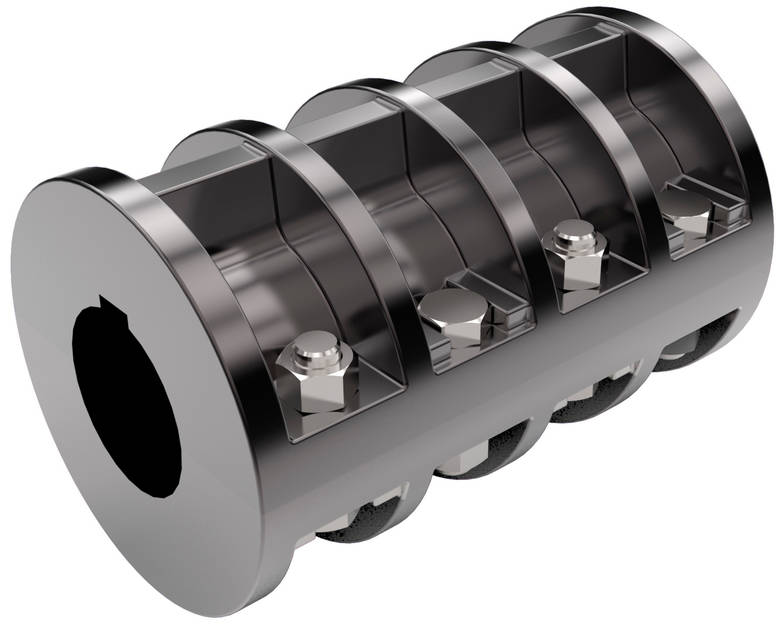
Product Description
GR-65×81 GR Shaft Coupler Rigid Coupling Servo Shaft Coupling
Description of GR-65×81 GR Shaft Coupler Rigid Coupling Servo Shaft Coupling
>The material is aluminum alloy, and the middle bellows is made of stainless steel with excellent corrosion resistance
>Laser welding is used between bellows and shaft sleeve, with zero rotation clearance, suitable for CHINAMFG and reverse rotation
>Bellows structure can effectively compensate radial, angular and axial deviation
>Designed for servo motor stepper motor
>Fastening method of setscrew
Catalogue of GR-65×81 GR Shaft Coupler Rigid Coupling Servo Shaft Coupling
|
model parameter |
common bore diameter d1,d2 |
ΦD |
L |
LI |
L2 |
L3 |
N |
F |
tightening screw torque |
|
GR-16×27 |
4,5,6,6.35,7,8 |
16 |
27 |
7.5 |
2 |
8 |
13.5 |
3 |
0.7 |
|
GR-20×32 |
5,6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10,11,12 |
20 |
32 |
7.2 |
2.8 |
12 |
18 |
3.5 |
0.7 |
|
GR-22.5×34 |
5,6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10,11,12 |
22.5 |
34 |
8.05 |
2.8 |
12.3 |
20.2 |
4.5 |
1.7 |
|
GR-25×37 |
6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10,11,12 |
25 |
37 |
9.5 |
3 |
12 |
20.2 |
4.5 |
1.7 |
|
GR-32×42 |
8,9,10,11,12,12.7,14,15 |
32 |
42 |
8 |
4 |
18 |
27.2 |
5.5 |
4 |
|
GR-40×51 |
8,9,9.525,10,11,12,12.7,14,15,16,17,18,19,20 |
40 |
51 |
9.5 |
6 |
20 |
34.5 |
5.5 |
4 |
|
GR-55×57 |
10,11,12,12.7,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,24,25 |
55 |
57 |
9 |
6 |
27 |
51.9 |
6.25 |
7 |
|
GR-65×81 |
10,11,12,12.7,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,24,25,28,30,32,35,38 |
65 |
81 |
19.5 |
7 |
28 |
60.5 |
8.9 |
7 |
|
model parameter |
Rated torque(N.m) |
allowable eccentricity (mm) |
allowable deflection angle (°) |
allowable axial deviation (mm) |
maximum speed (rpm) |
static torsional stiffness (N.M/rad) |
weight (g) |
|
GR-16×27 |
0.8 |
0.1 |
2 |
-0.8 |
20000 |
150 |
8 |
|
GR-20×32 |
1.5 |
0.1 |
2 |
-1.2 |
18000 |
220 |
13 |
|
GR-22.5×34 |
1.8 |
0.15 |
2 |
-1.2 |
16000 |
300 |
22 |
|
GR-25×37 |
2 |
0.15 |
2 |
-1.2 |
15000 |
330 |
30 |
|
GR-32×42 |
2.5 |
0.2 |
2 |
-1.7 |
11000 |
490 |
53 |
|
GR-40×51 |
6.4 |
0.3 |
2 |
-1.7 |
10000 |
530 |
85 |
|
GR-55×57 |
12 |
0.3 |
2 |
-1.7 |
9000 |
860 |
170 |
|
GR-65×81 |
18 |
0.2 |
2 |
-1.8 |
4500 |
900 |
280 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

How to Properly Install a Rigid Shaft Coupling for Optimal Performance and Reliability
Proper installation of a rigid shaft coupling is essential to ensure optimal performance and reliability in mechanical systems. Here are the steps to follow for a successful installation:
- Shaft Preparation: Ensure that the shafts to be connected are clean, smooth, and free from any burrs or contaminants that could affect the coupling’s performance.
- Alignment: Align the two shafts accurately to minimize misalignment during installation. The alignment process is critical as any misalignment can lead to premature wear and reduced coupling efficiency.
- Fitment: Choose the appropriate size of the rigid shaft coupling that matches the shaft diameters. Carefully slide the coupling onto one shaft at a time.
- Fastening: For one-piece rigid couplings, ensure that the coupling is fitted snugly onto both shafts. For two-piece couplings, bolt the two halves together securely around the shafts.
- Tightening: Use the recommended torque value and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to tighten the coupling bolts properly. Over-tightening can cause distortion, while under-tightening can lead to slippage and reduced torque transmission.
- Inspection: After installation, inspect the coupling to ensure that it is centered and aligned correctly. Check for any signs of misalignment or interference during rotation.
- Lubrication: Some rigid couplings may require lubrication at the friction points to reduce wear and friction. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and types.
- Load Testing: Perform load testing on the system to verify the coupling’s performance and check for any unusual vibrations or noises during operation.
- Regular Maintenance: Include the rigid coupling in your regular maintenance schedule. Periodically check for signs of wear, misalignment, or damage, and replace the coupling if necessary.
By following these installation steps and best practices, you can ensure that the rigid shaft coupling operates optimally, providing reliable torque transmission and contributing to the overall efficiency and longevity of the mechanical system.

Are there any real-world case studies or success stories of using rigid shaft couplings in various engineering projects?
While specific case studies might not be readily available, there are numerous real-world examples of using rigid shaft couplings in various engineering projects across industries. These projects highlight the versatility and benefits of rigid shaft couplings in different applications:
- Industrial Machinery: Rigid shaft couplings are commonly used in industrial machinery such as conveyor systems, pumps, compressors, and machine tools. They ensure precise torque transmission, alignment, and stability in these critical applications, contributing to reliable and efficient operation.
- Robotics: Robotics often require accurate and repeatable motion control. Rigid couplings provide a rigid connection between robotic joints and actuators, ensuring precise movement and positioning.
- Aerospace: In aerospace applications, where safety and reliability are paramount, rigid shaft couplings play a role in connecting various components, such as engine components and control surfaces, ensuring consistent and reliable performance.
- Medical Equipment: Rigid couplings are used in medical devices such as diagnostic equipment, laboratory instruments, and surgical tools. They contribute to accurate motion control and sample manipulation.
- Automotive: Rigid shaft couplings can be found in automotive systems, including drivetrains and transmission systems. They ensure efficient torque transmission and alignment in components such as steering columns.
- Printing and Packaging: Printing presses and packaging machinery rely on rigid couplings to maintain precise alignment between rollers and components, ensuring consistent print quality and packaging accuracy.
While these examples illustrate the broad range of applications where rigid shaft couplings are used, it’s important to note that the success of each project is influenced by factors beyond just the coupling. Proper installation, maintenance, and integration into the overall system are crucial for achieving optimal results.
When considering the implementation of rigid shaft couplings in a project, engineers should collaborate with coupling manufacturers, suppliers, and experienced professionals to ensure proper selection, installation, and operation. By leveraging the advantages of rigid couplings, engineering projects can benefit from improved efficiency, reliability, and performance.

