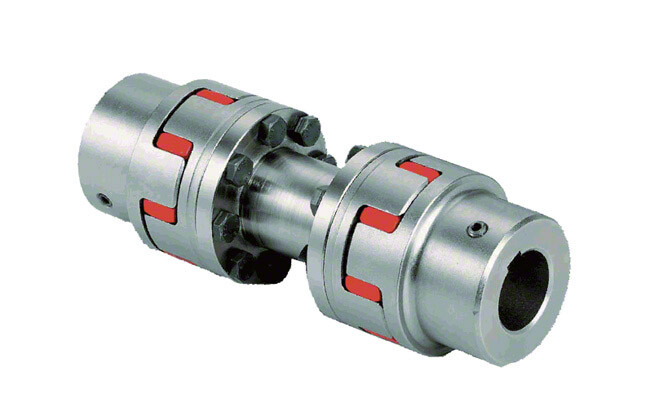
Product Description
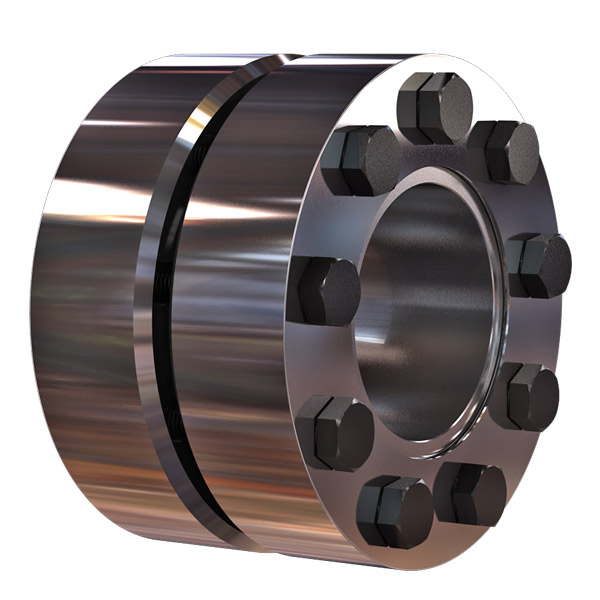
GNC-32×32 Rigid Shaft Coupling Rigid Clamping Coupling
GNC-32×32 Rigid Shaft Coupling Rigid Clamping Coupling
|
model parameter |
common bore diameter d1,d2 |
ΦD |
L |
F |
M |
tightening screw torque |
|
GNC-16×16 |
3,4,5,6,6.35,7,8 |
16 |
16 |
3.75 |
M2.5 |
1 |
|
GNC-16×24 |
3,4,5,6,6.35,7,8 |
16 |
24 |
3.75 |
M2.5 |
1 |
|
GNC-20×20 |
4,5,6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10 |
20 |
20 |
3.75 |
M2.5 |
1 |
|
GNC-20×30 |
4,5,6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10 |
20 |
30 |
3.75 |
M2.5 |
1 |
|
GNC-25×25 |
5,6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10,12 |
25 |
25 |
6 |
M3 |
1.5 |
|
GNC-25×36 |
5,6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10,12 |
25 |
36 |
6 |
M3 |
1.5 |
|
GNC-28.5×38 |
6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10,12,12.7,14 |
28.5 |
38 |
7.8 |
M4 |
2.5 |
|
GNC-32×32 |
6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10,12,12.7,14,15,16 |
32 |
32 |
7 |
M4 |
2.5 |
|
GNC-32×41 |
6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10,12,12.7,14,15,16 |
32 |
41 |
7.75 |
M4 |
2.5 |
|
GNC-40×44 |
8,9,9.525,10,11,12,12.7,14,15,15,17,18,19,20 |
40 |
44 |
10.5 |
M5 |
7 |
|
GNC-40×52 |
8,9,9.525,10,11,12,12.7,14,15,15,17,18,19,20 |
40 |
52 |
10.5 |
M5 |
7 |
|
GNC-50×55 |
10,11,12,12.7,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,24,25 |
50 |
55 |
13 |
M6 |
12 |
|
GNC-50×66 |
10,11,12,12.7,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,24,25 |
50 |
66 |
16 |
M6 |
12 |
|
GNC-63×71 |
10,11,12,12.7,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,24,25,28,30,32,35 |
63 |
71 |
16.5 |
M6 |
12 |
|
model parameter |
Rated torque(N.m) |
maximum speed (rpm) |
weight (g) |
|
GNC-16×16 |
5 |
1000 |
7 |
|
GNC-16×24 |
5 |
9400 |
13 |
|
GNC-20×20 |
10 |
7500 |
15 |
|
GNC-20×30 |
10 |
7500 |
25 |
|
GNC-25×25 |
12 |
6000 |
29 |
|
GNC-25×36 |
12 |
6000 |
43 |
|
GNC-28.5×38 |
14 |
5500 |
48 |
|
GNC-32×32 |
15 |
4700 |
55 |
|
GNC-32×41 |
15 |
4700 |
65 |
|
GNC-40×44 |
19 |
4000 |
123 |
|
GNC-40×52 |
19 |
4000 |
150 |
|
GNC-50×55 |
45 |
4000 |
240 |
|
GNC-50×66 |
45 |
4000 |
280 |
|
|
|
|
320 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Common Industries and Use Cases for Rigid Shaft Couplings
Rigid shaft couplings find applications in various industries where precise and torque-resistant shaft connections are required. Some of the common industries that use rigid shaft couplings include:
- Manufacturing: Rigid shaft couplings are widely used in manufacturing machinery, such as lathes, milling machines, and CNC equipment, to provide rigid and accurate power transmission.
