 12000mm, single piece weight: Max 16 Tons, at the same time we are good at terminal machining of complex products, dimension accuracy: Min 0.01mm, roughness: Min Ra0.6.
Products can be strictly examined by chemical composition, tensile strength, yield strength, reduction of area, impact at low temperature, intergranular corrosion, hardness, metallographic, NDT, size, static balance etc performance parameter.
Products are widely used in: aerospace, ships, trains, automobiles, engineering vehicles, chemical industry and petroleum refining, wellheads, x-mas tree equipment, mining machinery, food machinery, hydraulic and wind power generation, new energy equipment etc field.
Welcome to send: PDF, IGS, STP and other format drawings, of course we could also make material judgment and size survey according to your samples.
With more than 20 years of manufacturing experience and overseas sales team, we have achieved 100% customer satisfaction. The warranty period of products sold is 365 days. We look CHINAMFG to your consultation and cooperation at any time and common prosperity development.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Is It Possible to Replace a Shaft Coupling Without Professional Assistance?
Yes, it is possible to replace a shaft coupling without professional assistance, especially if you have some mechanical knowledge and the necessary tools. However, the ease of replacement can vary depending on the type of coupling and the complexity of the equipment. Here are some general steps to guide you through the process:
1. Safety First:
Before starting any work, ensure that the equipment is turned off and disconnected from the power source. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to protect yourself from potential hazards.
2. Assess the Coupling Type:
Different types of couplings may have specific installation and removal methods. Identify the type of coupling you need to replace, and consult the manufacturer’s documentation or online resources for guidance.
3. Gather Tools and Materials:
Collect the necessary tools, such as wrenches, sockets, and a puller (if required), to safely remove the old coupling. Have the new coupling ready for installation, ensuring it matches the specifications of the old one.
4. Disassembly:
If your coupling is a split or clamp-style coupling, you may be able to replace it without fully disassembling the connected equipment. Otherwise, you may need to remove other components to access the coupling.
5. Remove Fasteners:
Loosen and remove any fasteners, such as set screws, that secure the old coupling to the shafts. Take care not to damage the shafts during this process.
6. Extraction:
If the old coupling is tightly fitted on the shafts, you may need to use a coupling puller or other appropriate extraction tools to safely remove it.
7. Clean and Inspect:
After removing the old coupling, clean the shaft ends and inspect them for any signs of damage or wear. Also, check for any misalignment issues that may have contributed to the old coupling’s failure.
8. Install New Coupling:
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installing the new coupling. Apply appropriate lubrication and ensure the coupling is correctly aligned with the shafts.
9. Fasten Securely:
Tighten the fasteners to the manufacturer’s recommended torque values to securely attach the new coupling to the shafts.
10. Test Run:
After installation, perform a test run of the equipment to ensure the new coupling operates smoothly and without issues.
While it is possible to replace a shaft coupling without professional assistance, keep in mind that some couplings and equipment may require specialized knowledge and tools for safe and proper replacement. If you are uncertain about the process or encounter any difficulties, it is advisable to seek help from a qualified professional or technician to avoid potential damage to the equipment or injury to yourself.
“`
Explaining the Concept of Backlash and How It Affects Shaft Coupling Performance
Backlash is the angular movement or play between the mating components of a mechanical system when the direction of motion is reversed. In the context of shaft couplings, backlash refers to the free rotational movement between the connected shafts before the coupling transmits torque from one shaft to the other.
Backlash occurs in certain coupling designs that have features allowing relative movement between the coupling’s mating parts. Common coupling types that may exhibit some degree of backlash include elastomeric couplings (such as jaw couplings), gear couplings, and Oldham couplings.
How Backlash Affects Shaft Coupling Performance:
1. Loss of Precision: In applications requiring precise motion control, backlash can lead to inaccuracies and reduced positional accuracy. For example, in CNC machines or robotics, any rotational play due to backlash can result in positioning errors and decreased machining or movement precision.
2. Reversal Impact: When a reversing load is applied to a coupling, the presence of backlash can lead to a brief period of rotational play before the coupling re-engages, causing a momentary jolt or impact. This impact can lead to increased stress on the coupling and connected components, potentially reducing their lifespan.
3. Dynamic Response: Backlash can affect the dynamic response of the mechanical system. In systems requiring rapid acceleration or deceleration, the initial play due to backlash may create a delay in torque transmission, affecting the system’s responsiveness.
4. Noise and Vibration: Backlash can cause noise and vibration in the system, leading to increased wear and potential fatigue failure of components.
5. Misalignment Compensation: In some flexible coupling designs, a certain amount of backlash is intentionally incorporated to allow for misalignment compensation. While this is a beneficial feature, excessive backlash can compromise the coupling’s performance.
Minimizing Backlash:
Manufacturers often design couplings with specific features to minimize backlash. For instance, some gear couplings employ crowned gear teeth to reduce clearance, while elastomeric couplings may have preloaded elastomeric elements. Precision couplings like zero-backlash or torsionally rigid couplings are engineered to eliminate or minimize backlash for applications requiring high accuracy and responsiveness.
When selecting a coupling, it’s essential to consider the application’s specific requirements regarding precision, speed, reversing loads, and misalignment compensation, as these factors will determine the acceptable level of backlash for optimal performance.
“`
Can a Damaged Shaft Coupling Lead to Equipment Failure and Downtime?
Yes, a damaged shaft coupling can lead to equipment failure and downtime in mechanical power transmission systems. Shaft couplings play a critical role in connecting rotating shafts and transmitting power between them. When a coupling becomes damaged or fails to function properly, several negative consequences can arise:
1. Misalignment Issues:
A damaged coupling may no longer be able to compensate for misalignments between the connected shafts. Misalignment can cause excessive vibration, increased wear, and premature failure of bearings and other connected components. Over time, these issues can lead to equipment breakdown and unplanned downtime.
2. Vibration and Shock Loads:
Without the damping properties of a functional coupling, vibrations and shock loads from the driven equipment can transmit directly to the driving shaft and other parts of the system. Excessive vibrations can lead to fatigue failure, cracking, and damage to the equipment, resulting in reduced operational efficiency and increased downtime.
3. Overloading and Torque Transmission:
A damaged coupling may not effectively transmit the required torque between the driving and driven shafts. In applications where the coupling is a safety device (e.g., shear pin couplings), failure to disengage during overloading situations can lead to equipment overload and damage.
4. Increased Wear and Tear:
A damaged coupling can lead to increased wear on other parts of the system. Components such as bearings, seals, and gears may experience higher stress and wear, reducing their lifespan and increasing the likelihood of breakdowns.
5. Reduced System Reliability:
A functional shaft coupling contributes to the overall reliability of the mechanical system. A damaged coupling compromises this reliability, making the system more prone to failures and unplanned maintenance.
6. Downtime and Production Loss:
When a shaft coupling fails, it often results in unscheduled downtime for repairs or replacement. Downtime can be costly for industries that rely on continuous production processes and can lead to production losses and missed delivery deadlines.
7. Safety Hazards:
In certain applications, such as heavy machinery or industrial equipment, a damaged coupling can create safety hazards for workers and surrounding equipment. Sudden failures or uncontrolled movements may pose risks to personnel and property.
Regular inspection, maintenance, and prompt replacement of damaged shaft couplings are essential to prevent equipment failure, minimize downtime, and ensure safe and efficient operation of mechanical systems. It is crucial to address any signs of coupling wear or damage immediately to avoid potential catastrophic failures and costly disruptions to operations.
“`

editor by CX 2024-01-10