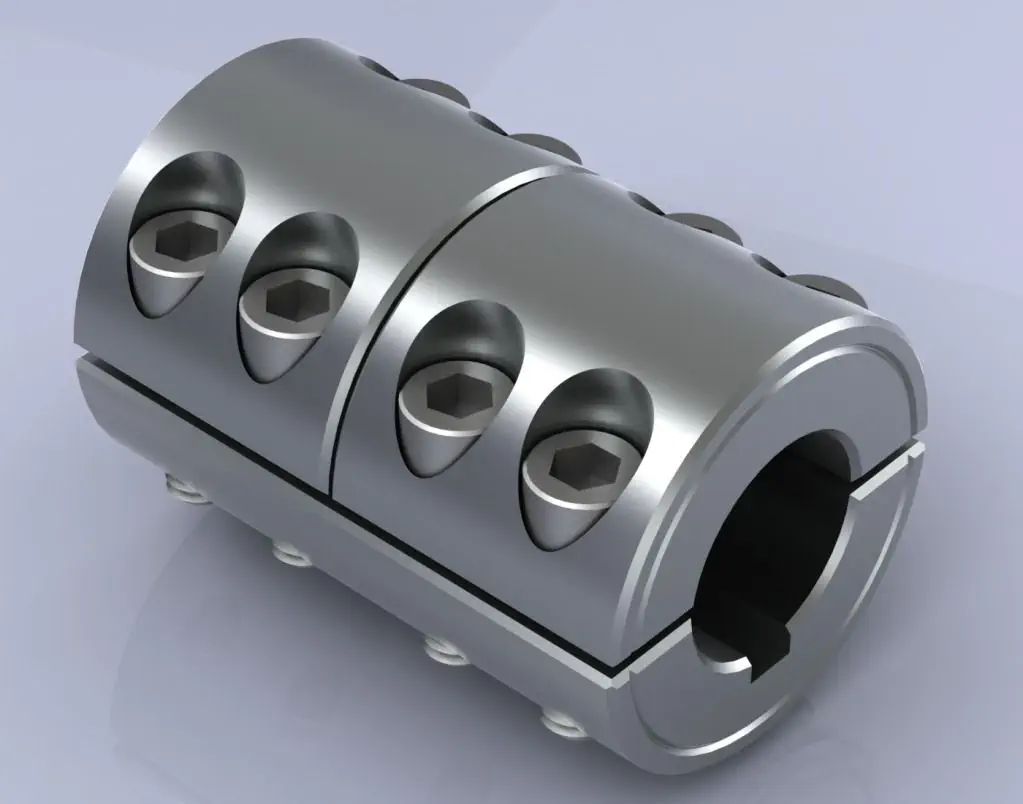
Are There Different Types of Rigid Shaft Couplings Available, and What Are Their Specific Applications?
Yes, there are different types of rigid shaft couplings available, each with its own specific applications. Some common types of rigid shaft couplings include:
- Sleeve Couplings: Sleeve couplings are simple and cost-effective couplings that connect two shafts together using a solid sleeve or tube. They are commonly used in applications with moderate torque requirements and where shaft alignment can be maintained with high precision.
- Clamp or Split Couplings: Clamp or split couplings consist of two halves that are clamped together around the shafts using screws or bolts. They are easy to install and suitable for applications where frequent maintenance or disassembly is required.
- Flanged Couplings: Flanged couplings have flanges on both ends that are bolted together. They are used in applications where shafts need to be rigidly connected and where some degree of axial movement is expected.
- Tapered Shaft Couplings: Tapered shaft couplings have tapered bores that fit tightly onto tapered shafts, creating a friction-based connection. They are often used in applications where precise alignment and torque transmission are essential.
- Keyed Shaft Couplings: Keyed shaft couplings use a key and keyway arrangement to connect the shafts securely. They are commonly used in heavy-duty applications where high torque transmission is required.
The choice of rigid shaft coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application. Factors such as torque transmission, shaft size, alignment precision, ease of installation, and maintenance needs play a crucial role in selecting the appropriate coupling type.
Rigid shaft couplings are widely used in various industries, including manufacturing, power generation, robotics, aerospace, and automotive. They are often employed in applications such as pumps, compressors, conveyors, and high-precision machinery.
It is essential to consider the specific demands of the application and consult with coupling manufacturers or experts to determine the most suitable rigid coupling type for optimal performance and reliability.


editor by CX 2024-05-15
China manufacturer Customized CNC Machined Rigid Shaft Coupler / Coupling for Motor Connector
Product Description
Customized OEM anodizied Aluminium 3/4/5 axis CNC turning /milling fitting machining parts
Product Description
| Products | CNC turning /milling fitting machining parts |
| Material available | SS , Carbon steel ,Aluminum ,6061 6063 ,7075 etc. |
| Finish | Polishing , sandblasting , anodizing,powder coating , etc |
| Size | 0-800mm ,non-standard according to drawing or samples |
| Tolerance | ‘+/-0.003mm or +/- 0.0001″ |
| Quality Policy | All the parts manufactured 100% inpection from OQC before shipping. |
| Sample | provide free sample if in stock or charged sample if need to produce |
| Packaging | standard export carton with pallet or as per customes’requirement |
| Capacity | 5000pcs/day |
| Lead time | 5-10 working days as usual |
| After sales service | we will follow up goods for every customer and help solve problem after sales. |
| Term of Payment | T/T, L/C |
Detailed Photos
Production workshop show
Inspection
Packaging & Shipping
FAQ
1.How can customize products?
Attach your drawings with details(Suface treatment,material,quantity and special requirements etc).
2.How long can I get the quaotation?
We will give you the quotation within 8 hours(Considering the time difference).
3.How can I get a sample for testing?
We will provide free or charged samples depends on the products.
4.How long will produce the parts?
Normally within 10 working days ,we will arrange the produce schedule depends on the quantity and the delivery.
5.What’s your payment terms?
We accept Western Union or Paypal for small account, big amount, T/T is preferred.
6.How about the transportation?
Samples by air (if not too heavy),otherwise by sea or air.
7.What if the products we received are not good?
contact us without hesitation,our special after-sales service will take the responsibility
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Industry Standards and Certifications for Rigid Shaft Couplings
Yes, there are industry standards and certifications that apply to rigid shaft couplings to ensure their quality, performance, and safety. Some of the common standards and certifications include:
- ISO 14691: This International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standard specifies the requirements and dimensions for metallic straight-toothed rigid couplings with external clamping for shaft connections.
- ANSI/AGMA 9002-C16: The American Gear Manufacturers Association (AGMA) standard covers measurement methods for evaluating the torsional stiffness of rigid couplings.
- API 671: This American Petroleum Institute (API) standard applies to special-purpose couplings used in petroleum, chemical, and gas industry services, ensuring reliable operation and safety.
- DNV GL: Rigid couplings used in marine and offshore applications may require certification from DNV GL, an international accredited registrar and classification society.
- ATEX: For couplings used in explosive atmospheres, compliance with the ATEX directive is crucial to ensure that the coupling does not become a source of ignition.
When selecting a rigid shaft coupling, it is essential to look for products that comply with these relevant industry standards and certifications. Meeting these standards guarantees that the couplings have undergone rigorous testing and adhere to recognized quality and safety guidelines.

Can rigid shaft couplings reduce vibrations and noise in mechanical systems?
Rigid shaft couplings are primarily designed for accurate torque transmission and shaft alignment. While they are not specifically intended to reduce vibrations and noise, they can indirectly contribute to minimizing vibrations and noise in mechanical systems.
Here’s how rigid shaft couplings can help mitigate vibrations and noise:
- Shaft Alignment: Rigid couplings ensure precise alignment between connected shafts. Proper alignment reduces angular and axial misalignment, which can lead to vibrations and noise. By maintaining alignment, rigid couplings prevent the generation of excessive forces that contribute to vibration.
- Reduced Dynamic Imbalance: Accurate alignment achieved by rigid couplings helps in minimizing dynamic imbalance, which is a common cause of vibrations. When shafts are misaligned, it can lead to uneven distribution of forces and create vibrations in rotating machinery.
- Minimized Wear: Rigid couplings prevent misalignment-induced wear and excessive friction between shafts. This helps in reducing the potential for vibration-producing irregularities that can arise from worn or damaged components.
- Stable Connection: Rigid couplings create a solid and stable connection between shafts. This stability minimizes the likelihood of resonances and vibrations caused by flexible components that might amplify vibrations in the system.
- Uniform Torque Transmission: Rigid couplings facilitate even torque distribution between shafts. Uneven torque transmission can lead to fluctuations and vibration-causing oscillations in the system.
While rigid couplings can provide some indirect benefits in reducing vibrations and noise, they might not be as effective as specialized vibration-damping couplings or other mechanical solutions explicitly designed for vibration and noise reduction. In cases where vibration and noise reduction are critical, engineers might consider incorporating additional measures such as damping materials, flexible couplings, or vibration isolators.
Ultimately, the choice of coupling and vibration reduction strategy depends on the specific requirements of the application. If vibration and noise reduction are primary concerns, it’s advisable to consult with engineering experts and consider coupling designs that prioritize these attributes.

How Rigid Shaft Couplings Ensure Precise and Torque-Resistant Shaft Connections
Rigid shaft couplings are designed to provide a solid and inflexible connection between two shafts, ensuring precise alignment and efficient torque transmission. The key features that enable rigid couplings to achieve this include:
- One-Piece Construction: Rigid shaft couplings are typically made from a single piece of material, often metal, without any moving parts or flexible elements. This one-piece construction eliminates the risk of component failure and ensures a stable connection between the shafts.
- Accurate Machining: Rigid couplings undergo precise machining processes to achieve tight tolerances and accurate dimensions. This precision machining ensures that the coupling fits perfectly onto the shafts without any gaps or misalignments.
- High-Quality Materials: Rigid couplings are commonly manufactured from materials such as steel or aluminum, which offer excellent strength and durability. These high-quality materials contribute to the coupling’s ability to handle high torque loads without deformation or wear.
- Keyways and Set Screws: Many rigid shaft couplings feature keyways and set screws for additional security. Keyways are slots on the coupling and shafts that allow the transmission of torque without slippage. Set screws, when tightened against the shafts, create a firm grip, preventing axial movement and enhancing torque resistance.
- Clamping Force: Rigid couplings rely on a clamping force to hold the shafts firmly together. When the coupling is fastened around the shafts, the clamping force creates a strong bond between the coupling and shafts, minimizing any relative movement.
By combining these design elements, rigid shaft couplings ensure that the connected shafts remain in perfect alignment during operation. This precise alignment reduces the risk of misalignment-related issues such as vibrations, premature wear, and decreased efficiency. Additionally, the rigid nature of these couplings allows them to transmit torque without any backlash, providing immediate and accurate responsiveness to changes in torque and rotational direction.
Overall, rigid shaft couplings are an excellent choice for applications that demand precise shaft connections and reliable torque transmission. However, it’s essential to consider factors such as shaft alignment, load capacity, and environmental conditions when selecting the appropriate coupling for a specific application.
“`