- Robotics: Robots and robotic arms often use rigid shaft couplings to ensure precise motion and synchronization between motors and actuators.
- Aerospace: In aerospace applications, rigid couplings are used in aircraft engines, landing gear systems, and control surfaces.
- Automotive: Rigid couplings are utilized in automotive powertrains and drivetrains to transmit torque efficiently and withstand high loads.
- Marine: Marine propulsion systems and shipboard equipment often employ rigid shaft couplings for reliable torque transmission in challenging environments.
- Packaging: Packaging machinery relies on rigid couplings to achieve accurate and synchronized movements in filling, sealing, and labeling operations.
- Steel and Metal Processing: Rigid shaft couplings are essential in steel mills and metal processing equipment to handle heavy loads and maintain precision.
- Printing and Paper: Printing presses and paper handling machinery use rigid couplings to ensure precise registration and consistent operation.
- Mining and Construction: Mining equipment and construction machinery utilize rigid couplings for robust power transmission in harsh environments.
- Energy and Utilities: In power generation plants and utilities, rigid couplings are employed in pumps, compressors, and turbines.
Rigid shaft couplings are versatile and can be found in numerous other industries where precise and efficient power transmission is critical for smooth operation and high-performance machinery.

Can rigid shaft couplings be used for shafts with different rotational speeds and directions?
Rigid shaft couplings are typically designed for applications where the connected shafts have the same rotational speed and direction. They are not well-suited for scenarios involving significant speed differences or reverse rotation between shafts. The limitations arise from the coupling’s rigid construction, which does not allow for the compensation of speed differentials or changes in direction.
When shafts have different rotational speeds or need to rotate in opposite directions, it can result in uneven loading, increased wear, vibrations, and even coupling failure. Rigid couplings lack the flexibility required to accommodate the variations in speed and direction, which can lead to undesirable consequences in the system.
If your application involves shafts with varying speeds or reverse rotation, it’s recommended to explore flexible coupling options. Flexible couplings, such as gear couplings, elastomeric couplings, or universal joints, are designed to handle these situations by providing a degree of angular and radial flexibility. These couplings can help distribute the loads more evenly, reduce vibrations, and compensate for speed differences, ultimately contributing to smoother and more reliable operation.