editor by CX 2024-05-14
China Standard Manufacturer Customized Pump Rigid Shaft Coupler Steel Coupling Gl Roller Chain Shaft Coupling
Product Description
Manufacturer customized pump Rigid shaft coupler steel coupling GL roller chain shaft coupling
Description:
The chain coupling consists of two-strand roller chains, 2 sprockets and AL-Alloy cover, features simple and compact structure, and high flexibility, power transmission capability and durability.
What’s more ,the chain coupling allows simple connection/disconnection, and the use of the housing enhances safety and durability.
Advantages:
1. Material: C45 steel, Aluminum, Rubber and plastic etc.
2. High efficiency in transmission
3. Finishing: blacken, phosphate-coat, and oxidation.
4. Different models suitable for your different demands
5. Application in wide range of environment.
6. Quick and easy mounting and disassembly.
7. Resistant to oil and electrical insulation.
8. Identical clockwise and anticlockwise rotational characteristics.
9. Small dimension, low weight, high transmitted torque.
10. It has good performance.
Packing & shipping:
1 Prevent from damage.
2. As customers’ requirements, in perfect condition.
3. Delivery : As per contract delivery on time
4. Shipping : As per client request. We can accept CIF, Door to Door etc. or client authorized agent we supply all the necessary assistant.
FAQ:
Q 1: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We are a professional manufacturer specializing in manufacturing various series of couplings.
Q 2:Can you do OEM?
Yes, we can. We can do OEM & ODM for all the customers with customized artworks in PDF or AI format.
Q 3:How long is your delivery time?
Generally, it is 20-30 days if the goods are not in stock. It is according to quantity.
Q 4: How long is your warranty?
A: Our Warranty is 12 months under normal circumstances.
Q 5: Do you have inspection procedures for coupling?
A:100% self-inspection before packing.
Q 6: Can I have a visit to your factory before the order?
A: Sure, welcome to visit our factory. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can Rigid Couplings Handle Misalignment Between Shafts?
Rigid couplings are not designed to handle misalignment between shafts. Unlike flexible couplings that can accommodate slight misalignment through their bending or elastic properties, rigid couplings are intended to provide a fixed and immovable connection between two shafts. As a result, any misalignment between the shafts can lead to increased stress and uneven loading on connected components.
It is essential to ensure precise alignment when using rigid couplings to avoid premature wear and failure of the system. The shafts must be perfectly aligned in both the axial and angular directions before installing the rigid coupling. Proper alignment helps distribute the load evenly and reduces stress concentration on specific areas, such as bearings and keyways.
If a system requires some level of misalignment compensation due to factors like thermal expansion or slight shaft deflection, a flexible coupling should be considered instead. Flexible couplings can tolerate small degrees of angular and axial misalignment while still transmitting torque efficiently and protecting the connected equipment from excessive stress and wear.
In summary, rigid couplings are best suited for applications where precise shaft alignment can be achieved and maintained, while flexible couplings are more appropriate for systems with potential misalignment or other dynamic factors that require some degree of flexibility.

Use of Rigid Couplings for Motor-to-Shaft and Shaft-to-Shaft Connections
Yes, rigid couplings can be used for both motor-to-shaft and shaft-to-shaft connections in mechanical systems. Rigid couplings are designed to provide a solid and non-flexible connection between two shafts. This characteristic makes them versatile for various applications, including motor-to-shaft and shaft-to-shaft connections.
1. Motor-to-Shaft Connections: In motor-to-shaft connections, a rigid coupling is used to connect the output shaft of an electric motor to the driven shaft of a machine or equipment. This ensures direct power transmission without any flexibility. Motor-to-shaft connections are common in applications where the motor’s rotational motion needs to be transferred to the driven equipment with high precision and efficiency.
2. Shaft-to-Shaft Connections: In shaft-to-shaft connections, a rigid coupling joins two shafts directly, providing a solid and immovable link between them. This is beneficial in applications where precise alignment and torque transmission are essential, such as in precision motion control systems or heavy-duty industrial machinery.
Rigid couplings are available in various designs, such as one-piece, two-piece, and split types, to accommodate different shaft arrangements. The type of rigid coupling used depends on the specific application and the shaft sizes to be connected.
Advantages of Using Rigid Couplings:
– Zero backlash ensures accurate motion transfer and positioning.
– Efficient power transmission without loss due to flexibility.
– Minimal maintenance requirements due to their simple design.
– High torque capacity suitable for heavy-duty applications.
– Tolerance to misalignment (within design limits) enhances versatility.
– Provides system stiffness, reducing the risk of resonance and vibration-related issues.
– Suitable for high-speed applications.
– Versatility for various industrial applications.
Whether it’s connecting a motor to a driven shaft or joining two shafts together, rigid couplings offer reliability, precision, and efficiency, making them a popular choice in numerous mechanical systems.

Limitations and Disadvantages of Using Rigid Couplings:
Rigid couplings offer several advantages in providing a strong and direct connection between shafts, but they also have certain limitations and disadvantages that should be considered in certain applications:
- No Misalignment Compensation: Rigid couplings are designed to provide a fixed connection with no allowance for misalignment between shafts. As a result, any misalignment, even if slight, can lead to increased stress on connected components and cause premature wear or failure.
- Transmit Shock and Vibration: Rigid couplings do not have any damping or vibration-absorbing properties, which means they can transmit shock and vibration directly from one shaft to another. In high-speed or heavy-duty applications, this can lead to increased wear on bearings and other components.
- No Torque Compensation: Unlike flexible couplings, rigid couplings cannot compensate for torque fluctuations or angular displacement between shafts. This lack of flexibility may not be suitable for systems with varying loads or torque requirements.
- Higher Stress Concentration: Rigid couplings can create higher stress concentration at the points of connection due to their inflexibility. This can be a concern in applications with high torque or when using materials with lower fatigue strength.
- More Challenging Installation: Rigid couplings require precise alignment during installation, which can be more challenging and time-consuming compared to flexible couplings that can tolerate some misalignment.
- Increased Wear: The absence of misalignment compensation and vibration absorption can lead to increased wear on connected components, such as bearings, shafts, and seals.
- Not Suitable for High Misalignment: While some rigid couplings have limited ability to accommodate minor misalignment, they are not suitable for applications with significant misalignment, which could lead to premature failure.
Despite these limitations, rigid couplings are still widely used in many applications where precise alignment and a strong, permanent connection are required. However, in systems with significant misalignment, vibration, or shock loads, flexible couplings may be a more suitable choice to protect the connected components and improve overall system performance and longevity.


editor by CX 2024-05-09
China Professional Auto Parts Multi Sizes Spline Coupler Motor Connector Spiral Beam Shaft Couplings
Product Description
|
Product Name |
Auto Parts Multi Sizes Spline Coupler Motor Connector Spiral Beam Shaft Couplings |
|
Material |
Aluminum alloy |
|
Surface treatment |
Natural color anode |
|
Customized service |
Support light customization and logo customization |
|
Remarks |
The default engraving brand name and size of the product. If you need not engraving, please contact the customer service for comments |
| Packaging Details | Carton box with anti-static package,carton plus with wooden case. |
| Main Products | Shaft Parts, Timing Belt Pulley, Gears, CNC Machining Parts, Sheet Metal Fabrication |
| Certifications(2) | ISO9001:2015, IPMS |
| Applicable Industries | Building Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Food & Beverage Factory, Farms |
| Supply Ability | 100000 Piece/Pieces per Month |
| Dimension | oem provided |
| Surface finish | anodized |
| Lead Time | 25 days |
| Application | Furniture,cabinet |
| Custom | OEM and ODM services are welcome,we can make cutom LOGO and products according to customer’s requests. |
| Quality control Our | Finished product inspection,Warranty available |
| service | Swiss machining;deburring;lathe/turning;5 axis;micromachining |
| Color |
silver,gold,black,red,bulue,and according to the customer requests. |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Exploring the Use of Elastomeric Materials in Flexible Shaft Couplings
Elastomeric materials play a crucial role in the design and function of flexible shaft couplings. These materials, commonly known as elastomers, are rubber-like substances that exhibit high elasticity and flexibility. They are widely used in various types of flexible couplings due to their unique properties and benefits:
1. Damping and Vibration Absorption:
Elastomeric materials have excellent damping characteristics, meaning they can absorb and dissipate vibrations and shocks. This property is particularly useful in applications where vibration control is essential to protect sensitive equipment and improve overall system performance.
2. Misalignment Compensation:
Flexible shaft couplings with elastomeric elements can accommodate different types of misalignments, including angular, parallel, and radial misalignments. The elasticity of the material allows for limited movement between the shafts while still transmitting torque efficiently.
3. Torsional Flexibility:
Elastomers offer torsional flexibility, which allows them to twist and deform under torque loads. This feature helps to minimize torsional stresses and torsional backlash, making them suitable for applications requiring precise motion control.
4. Shock and Impact Resistance:
Due to their high resilience, elastomers can withstand sudden shocks and impacts without permanent deformation. This property makes them ideal for use in machinery subjected to varying loads or rapid changes in torque.
5. No Lubrication Requirement:
Elastomeric couplings are often maintenance-free because the elastomer material does not require additional lubrication. This reduces maintenance costs and simplifies the overall system upkeep.
6. Electric Isolation:
In certain applications, elastomeric materials can provide electrical isolation between the driving and driven components. This can help prevent the transmission of electrical currents or static charges through the coupling.
7. Corrosion Resistance:
Many elastomers used in couplings are resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for use in challenging environments where exposure to chemicals or moisture is a concern.
8. Easy Installation:
Elastomeric couplings are often designed for ease of installation and replacement. Their flexibility allows for simple and quick assembly onto the shafts without the need for special tools or complex procedures.
Given these advantages, elastomeric materials are popular choices for various flexible shaft couplings, including jaw couplings, tire couplings, and spider couplings. However, it is essential to select the right elastomer material based on the specific application requirements, such as temperature range, chemical compatibility, and torque capacity.
“`
Real-World Examples of Shaft Coupling Applications in Different Industries
Shaft couplings play a crucial role in various industries by connecting rotating shafts and transmitting torque between them. Here are some real-world examples of shaft coupling applications in different industries:
1. Manufacturing Industry:
In manufacturing plants, shaft couplings are used in various equipment such as conveyor systems, pumps, compressors, and mixers. For example, in a conveyor system, shaft couplings connect the motor shaft to the conveyor belt, allowing efficient material handling and transportation.
2. Oil and Gas Industry:
The oil and gas industry utilizes shaft couplings in applications like drilling rigs, pumps, and generators. In drilling rigs, couplings connect the motor to the drill shaft, enabling the drilling process.
3. Marine Industry:
In the marine industry, shaft couplings are found in propulsion systems, water pumps, and winches. They connect the ship’s engine to the propeller shaft, providing the necessary torque for propulsion.
4. Power Generation:
Power plants use shaft couplings in turbines, generators, and cooling systems. For instance, in a steam turbine, couplings connect the turbine to the electrical generator, allowing the conversion of steam energy into electrical power.
5. Aerospace Industry:
Aerospace applications use shaft couplings in aircraft engines, landing gear systems, and auxiliary power units. Couplings enable power transmission between different components of the aircraft systems.
6. Automotive Industry:
In vehicles, shaft couplings are present in the drivetrain, steering systems, and transmission. For example, in a car’s transmission system, couplings connect the engine to the gearbox, enabling smooth gear changes and power transmission to the wheels.
7. Mining Industry:
The mining industry relies on shaft couplings in heavy-duty machinery such as crushers, conveyor belts, and pumps. Couplings connect motors to various mining equipment, facilitating material extraction and transportation.
8. Agriculture:
Agricultural machinery like tractors and harvesters use shaft couplings to connect the engine to implements such as plows, harvesters, and irrigation pumps.
These examples demonstrate the wide-ranging applications of shaft couplings across industries. In each case, the specific coupling type is chosen based on factors such as torque requirements, misalignment compensation, environmental conditions, and load characteristics to ensure reliable and efficient operation.
“`
Diagnosing and Fixing Common Issues with Shaft Couplings
Regular inspection and maintenance of shaft couplings are essential to detect and address common issues that may arise during operation. Here are steps to diagnose and fix some common coupling problems:
1. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:
If you notice unusual noise or excessive vibration during equipment operation, it may indicate misalignment, wear, or damage in the coupling. Check for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks or deformations, and inspect the coupling for proper alignment.
Diagnosis:
Use a vibration analysis tool to measure the vibration levels and identify the frequency of the abnormal vibrations. This can help pinpoint the source of the problem.
Fix:
If misalignment is the cause, adjust the coupling to achieve proper alignment between the shafts. Replace any damaged or worn coupling components, such as spiders or elastomeric inserts, as needed.
2. Excessive Heat:
Feeling excessive heat on the coupling during operation can indicate friction, improper lubrication, or overload conditions.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the coupling and surrounding components for signs of rubbing, lack of lubrication, or overloading.
Fix:
Ensure proper lubrication of the coupling, and check for any interference between the coupling and adjacent parts. Address any overloading issues by adjusting the equipment load or using a coupling with a higher torque capacity.
3. Shaft Movement:
If you observe axial or radial movement in the connected shafts, it may indicate wear or improper installation of the coupling.
Diagnosis:
Check the coupling’s set screws, keyways, or other fastening methods to ensure they are secure and not causing the shaft movement.
Fix:
If the coupling is worn or damaged, replace it with a new one. Ensure proper installation and use appropriate fastening methods to secure the coupling to the shafts.
4. Sheared Shear Pin:
In shear pin couplings, a sheared shear pin indicates overloading or shock loads that exceeded the coupling’s torque capacity.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the shear pin for damage or breakage.
Fix:
Replace the sheared shear pin with a new one of the correct specifications. Address any overloading issues or adjust the equipment to prevent future shearing.
5. Coupling Wear:
Regular wear is normal for couplings, but excessive wear may lead to decreased performance and increased misalignment.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the coupling components for signs of wear, such as worn elastomeric elements or damaged teeth.
Fix:
Replace the worn or damaged components with new ones of the appropriate specifications.
Remember, regular maintenance and periodic inspection are key to diagnosing issues early and preventing severe problems. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and replacement schedules to ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the shaft coupling.
“`

editor by CX 2024-05-08
China Good quality CNC Aluminum Elastic Rubber Spider Jaw Shaft Coupler GF14*22 20*25 25*30 40*50 Shaft Flexible Coupling Ball Screw Plum Coupling
Product Description
Product Description
Coupling Deatails
Name: High precision plum blossom
coupling Model: LM-Material: Aviation Aluminum Alloy
Working temperature: -40 ° C ~ 100 ° C
Support customization: Factory direct sales support customization.
Features:
1.Intermediate Elastomer Connection-Absorbs vibration, compensates for radial, angular, and axial 2.misalignment
3.Oil resistance and electrical insulation
4.Clockwise and counterclockwise rotation characteristics are identical-there are 3 different hardness 5.elastomer
6.Fixation by clamping screw.
|
Model parameter |
ΦD |
L |
LF |
LP |
F |
M |
Tightening screw torque |
|
(N.M) |
|||||||
|
GF-14X22 |
14 |
22 |
14.3 |
6.6 |
3.8 |
M 3 |
0.7 |
|
GF-20X25 |
20 |
25 |
16.7 |
8.6 |
4 |
M 3 |
0.7 |
|
GF-20X30 |
20 |
30 |
19.25 |
8.6 |
5.3 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-25X30 |
25 |
30 |
20.82 |
11.6 |
5.6 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-25X34 |
25 |
34 |
22.82 |
11.6 |
5.6 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-30X35 |
30 |
35 |
23 |
11.5 |
5.75 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-30X40 |
30 |
40 |
25.6 |
11.5 |
10 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-40X50 |
40 |
50 |
32.1 |
14.5 |
10 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-40X55 |
40 |
55 |
34.5 |
14.5 |
10 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-40X66 |
40 |
66 |
40 |
14.5 |
12.75 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-55X49 |
55 |
49 |
32 |
16.1 |
13.5 |
M 6 |
8.4 |
|
GF-55X78 |
55 |
78 |
46.4 |
16.1 |
15.5 |
M 6 |
8.4 |
|
GF-65X80 |
65 |
80 |
48.5 |
17.3 |
18.1 |
M 8 |
10.5 |
|
GF-65X90 |
65 |
90 |
53.5 |
17.3 |
18.1 |
M 8 |
10.5 |
Product Parameters
Detailed Photos
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Understanding the Torque and Misalignment Capabilities of Shaft Couplings
Shaft couplings play a critical role in transmitting torque and accommodating misalignment between rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. Understanding their torque and misalignment capabilities is essential for selecting the right coupling for a specific application. Here’s an overview:
Torque Transmission:
The torque capacity of a shaft coupling refers to its ability to transmit rotational force from one shaft to another. It is typically specified in torque units, such as Nm (Newton-meters) or lb-ft (pound-feet). The coupling’s torque capacity depends on its design, size, and material.
When selecting a coupling, it’s crucial to ensure that its torque capacity meets or exceeds the torque requirements of the application. Overloading a coupling beyond its torque capacity can lead to premature failure or damage to the coupling and connected equipment.
Misalignment Compensation:
Shaft misalignment can occur due to various factors, including thermal expansion, manufacturing tolerances, or foundation settling. Misalignment puts additional stress on the coupling and connected components, potentially leading to increased wear and reduced efficiency.
Shaft couplings are designed to compensate for different types of misalignment:
- Angular Misalignment: Occurs when the shafts are not parallel and have an angle between them.
- Parallel Misalignment: Occurs when the shafts are not collinear, resulting in axial displacement.
- Radial Misalignment: Occurs when the shafts have lateral displacement but remain parallel.
The coupling’s misalignment capabilities are specified in terms of angular and axial misalignment values, usually in degrees or millimeters. Different coupling designs can accommodate varying degrees of misalignment, and the choice depends on the specific application and operating conditions.
Flexible Couplings:
Flexible couplings, such as elastomeric or jaw couplings, offer good misalignment compensation. They can handle a combination of angular, parallel, and axial misalignments. However, their torque capacity may be limited compared to rigid couplings.
Rigid Couplings:
Rigid couplings, such as clamp or sleeve couplings, have high torque transmission capabilities but offer minimal misalignment compensation. They are best suited for applications where shafts are well-aligned and precise torque transmission is critical.
Torsional Stiffness:
Another factor to consider is the coupling’s torsional stiffness, which determines how much torsional deflection or twist occurs under load. Some applications, like precision systems, may require couplings with high torsional stiffness to maintain accurate positioning and avoid torsional backlash.
By understanding the torque and misalignment capabilities of shaft couplings, engineers can make informed decisions when selecting a coupling to ensure efficient power transmission and reliable performance in their mechanical systems.
“`
Do Shaft Couplings Require Regular Maintenance, and if so, What Does it Involve?
Yes, shaft couplings do require regular maintenance to ensure their optimal performance, extend their service life, and prevent unexpected failures. The maintenance frequency may vary based on factors such as the coupling type, application, operating conditions, and the manufacturer’s recommendations. Here’s what regular maintenance for shaft couplings typically involves:
1. Visual Inspection:
Regularly inspect the coupling for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Check for cracks, corrosion, and worn-out elastomeric elements (if applicable). Look for any abnormal movement or rubbing between the coupling components during operation.
2. Lubrication:
If the shaft coupling requires lubrication, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the appropriate lubricant type and frequency. Lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and noise in the coupling.
3. Alignment Check:
Monitor shaft alignment periodically. Misalignment can lead to premature coupling failure and damage to connected equipment. Make adjustments as needed to keep the shafts properly aligned.
4. Torque Check:
For bolted couplings, periodically check the torque on the bolts to ensure they remain securely fastened. Loose bolts can lead to misalignment and reduce coupling performance.
5. Replace Worn Components:
If any coupling components show signs of wear or damage beyond acceptable limits, replace them promptly with genuine replacement parts from the manufacturer.
6. Environmental Considerations:
In harsh environments with exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures, take additional measures to protect the coupling, such as applying corrosion-resistant coatings or using special materials.
7. Monitoring Coupling Performance:
Implement a monitoring system to track coupling performance and detect any changes or abnormalities early on. This could include temperature monitoring, vibration analysis, or other condition monitoring techniques.
8. Professional Inspection:
Periodically have the coupling and connected machinery inspected by qualified professionals to identify any potential issues that may not be apparent during regular inspections.
By adhering to a regular maintenance schedule and taking proactive measures to address potential issues, you can ensure that your shaft couplings operate reliably and efficiently throughout their service life, minimizing downtime and improving overall system performance.
“`
Diagnosing and Fixing Common Issues with Shaft Couplings
Regular inspection and maintenance of shaft couplings are essential to detect and address common issues that may arise during operation. Here are steps to diagnose and fix some common coupling problems:
1. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:
If you notice unusual noise or excessive vibration during equipment operation, it may indicate misalignment, wear, or damage in the coupling. Check for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks or deformations, and inspect the coupling for proper alignment.
Diagnosis:
Use a vibration analysis tool to measure the vibration levels and identify the frequency of the abnormal vibrations. This can help pinpoint the source of the problem.
Fix:
If misalignment is the cause, adjust the coupling to achieve proper alignment between the shafts. Replace any damaged or worn coupling components, such as spiders or elastomeric inserts, as needed.
2. Excessive Heat:
Feeling excessive heat on the coupling during operation can indicate friction, improper lubrication, or overload conditions.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the coupling and surrounding components for signs of rubbing, lack of lubrication, or overloading.
Fix:
Ensure proper lubrication of the coupling, and check for any interference between the coupling and adjacent parts. Address any overloading issues by adjusting the equipment load or using a coupling with a higher torque capacity.
3. Shaft Movement:
If you observe axial or radial movement in the connected shafts, it may indicate wear or improper installation of the coupling.
Diagnosis:
Check the coupling’s set screws, keyways, or other fastening methods to ensure they are secure and not causing the shaft movement.
Fix:
If the coupling is worn or damaged, replace it with a new one. Ensure proper installation and use appropriate fastening methods to secure the coupling to the shafts.
4. Sheared Shear Pin:
In shear pin couplings, a sheared shear pin indicates overloading or shock loads that exceeded the coupling’s torque capacity.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the shear pin for damage or breakage.
Fix:
Replace the sheared shear pin with a new one of the correct specifications. Address any overloading issues or adjust the equipment to prevent future shearing.
5. Coupling Wear:
Regular wear is normal for couplings, but excessive wear may lead to decreased performance and increased misalignment.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the coupling components for signs of wear, such as worn elastomeric elements or damaged teeth.
Fix:
Replace the worn or damaged components with new ones of the appropriate specifications.
Remember, regular maintenance and periodic inspection are key to diagnosing issues early and preventing severe problems. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and replacement schedules to ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the shaft coupling.
“`