It’s essential to accurately assess the requirements of your application and choose the appropriate coupling type based on the specific operational conditions. If there are varying speeds or reverse rotation involved, opting for flexible couplings designed for such scenarios will help ensure the longevity, efficiency, and performance of your machinery.
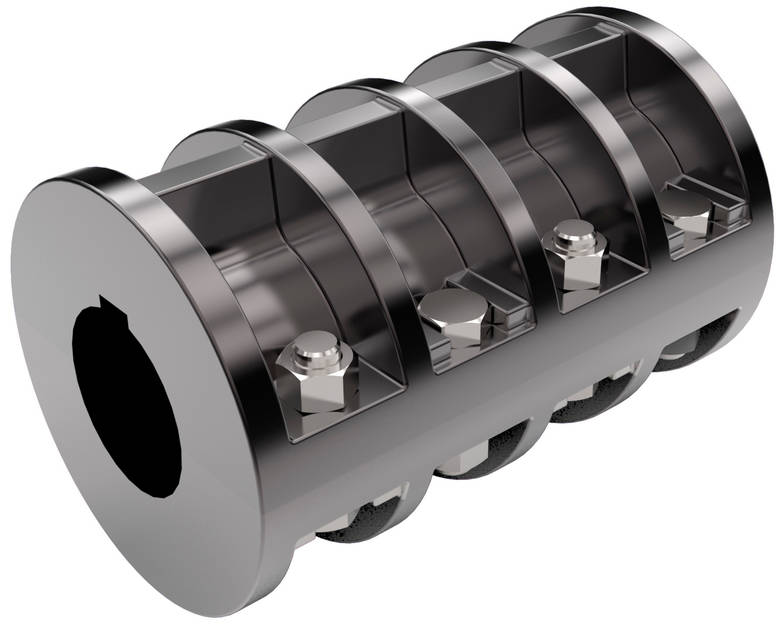

Are There Different Types of Rigid Shaft Couplings Available, and What Are Their Specific Applications?
Yes, there are different types of rigid shaft couplings available, each with its own specific applications. Some common types of rigid shaft couplings include:
- Sleeve Couplings: Sleeve couplings are simple and cost-effective couplings that connect two shafts together using a solid sleeve or tube. They are commonly used in applications with moderate torque requirements and where shaft alignment can be maintained with high precision.
- Clamp or Split Couplings: Clamp or split couplings consist of two halves that are clamped together around the shafts using screws or bolts. They are easy to install and suitable for applications where frequent maintenance or disassembly is required.
- Flanged Couplings: Flanged couplings have flanges on both ends that are bolted together. They are used in applications where shafts need to be rigidly connected and where some degree of axial movement is expected.
- Tapered Shaft Couplings: Tapered shaft couplings have tapered bores that fit tightly onto tapered shafts, creating a friction-based connection. They are often used in applications where precise alignment and torque transmission are essential.
- Keyed Shaft Couplings: Keyed shaft couplings use a key and keyway arrangement to connect the shafts securely. They are commonly used in heavy-duty applications where high torque transmission is required.
The choice of rigid shaft coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application. Factors such as torque transmission, shaft size, alignment precision, ease of installation, and maintenance needs play a crucial role in selecting the appropriate coupling type.
Rigid shaft couplings are widely used in various industries, including manufacturing, power generation, robotics, aerospace, and automotive. They are often employed in applications such as pumps, compressors, conveyors, and high-precision machinery.
It is essential to consider the specific demands of the application and consult with coupling manufacturers or experts to determine the most suitable rigid coupling type for optimal performance and reliability.


editor by CX 2024-04-03
China high quality CHINAMFG Customized Torsionally Rigid Coupling, Rigid Couplings, Sleeve Gear Shaft Coupling
Product Description
Densen customized torsionally rigid coupling,rigid couplings,sleeve gear shaft coupling
Product show
| Product Name | Densen customized gear sleeve coupling,steel sleeve coupling,shaft sleeve coupling |
| DN mm | 16-1040mm |
| Rated Torque | N·m |
| Max Allowalbe Speed | 460~4000RPM |
| Material | 45# Steel/Cast iron |
| Application | Widely used in metallurgy, mining, engineering and other fields. |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can Rigid Couplings Be Used in Both Horizontal and Vertical Shaft Arrangements?