editor by CX 2024-05-06
China supplier Manufacturer Customized Pump Rigid Shaft Coupler Steel Coupling Gl Roller Chain Shaft Coupling
Product Description
Manufacturer customized pump Rigid shaft coupler steel coupling GL roller chain shaft coupling
Description:
The chain coupling consists of two-strand roller chains, 2 sprockets and AL-Alloy cover, features simple and compact structure, and high flexibility, power transmission capability and durability.
What’s more ,the chain coupling allows simple connection/disconnection, and the use of the housing enhances safety and durability.
Advantages:
1. Material: C45 steel, Aluminum, Rubber and plastic etc.
2. High efficiency in transmission
3. Finishing: blacken, phosphate-coat, and oxidation.
4. Different models suitable for your different demands
5. Application in wide range of environment.
6. Quick and easy mounting and disassembly.
7. Resistant to oil and electrical insulation.
8. Identical clockwise and anticlockwise rotational characteristics.
9. Small dimension, low weight, high transmitted torque.
10. It has good performance.
Packing & shipping:
1 Prevent from damage.
2. As customers’ requirements, in perfect condition.
3. Delivery : As per contract delivery on time
4. Shipping : As per client request. We can accept CIF, Door to Door etc. or client authorized agent we supply all the necessary assistant.
FAQ:
Q 1: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We are a professional manufacturer specializing in manufacturing various series of couplings.
Q 2:Can you do OEM?
Yes, we can. We can do OEM & ODM for all the customers with customized artworks in PDF or AI format.
Q 3:How long is your delivery time?
Generally, it is 20-30 days if the goods are not in stock. It is according to quantity.
Q 4: How long is your warranty?
A: Our Warranty is 12 months under normal circumstances.
Q 5: Do you have inspection procedures for coupling?
A:100% self-inspection before packing.
Q 6: Can I have a visit to your factory before the order?
A: Sure, welcome to visit our factory. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can Rigid Couplings Accommodate High Torque and High-Speed Applications?
Yes, rigid couplings are well-suited for high torque and high-speed applications. Their design and construction allow them to efficiently transmit large amounts of torque and handle high rotational speeds without compromising performance or introducing backlash.
Rigid couplings are typically made from robust materials, such as steel or aluminum, which provide high strength and stiffness. This allows them to withstand substantial torque loads without deformation or failure. Additionally, rigid couplings do not have flexible elements, such as elastomers or springs, which can be a limiting factor in high-torque applications.
The absence of flexible elements also means that rigid couplings have minimal backlash. Backlash is the clearance between mating teeth in a coupling and can cause position inaccuracies, especially in high-precision systems. Since rigid couplings have a solid, one-piece design, they offer precise and immediate torque transmission, making them suitable for applications requiring high accuracy and repeatability.
Furthermore, the solid construction of rigid couplings allows them to handle high rotational speeds. They do not exhibit the bending or torsional flexibility seen in some other coupling types, which can be limiting factors in high-speed applications. As a result, rigid couplings are commonly used in various high-speed machinery, such as power transmission systems, motors, pumps, and industrial equipment.
However, it is essential to ensure proper alignment and installation when using rigid couplings in high-torque and high-speed applications. Any misalignment between the shafts can lead to increased stresses and premature failure. Regular maintenance, including shaft alignment checks, can help ensure optimal performance and longevity in such demanding applications.
In summary, rigid couplings are an excellent choice for high torque and high-speed applications due to their robust design, minimal backlash, and ability to provide precise torque transmission. When correctly installed and maintained, rigid couplings can reliably handle the demands of various industrial and mechanical systems.

Factors to Consider When Choosing a Rigid Coupling for a Specific System
Choosing the right rigid coupling for a specific system is crucial to ensure proper functionality and reliable performance. Several factors should be considered when making this decision:
1. Shaft Size and Compatibility: The most fundamental factor is ensuring that the rigid coupling is compatible with the shaft sizes of the connected components. The coupling should have the appropriate bore size and keyway dimensions to fit securely onto the shafts.
2. Operating Torque: Consider the torque requirements of the application. The rigid coupling should have a torque rating that exceeds the maximum torque expected during operation to prevent failures and ensure safety.
3. Speed: Determine the rotational speed (RPM) of the connected shafts. Rigid couplings have maximum RPM limits, and the selected coupling should be capable of handling the system’s operating speed.
4. Misalignment Tolerance: Assess the potential misalignment between the shafts. Rigid couplings provide no flexibility, so the system must have minimal misalignment to prevent excessive forces on the components.
5. Temperature and Environment: Consider the operating temperature range and the environment where the coupling will be used. Ensure the chosen material can withstand the temperature and any corrosive or harsh conditions present.
6. Space Limitations: Evaluate the available space for the coupling. Rigid couplings have a compact design, but ensure that there is enough clearance for installation and maintenance.
7. Backlash and Torsional Stiffness: In some precision systems, backlash must be minimized to maintain accurate positioning. Additionally, the torsional stiffness of the coupling can impact system response and stability.
8. Keyway or Keyless Design: Decide between a coupling with a keyway or a keyless design based on the specific application requirements and ease of installation.
9. Material Selection: Consider the material properties of the rigid coupling. Common materials include steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, each with its own advantages and limitations.
10. Maintenance: Determine the maintenance requirements of the coupling. Some couplings may need periodic lubrication or inspections, while others may be maintenance-free.
11. Cost: While cost should not be the sole consideration, it is essential to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of the coupling, taking into account its performance and longevity.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the most suitable rigid coupling for your specific system, ensuring optimal performance, and longevity of your mechanical setup.

Types of Rigid Coupling Designs:
There are several types of rigid coupling designs available, each designed to meet specific application requirements. Here are some common types of rigid couplings:
- 1. Sleeve Couplings: Sleeve couplings are the simplest type of rigid couplings. They consist of a cylindrical sleeve with a bore in the center that fits over the shaft ends. The coupling is secured in place using setscrews or keyways. Sleeve couplings provide a solid and rigid connection between shafts and are easy to install and remove.
- 2. Clamp or Split Couplings: Clamp couplings, also known as split couplings, are designed with two halves that fit around the shafts and are fastened together with bolts or screws. The split design allows for easy installation and removal without the need to disassemble other components in the system. These couplings are ideal for applications where the shafts cannot be easily moved.
- 3. Flanged Couplings: Flanged couplings have flanges on each end that are bolted together to form a rigid connection. The flanges add stability and strength to the coupling, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. They are commonly used in industrial machinery and equipment.
- 4. Tapered Couplings: Tapered couplings have a tapered inner diameter that matches the taper of the shaft ends. When the coupling is tightened, it creates a frictional fit between the coupling and the shafts, providing a rigid connection. These couplings are often used in applications where high torque transmission is required.
- 5. Marine or Clampshell Couplings: Marine couplings, also known as clampshell couplings, consist of two halves that encase the shaft ends and are bolted together. These couplings are commonly used in marine applications, such as propeller shafts in boats and ships.
- 6. Diaphragm Couplings: Diaphragm couplings are a type of rigid coupling that provides some flexibility to accommodate misalignment while maintaining a nearly torsionally rigid connection. They consist of thin metal diaphragms that transmit torque while compensating for minor shaft misalignments.
The choice of rigid coupling design depends on factors such as shaft size, torque requirements, ease of installation, and the level of misalignment that needs to be accommodated. It is essential to select the appropriate coupling design based on the specific needs of the application to ensure optimal performance and reliability.


editor by CX 2024-05-02
China Standard Precision CNC Machined Rigid Brass Motor Shaft Coupler Sleeve Coupling
Product Description
Company Profile
Workshop
Detailed Photos
Product Description
| Material | Alloy Steel, Copper alloy(brass,silicon bronze,phosphor bronze,aluminum bronze,beryllium copper),Stainless Steel,Aluminum,Titanium, Magnesium, Superalloys,Molybdenum, Invar,,Zinc,Tungsten steel,incoloy,Nickel 200,Hastelloy, Inconel,Monel,ABS, PEEK,PTFE,PVC,Acetal. |
| Surface Treatment | Zn-plating, Ni-plating, Cr-plating, Tin-plating, copper-plating, the wreath oxygen resin spraying, the heat disposing, hot-dip galvanizing, black oxide coating, painting, powdering, color zinc-plated, blue black zinc-plated, rust preventive oil, titanium alloy galvanized, silver plating, plastic, electroplating, anodizing etc. |
| Producing Equipment | CNC machine,automatic lathe machine,CNC milling machine,lasering,tag grinding machine etc. |
| Drawing Format | Pro/E, Auto CAD, CHINAMFG Works, UG, CAD/CAM, PDF |
| Managing Returned Goods | With quality problem or deviation from drawings |
| Warranty | Replacement at all our cost for rejected products |
| Main Markets | North America, South America, Eastern Europe , West Europe , North Europe, South Europe, Asia |
| How to order | * You send us drawing or sample |
| * We carry through project assessment | |
| * We make the sample and send it to you after you confirmed our design | |
| * You confirm the sample then place an order and pay us 30% deposit | |
| * We start producing | |
| * When the goods is done, you pay us the balance after you confirmed pictures or tracking numbers. | |
| * Trade is done, thank you!! |
Quality Control
Packaging & Shipping
Customer Reviews
FAQ
Q1:What kind of information do you need for quotation?
A: You can provide 2D/3D drawing or send your sample to our factory, then we can make according to your sample.
Q2: Can we CHINAMFG NDA?
A: Sure. We can CHINAMFG the NDA before got your drawings.
Q3: Do you provide sample?
A: Yes, we can provide you sample before mass order.
Q4: How can you ensure the quality?
A: We have profesional QC,IQC, OQC to guarantee the quality.
Q5: Delivery time?
A: For samples genearlly need 25 days. Mass production: around 30~45 days after receipt of deposit (Accurate delivery time
depends on specific items and quantities)
Q6: How about the transportation?
A: You can choose any mode of transportation you want, sea delivery, air delivery or door to door express.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

What are the potential drawbacks or limitations of using rigid shaft couplings in certain applications?
Rigid shaft couplings, while offering benefits in certain scenarios, also have limitations that should be considered when selecting them for specific applications:
- Minimal Misalignment Compensation: Rigid couplings have limited ability to compensate for shaft misalignment, making them less suitable for applications with significant misalignment.
- Transmits Vibrations: Rigid couplings do not dampen vibrations, which can lead to increased wear and fatigue in connected components and decrease overall system lifespan.
- Higher Stress Concentration: Due to their rigid nature, these couplings can result in higher stress concentrations at the coupling ends, potentially leading to premature failure.
- Noisy Operation: Rigid couplings can amplify noise generated by connected equipment, contributing to a noisier operating environment.
- Requires Precise Alignment: Proper alignment during installation is crucial to prevent excessive loads on equipment and ensure reliable operation.
- Less Torsional Damping: Rigid couplings lack the torsional damping capabilities of some other coupling types, which may be necessary in systems with varying loads.
- Less Forgiving: Rigid couplings can transmit shocks and impacts directly to connected equipment, which may not be suitable for applications with frequent starts, stops, or heavy loads.
It’s important to carefully assess the specific requirements of an application and consider factors such as misalignment, vibration, torque transmission, and environmental conditions when deciding whether to use a rigid shaft coupling. In cases where the limitations of rigid couplings may pose challenges, other coupling types such as flexible, torsionally soft, or damping couplings could be more appropriate alternatives.

Are there any safety considerations when using rigid shaft couplings in critical applications?
Yes, when using rigid shaft couplings in critical applications, several safety considerations should be taken into account:
- Torsional Stiffness: Rigid couplings have high torsional stiffness, which can lead to increased stresses and potential failures in the connected equipment. Proper analysis of torsional vibrations and stiffness compatibility with the connected components is crucial.
- Shaft Alignment: Inaccurate shaft alignment can lead to additional loads on the coupling and connected machinery. Precision alignment is essential to prevent premature wear, increased stress, and potential breakdowns.
- Overloading: Exceeding the rated torque capacity of the coupling can result in sudden failures and damage to machinery. It’s essential to operate within the coupling’s specified limits to ensure safe operation.
- Maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance are critical to identify signs of wear, fatigue, or misalignment. Neglecting maintenance can lead to unexpected failures and safety hazards.
- Environmental Factors: Harsh environments, extreme temperatures, and corrosive substances can impact the integrity of rigid couplings. Choosing appropriate materials and protective measures can mitigate these effects.
For critical applications, it’s recommended to work closely with experienced engineers, perform thorough risk assessments, and follow industry standards and best practices to ensure the safe and reliable use of rigid shaft couplings.

What are the Materials Commonly Used to Manufacture Rigid Shaft Couplings, and How Do They Impact Performance?
Rigid shaft couplings are typically made from a variety of materials, and the choice of material can significantly impact the performance of the coupling in specific applications. Some common materials used in manufacturing rigid shaft couplings include:
- Steel: Steel is one of the most commonly used materials for rigid shaft couplings. It offers excellent strength and durability, making it suitable for high-torque and heavy-duty applications. Steel couplings can withstand significant stresses and provide reliable torque transmission.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel couplings offer the same benefits as regular steel couplings but with the added advantage of corrosion resistance. They are commonly used in applications where the coupling may be exposed to harsh environments or moisture.
- Aluminum: Aluminum couplings are lightweight and have good corrosion resistance. They are often used in applications where weight reduction is essential, such as in aerospace and automotive industries.
- Brass: Brass couplings are known for their excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. They are commonly used in applications where electrical conductivity is required.
- Cast Iron: Cast iron couplings are robust and offer good resistance to wear and tear. They are commonly used in industrial machinery and equipment.
The choice of material depends on various factors, including the application’s operating conditions, such as torque requirements, temperature, and environmental conditions. For example, in high-torque applications, steel or stainless steel couplings are often preferred due to their high strength. On the other hand, aluminum couplings are favored in applications where weight reduction is critical.
It is essential to consider the specific needs of the application and the coupling’s material properties to ensure optimal performance, longevity, and reliability of the rigid shaft coupling.


editor by CX 2024-05-02
China high quality Gn-25X36 Shaft Coupler Rigid Shaft Coupling
Product Description
GN-25×36 Shaft Coupler Rigid Shaft Coupling
GN-25×36 Shaft Coupler Rigid Shaft Coupling
|
model parameter |
common bore diameter d1,d2 |
ΦD |
L |
F |
M |
tightening screw torque |
|
GNC-16×16 |
3,4,5,6,6.35,7,8 |
16 |
16 |
3.75 |
M2.5 |
1 |
|
GNC-16×24 |
3,4,5,6,6.35,7,8 |
16 |
24 |
3.75 |
M2.5 |
1 |
|
GNC-20×20 |
4,5,6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10 |
20 |
20 |
3.75 |
M2.5 |
1 |
|
GNC-20×30 |
4,5,6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10 |
20 |
30 |
3.75 |
M2.5 |
1 |
|
GNC-25×25 |
5,6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10,12 |
25 |
25 |
6 |
M3 |
1.5 |
|
GNC-25×36 |
5,6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10,12 |
25 |
36 |
6 |
M3 |
1.5 |
|
GNC-28.5×38 |
6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10,12,12.7,14 |
28.5 |
38 |
7.8 |
M4 |
2.5 |
|
GNC-32×32 |
6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10,12,12.7,14,15,16 |
32 |
32 |
7 |
M4 |
2.5 |
|
GNC-32×41 |
6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10,12,12.7,14,15,16 |
32 |
41 |
7.75 |
M4 |
2.5 |
|
GNC-40×44 |
8,9,9.525,10,11,12,12.7,14,15,15,17,18,19,20 |
40 |
44 |
10.5 |
M5 |
7 |
|
GNC-40×52 |
8,9,9.525,10,11,12,12.7,14,15,15,17,18,19,20 |
40 |
52 |
10.5 |
M5 |
7 |
|
GNC-50×55 |
10,11,12,12.7,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,24,25 |
50 |
55 |
13 |
M6 |
12 |
|
GNC-50×66 |
10,11,12,12.7,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,24,25 |
50 |
66 |
16 |
M6 |
12 |
|
GNC-63×71 |
10,11,12,12.7,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,24,25,28,30,32,35 |
63 |
71 |
16.5 |
M6 |
12 |
|
model parameter |
Rated torque(N.m) |
maximum speed (rpm) |
weight (g) |
|
GNC-16×16 |
5 |
1000 |
7 |
|
GNC-16×24 |
5 |
9400 |
13 |
|
GNC-20×20 |
10 |
7500 |
15 |
|
GNC-20×30 |
10 |
7500 |
25 |
|
GNC-25×25 |
12 |
6000 |
29 |
|
GNC-25×36 |
12 |
6000 |
43 |
|
GNC-28.5×38 |
14 |
5500 |
48 |
|
GNC-32×32 |
15 |
4700 |
55 |
|
GNC-32×41 |
15 |
4700 |
65 |
|
GNC-40×44 |
19 |
4000 |
123 |
|
GNC-40×52 |
19 |
4000 |
150 |
|
GNC-50×55 |
45 |
4000 |
240 |
|
GNC-50×66 |
45 |
4000 |
280 |
|
|
|
|
320 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

What are the potential drawbacks or limitations of using rigid shaft couplings in certain applications?
Rigid shaft couplings, while offering benefits in certain scenarios, also have limitations that should be considered when selecting them for specific applications:
- Minimal Misalignment Compensation: Rigid couplings have limited ability to compensate for shaft misalignment, making them less suitable for applications with significant misalignment.
- Transmits Vibrations: Rigid couplings do not dampen vibrations, which can lead to increased wear and fatigue in connected components and decrease overall system lifespan.
- Higher Stress Concentration: Due to their rigid nature, these couplings can result in higher stress concentrations at the coupling ends, potentially leading to premature failure.
- Noisy Operation: Rigid couplings can amplify noise generated by connected equipment, contributing to a noisier operating environment.
- Requires Precise Alignment: Proper alignment during installation is crucial to prevent excessive loads on equipment and ensure reliable operation.
- Less Torsional Damping: Rigid couplings lack the torsional damping capabilities of some other coupling types, which may be necessary in systems with varying loads.
- Less Forgiving: Rigid couplings can transmit shocks and impacts directly to connected equipment, which may not be suitable for applications with frequent starts, stops, or heavy loads.
It’s important to carefully assess the specific requirements of an application and consider factors such as misalignment, vibration, torque transmission, and environmental conditions when deciding whether to use a rigid shaft coupling. In cases where the limitations of rigid couplings may pose challenges, other coupling types such as flexible, torsionally soft, or damping couplings could be more appropriate alternatives.