Yes, rigid couplings can be used in both horizontal and vertical shaft arrangements. Rigid couplings are designed to provide a solid, non-flexible connection between two shafts, making them suitable for various types of shaft orientations.
Horizontal Shaft Arrangements: In horizontal shaft arrangements, the two shafts are positioned parallel to the ground or at a slight incline. Rigid couplings are commonly used in horizontal setups as they efficiently transmit torque and maintain precise alignment between the shafts. The horizontal orientation allows gravity to aid in keeping the coupling elements securely in place.
Vertical Shaft Arrangements: In vertical shaft arrangements, the two shafts are positioned vertically, with one shaft above the other. This type of setup is often found in applications such as pumps, compressors, and some gearboxes. Rigid couplings can also be used in vertical shaft arrangements, but additional considerations must be taken into account:
- Keyless Design: To accommodate the vertical orientation, some rigid couplings have a keyless design. Traditional keyed couplings may experience issues with keyway shear due to the force of gravity on the key, especially in overhung load situations.
- Set Screw Tightening: When installing rigid couplings in vertical shaft arrangements, set screws must be tightened securely to prevent any axial movement during operation. Locking compound can also be used to provide additional security.
- Thrust Load Considerations: Vertical shaft arrangements may generate thrust loads due to the weight of the equipment and components. Rigid couplings should be chosen or designed to handle these thrust loads to prevent axial displacement of the shafts.
It’s essential to select a rigid coupling that is suitable for the specific shaft orientation and operating conditions. Proper installation and alignment are critical for both horizontal and vertical shaft arrangements to ensure the rigid coupling’s optimal performance and reliability.

What Role Does a Rigid Coupling Play in Reducing Downtime and Maintenance Costs?
A rigid coupling can play a significant role in reducing downtime and maintenance costs in mechanical systems by providing a robust and reliable connection between two shafts. Here are the key factors that contribute to this:
1. Durability and Longevity: Rigid couplings are typically made from high-quality materials such as steel or stainless steel, which offer excellent durability and resistance to wear. As a result, they have a longer service life compared to some other types of couplings that may require frequent replacements due to wear and fatigue.
2. Elimination of Wear-Prone Components: Unlike flexible couplings that include moving parts or elements designed to accommodate misalignment, rigid couplings do not have any wear-prone components. This absence of moving parts means there are fewer components that can fail, reducing the need for regular maintenance and replacement.
3. Minimization of Misalignment-Related Issues: Rigid couplings require precise shaft alignment during installation. When installed correctly, they help minimize misalignment-related issues such as vibration, noise, and premature bearing failure. Proper alignment also reduces the risk of unexpected breakdowns and maintenance requirements.
4. Increased System Efficiency: The rigid connection provided by a rigid coupling ensures efficient power transmission between the two shafts. There is minimal power loss due to flexing or bending, leading to better overall system efficiency. This efficiency can result in reduced energy consumption and operating costs.
5. Low Maintenance Requirements: Rigid couplings generally require minimal maintenance compared to some other coupling types. Once properly installed and aligned, they can operate for extended periods without needing frequent inspection or adjustment.
6. Reduced Downtime: The robust and reliable nature of rigid couplings means that they are less likely to fail unexpectedly. This increased reliability helps reduce unscheduled downtime, allowing the mechanical system to operate smoothly and consistently.
7. Cost-Effective Solution: While rigid couplings may have a higher upfront cost than some other coupling types, their long-term durability and low maintenance requirements make them a cost-effective solution over the life cycle of the equipment.
In conclusion, a rigid coupling’s ability to provide a durable and dependable connection, along with its low maintenance requirements and efficient power transmission, contributes significantly to reducing downtime and maintenance costs in mechanical systems.