Can rigid shaft couplings be used for shafts with different rotational speeds and directions?
Rigid shaft couplings are typically designed for applications where the connected shafts have the same rotational speed and direction. They are not well-suited for scenarios involving significant speed differences or reverse rotation between shafts. The limitations arise from the coupling’s rigid construction, which does not allow for the compensation of speed differentials or changes in direction.
When shafts have different rotational speeds or need to rotate in opposite directions, it can result in uneven loading, increased wear, vibrations, and even coupling failure. Rigid couplings lack the flexibility required to accommodate the variations in speed and direction, which can lead to undesirable consequences in the system.
If your application involves shafts with varying speeds or reverse rotation, it’s recommended to explore flexible coupling options. Flexible couplings, such as gear couplings, elastomeric couplings, or universal joints, are designed to handle these situations by providing a degree of angular and radial flexibility. These couplings can help distribute the loads more evenly, reduce vibrations, and compensate for speed differences, ultimately contributing to smoother and more reliable operation.
It’s essential to accurately assess the requirements of your application and choose the appropriate coupling type based on the specific operational conditions. If there are varying speeds or reverse rotation involved, opting for flexible couplings designed for such scenarios will help ensure the longevity, efficiency, and performance of your machinery.

What are the Materials Commonly Used to Manufacture Rigid Shaft Couplings, and How Do They Impact Performance?
Rigid shaft couplings are typically made from a variety of materials, and the choice of material can significantly impact the performance of the coupling in specific applications. Some common materials used in manufacturing rigid shaft couplings include:
- Steel: Steel is one of the most commonly used materials for rigid shaft couplings. It offers excellent strength and durability, making it suitable for high-torque and heavy-duty applications. Steel couplings can withstand significant stresses and provide reliable torque transmission.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel couplings offer the same benefits as regular steel couplings but with the added advantage of corrosion resistance. They are commonly used in applications where the coupling may be exposed to harsh environments or moisture.
- Aluminum: Aluminum couplings are lightweight and have good corrosion resistance. They are often used in applications where weight reduction is essential, such as in aerospace and automotive industries.
- Brass: Brass couplings are known for their excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. They are commonly used in applications where electrical conductivity is required.
- Cast Iron: Cast iron couplings are robust and offer good resistance to wear and tear. They are commonly used in industrial machinery and equipment.
The choice of material depends on various factors, including the application’s operating conditions, such as torque requirements, temperature, and environmental conditions. For example, in high-torque applications, steel or stainless steel couplings are often preferred due to their high strength. On the other hand, aluminum couplings are favored in applications where weight reduction is critical.
It is essential to consider the specific needs of the application and the coupling’s material properties to ensure optimal performance, longevity, and reliability of the rigid shaft coupling.


editor by CX 2024-04-26
China best CNC Aluminum Elastic Rubber Spider Jaw Shaft Coupler GF14*22 20*25 25*30 40*50 Shaft Flexible Coupling Ball Screw Plum Coupling
Product Description
Product Description
Coupling Deatails
Name: High precision plum blossom
coupling Model: LM-Material: Aviation Aluminum Alloy
Working temperature: -40 ° C ~ 100 ° C
Support customization: Factory direct sales support customization.
Features:
1.Intermediate Elastomer Connection-Absorbs vibration, compensates for radial, angular, and axial 2.misalignment
3.Oil resistance and electrical insulation
4.Clockwise and counterclockwise rotation characteristics are identical-there are 3 different hardness 5.elastomer
6.Fixation by clamping screw.
|
Model parameter |
ΦD |
L |
LF |
LP |
F |
M |
Tightening screw torque |
|
(N.M) |
|||||||
|
GF-14X22 |
14 |
22 |
14.3 |
6.6 |
3.8 |
M 3 |
0.7 |
|
GF-20X25 |
20 |
25 |
16.7 |
8.6 |
4 |
M 3 |
0.7 |
|
GF-20X30 |
20 |
30 |
19.25 |
8.6 |
5.3 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-25X30 |
25 |
30 |
20.82 |
11.6 |
5.6 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-25X34 |
25 |
34 |
22.82 |
11.6 |
5.6 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-30X35 |
30 |
35 |
23 |
11.5 |
5.75 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-30X40 |
30 |
40 |
25.6 |
11.5 |
10 |
M 4 |
1.7 |
|
GF-40X50 |
40 |
50 |
32.1 |
14.5 |
10 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-40X55 |
40 |
55 |
34.5 |
14.5 |
10 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-40X66 |
40 |
66 |
40 |
14.5 |
12.75 |
M 5 |
4 |
|
GF-55X49 |
55 |
49 |
32 |
16.1 |
13.5 |
M 6 |
8.4 |
|
GF-55X78 |
55 |
78 |
46.4 |
16.1 |
15.5 |
M 6 |
8.4 |
|
GF-65X80 |
65 |
80 |
48.5 |
17.3 |
18.1 |
M 8 |
10.5 |
|
GF-65X90 |
65 |
90 |
53.5 |
17.3 |
18.1 |
M 8 |
10.5 |
Product Parameters
Detailed Photos
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can Shaft Couplings Compensate for Angular, Parallel, and Axial Misalignments?
Yes, shaft couplings are designed to compensate for different types of misalignments between rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. They can handle the following types of misalignments:
- Angular Misalignment: This occurs when the shafts are not parallel and have an angle between them. Flexible couplings, such as elastomeric, beam, or Oldham couplings, can accommodate angular misalignments by allowing slight angular movement between the shafts while transmitting torque.
- Parallel Misalignment: This happens when the shafts are not collinear, resulting in axial displacement. Flexible couplings with lateral flexibility, like elastomeric or bellows couplings, can handle parallel misalignment by allowing limited lateral movement between the shafts.
- Radial Misalignment: Radial misalignment occurs when the shafts have lateral displacement but remain parallel. Flexible couplings, such as jaw or grid couplings, can absorb radial misalignment by permitting some lateral deflection while transmitting torque.
It is essential to note that while shaft couplings can compensate for misalignments to some extent, they do have their limits. The magnitude of misalignment they can handle depends on the type and design of the coupling. Exceeding the specified misalignment capabilities of a coupling can lead to premature wear, reduced efficiency, and possible coupling failure.
Therefore, when selecting a shaft coupling for an application, it is crucial to consider the expected misalignment and choose a coupling that can accommodate the anticipated misalignment range. Additionally, maintaining proper alignment through regular maintenance and periodic inspections is essential to ensure the coupling’s optimal performance and extend its service life.
“`
Explaining the Concept of Backlash and How It Affects Shaft Coupling Performance
Backlash is the angular movement or play between the mating components of a mechanical system when the direction of motion is reversed. In the context of shaft couplings, backlash refers to the free rotational movement between the connected shafts before the coupling transmits torque from one shaft to the other.
Backlash occurs in certain coupling designs that have features allowing relative movement between the coupling’s mating parts. Common coupling types that may exhibit some degree of backlash include elastomeric couplings (such as jaw couplings), gear couplings, and Oldham couplings.
How Backlash Affects Shaft Coupling Performance:
1. Loss of Precision: In applications requiring precise motion control, backlash can lead to inaccuracies and reduced positional accuracy. For example, in CNC machines or robotics, any rotational play due to backlash can result in positioning errors and decreased machining or movement precision.
2. Reversal Impact: When a reversing load is applied to a coupling, the presence of backlash can lead to a brief period of rotational play before the coupling re-engages, causing a momentary jolt or impact. This impact can lead to increased stress on the coupling and connected components, potentially reducing their lifespan.
3. Dynamic Response: Backlash can affect the dynamic response of the mechanical system. In systems requiring rapid acceleration or deceleration, the initial play due to backlash may create a delay in torque transmission, affecting the system’s responsiveness.
4. Noise and Vibration: Backlash can cause noise and vibration in the system, leading to increased wear and potential fatigue failure of components.
5. Misalignment Compensation: In some flexible coupling designs, a certain amount of backlash is intentionally incorporated to allow for misalignment compensation. While this is a beneficial feature, excessive backlash can compromise the coupling’s performance.
Minimizing Backlash:
Manufacturers often design couplings with specific features to minimize backlash. For instance, some gear couplings employ crowned gear teeth to reduce clearance, while elastomeric couplings may have preloaded elastomeric elements. Precision couplings like zero-backlash or torsionally rigid couplings are engineered to eliminate or minimize backlash for applications requiring high accuracy and responsiveness.
When selecting a coupling, it’s essential to consider the application’s specific requirements regarding precision, speed, reversing loads, and misalignment compensation, as these factors will determine the acceptable level of backlash for optimal performance.
“`
Types of Shaft Couplings and Their Applications in Various Industries
Shaft couplings come in various types, each designed to meet specific application requirements and address different types of misalignment. Here are some common types of shaft couplings and their applications in various industries:
1. Jaw Couplings:
Applications: Jaw couplings are widely used in power transmission applications, including conveyor systems, pumps, compressors, and industrial machinery. They are suitable for moderate torque requirements and provide good misalignment compensation.
2. Gear Couplings:
Applications: Gear couplings are used in heavy-duty industrial applications such as steel mills, paper mills, and mining equipment. They offer high torque capacity and can handle significant misalignments.
3. Disc Couplings:
Applications: Disc couplings are commonly used in precision machinery and automation systems, such as printing presses, machine tools, and robotics. They provide excellent torsional stiffness and are ideal for applications requiring precise positioning.
4. Grid Couplings:
Applications: Grid couplings are used in various industrial applications, including fans, pumps, and compressors. They offer high torque capacity and good shock absorption.
5. Oldham Couplings:
Applications: Oldham couplings are used in applications requiring high misalignment compensation, such as stepper motor drives and motion control systems.
6. Diaphragm Couplings:
Applications: Diaphragm couplings are used in critical applications that demand high torque transmission accuracy, such as aerospace, medical equipment, and semiconductor manufacturing.
7. Elastomeric Couplings:
Applications: Elastomeric couplings, like spider couplings, find applications in general industrial machinery, HVAC systems, and conveyor systems. They provide damping properties and flexibility to accommodate misalignments.
8. Torsionally Rigid Couplings:
Applications: Torsionally rigid couplings are used in applications requiring precise torque transmission, such as precision machining equipment and high-speed spindles.
9. Fluid Couplings:
Applications: Fluid couplings are used in heavy machinery and drivetrains, such as mining equipment, crushers, and marine propulsion systems. They provide smooth acceleration and dampening of shock loads.
10. Magnetic Couplings:
Applications: Magnetic couplings are used in applications where hermetic sealing is required, such as chemical processing, pumps, and mixers. They allow for torque transmission without direct physical contact.
The selection of the appropriate shaft coupling type depends on factors such as torque requirements, speed, misalignment, operating conditions, and the specific needs of the application. Using the right coupling ensures efficient power transmission, protects equipment from misalignment-related issues, and enhances the overall reliability and performance of industrial machinery and systems.
“`

editor by CX 2024-04-25
China Good quality Auto Parts Multi Sizes Spline Coupler Motor Connector Spiral Beam Shaft Couplings
Product Description
|
Product Name |
Auto Parts Multi Sizes Spline Coupler Motor Connector Spiral Beam Shaft Couplings |
|
Material |
Aluminum alloy |
|
Surface treatment |
Natural color anode |
|
Customized service |
Support light customization and logo customization |
|
Remarks |
The default engraving brand name and size of the product. If you need not engraving, please contact the customer service for comments |
| Packaging Details | Carton box with anti-static package,carton plus with wooden case. |
| Main Products | Shaft Parts, Timing Belt Pulley, Gears, CNC Machining Parts, Sheet Metal Fabrication |
| Certifications(2) | ISO9001:2015, IPMS |
| Applicable Industries | Building Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Food & Beverage Factory, Farms |
| Supply Ability | 100000 Piece/Pieces per Month |
| Dimension | oem provided |
| Surface finish | anodized |
| Lead Time | 25 days |
| Application | Furniture,cabinet |
| Custom | OEM and ODM services are welcome,we can make cutom LOGO and products according to customer’s requests. |
| Quality control Our | Finished product inspection,Warranty available |
| service | Swiss machining;deburring;lathe/turning;5 axis;micromachining |
| Color |
silver,gold,black,red,bulue,and according to the customer requests. |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Exploring the Use of Elastomeric Materials in Flexible Shaft Couplings
Elastomeric materials play a crucial role in the design and function of flexible shaft couplings. These materials, commonly known as elastomers, are rubber-like substances that exhibit high elasticity and flexibility. They are widely used in various types of flexible couplings due to their unique properties and benefits:
1. Damping and Vibration Absorption:
Elastomeric materials have excellent damping characteristics, meaning they can absorb and dissipate vibrations and shocks. This property is particularly useful in applications where vibration control is essential to protect sensitive equipment and improve overall system performance.
2. Misalignment Compensation:
Flexible shaft couplings with elastomeric elements can accommodate different types of misalignments, including angular, parallel, and radial misalignments. The elasticity of the material allows for limited movement between the shafts while still transmitting torque efficiently.
3. Torsional Flexibility:
Elastomers offer torsional flexibility, which allows them to twist and deform under torque loads. This feature helps to minimize torsional stresses and torsional backlash, making them suitable for applications requiring precise motion control.
4. Shock and Impact Resistance:
Due to their high resilience, elastomers can withstand sudden shocks and impacts without permanent deformation. This property makes them ideal for use in machinery subjected to varying loads or rapid changes in torque.
5. No Lubrication Requirement:
Elastomeric couplings are often maintenance-free because the elastomer material does not require additional lubrication. This reduces maintenance costs and simplifies the overall system upkeep.
6. Electric Isolation:
In certain applications, elastomeric materials can provide electrical isolation between the driving and driven components. This can help prevent the transmission of electrical currents or static charges through the coupling.
7. Corrosion Resistance:
Many elastomers used in couplings are resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for use in challenging environments where exposure to chemicals or moisture is a concern.
8. Easy Installation:
Elastomeric couplings are often designed for ease of installation and replacement. Their flexibility allows for simple and quick assembly onto the shafts without the need for special tools or complex procedures.
Given these advantages, elastomeric materials are popular choices for various flexible shaft couplings, including jaw couplings, tire couplings, and spider couplings. However, it is essential to select the right elastomer material based on the specific application requirements, such as temperature range, chemical compatibility, and torque capacity.
“`
How to Identify Signs of Wear or Failure in a Shaft Coupling
Regular inspection and monitoring are essential to identify signs of wear or potential failure in a shaft coupling. Detecting issues early can help prevent costly downtime and equipment damage. Here are common signs to look for:
1. Visible Damage:
Inspect the coupling for visible signs of damage, such as cracks, chips, or deformation. These can indicate mechanical stress or overload.
2. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:
Unusual noise or excessive vibration during operation may indicate misalignment, worn-out components, or a coupling nearing its failure point.
3. Increased Temperature:
If the coupling becomes noticeably hotter during operation than usual, it could be a sign of friction or misalignment issues.
4. Shaft Misalignment:
Check for misalignment between the shafts connected by the coupling. Misalignment can lead to increased stress on the coupling and its components.
5. Excessive Backlash:
If the coupling exhibits too much free play or rotational play before torque transmission, it might indicate wear or fatigue in the coupling’s components.
6. Lubrication Issues:
Inspect the coupling for lubrication leaks or insufficient lubrication, which can lead to increased friction and wear.
7. Elastomeric Element Deterioration:
If the coupling uses elastomeric elements (e.g., rubber or polyurethane), check for signs of deterioration, such as cracking, softening, or deformation.
8. Bolts and Fasteners:
Examine the bolts and fasteners connecting the coupling components. Loose or damaged bolts can lead to misalignment and coupling failure.
9. Age and Service Life:
Consider the age and service life of the coupling. If it has been in use for a long time or exceeds the manufacturer’s recommended service life, it may be more susceptible to wear and failure.
10. Abnormal Performance:
Monitor the overall performance of the connected equipment. Any abnormal behavior, such as reduced power transmission or erratic operation, could be indicative of coupling issues.
If any of these signs are observed, it’s crucial to take immediate action. Depending on the severity of the issue, this may involve replacing worn components, realigning the shafts, or replacing the entire coupling. Regular maintenance and periodic inspections are key to identifying these signs early and ensuring the coupling operates optimally and safely.
“`
What is a Shaft Coupling and Its Role in Mechanical Power Transmission?
A shaft coupling is a mechanical device used to connect two shafts together at their ends, allowing for the transmission of mechanical power from one shaft to another. It serves as an essential component in various machinery and industrial applications where rotational motion needs to be transmitted between two shafts that are not perfectly aligned or are separated by a distance.
The role of a shaft coupling in mechanical power transmission includes the following:
1. Power Transmission:
The primary function of a shaft coupling is to transmit power from a driving shaft to a driven shaft. When the driving shaft rotates, the coupling transfers the rotational motion to the driven shaft, enabling the driven equipment to perform its intended function.
2. Misalignment Compensation:
In real-world applications, it is often challenging to achieve perfect alignment between two shafts due to manufacturing tolerances or dynamic conditions. Shaft couplings are designed to accommodate different types of misalignment, such as angular, parallel, and axial misalignment, allowing the equipment to function smoothly even when the shafts are not perfectly aligned.
3. Vibration Damping:
Shaft couplings can help dampen vibrations and shocks caused by uneven loads or sudden changes in the operating conditions. This vibration damping feature protects the connected components from damage and contributes to the overall system’s reliability.
4. Overload Protection:
In some cases, a shaft coupling can act as a safety device by providing overload protection. When the connected machinery experiences excessive torque or shock loads, certain types of couplings can disengage or shear to prevent damage to the equipment.
5. Torque and Speed Conversion:
Shaft couplings can be designed to provide torque and speed conversion between the driving and driven shafts. This allows for adaptation to different operating conditions and varying torque requirements in the connected machinery.
6. Flexible Connection:
Shaft couplings with flexible elements, such as elastomeric inserts or flexible discs, provide a flexible connection that can absorb shocks and misalignments. This flexibility helps reduce stress on the connected equipment and extends its lifespan.
Overall, shaft couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, enabling the efficient transfer of rotational motion between shafts while accommodating misalignments and providing protection against overloads and vibrations. The selection of the appropriate coupling type and design depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the type of misalignment, torque capacity, and operating conditions.
“`

editor by CX 2024-04-16