Materials Used in Manufacturing Rigid Couplings:
Rigid couplings are designed to provide a strong and durable connection between two shafts, and they are commonly made from a variety of materials to suit different applications. The choice of material depends on factors such as the application’s environment, load capacity, and cost considerations. Some common materials used in manufacturing rigid couplings include:
- 1. Steel: Steel is one of the most widely used materials for rigid couplings. It offers excellent strength, durability, and resistance to wear. Steel couplings are suitable for a wide range of applications, including industrial machinery, automotive systems, and power transmission.
- 2. Stainless Steel: Stainless steel couplings are used in applications where corrosion resistance is crucial. They are well-suited for environments with high humidity, moisture, or exposure to chemicals. Stainless steel couplings are commonly used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, marine, and outdoor applications.
- 3. Aluminum: Aluminum couplings are known for their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. They are often used in applications where weight reduction is essential, such as aerospace and automotive industries.
- 4. Brass: Brass couplings offer good corrosion resistance and are commonly used in plumbing and water-related applications.
- 5. Cast Iron: Cast iron couplings provide high strength and durability, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications and machinery.
- 6. Bronze: Bronze couplings are known for their excellent wear resistance and are often used in applications involving heavy loads and low speeds.
- 7. Plastics: Some rigid couplings are made from various plastics, such as nylon or Delrin. Plastic couplings are lightweight, non-conductive, and suitable for applications where electrical insulation is required.
It’s essential to consider the specific requirements of the application, including factors like load capacity, operating environment, and cost, when choosing the appropriate material for a rigid coupling. The right material selection ensures that the coupling can withstand the forces and conditions it will encounter, resulting in a reliable and long-lasting connection between the shafts.


editor by CX 2024-04-02
China manufacturer Aluminum Alloy Gfc-55X49 Type Shaft Coupler Rubber Flexible Coupling
Product Description
Aluminum Alloy GFC-55X49 Type Shaft Coupler Rubber Flexible Coupling
Aluminum Alloy GFC-55X49 Type Shaft Coupler Rubber Flexible Coupling
| model parameter | common bore diameter d1,d2 | ΦD | L | LF | LP | F | M | tightening screw torque (N.M) |
| GFC-14X22 | 3,4,5,6,6.35 | 14 | 22 | 14.3 | 6.6 | 5.0 | M2.5 | 1.0 |
| GFC-20×25 | 3,4,5,6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10 | 20 | 25 | 16.7 | 8.6 | 5.9 | M3 | 1.5 |
| GFC-20X30 | 3,4,5,6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10 | 20 | 30 | 19.25 | 8.6 | 5.9 | M3 | 1.5 |
| GFC-25X30 | 4,5,6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10,11,12 | 25 | 30 | 20.82 | 11.6 | 8.5 | M4 | 2.5 |
| GFC-25X34 | 4,5,6,6.35,7,8,9,9.525,10,11,12 | 25 | 34 | 22.82 | 11.6 | 8.5 | M4 | 2.5 |
| GFC-30×35 | 5,6,6.35,7,8,9,10,11,12,12.7,14,15,16 | 30 | 35 | 23 | 11.5 | 10 | M4 | 2.5 |
| GFC-30X40 | 5,6,6.35,7,8,9,10,11,12,12.7,14,15,16 | 30 | 40 | 25 | 11.5 | 10 | M4 | 2.5 |
| GFC-40X50 | 6,8,9,10,11,12,12.7,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,24 | 40 | 50 | 32.1 | 14.5 | 14 | M5 | 7 |
| GFC-40X55 | 6,8,9,10,11,12,12.7,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,24 | 40 | 55 | 34.5 | 14.5 | 14 | M5 | 7 |
| GFC-40X66 | 6,8,910,11,12,12.7,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,24 | 40 | 66 | 40 | 14.5 | 14 | M5 | 7 |
| GFC-55X49 | 10,11,12,12.7,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,24,25,28,30,32 | 55 | 49 | 32 | 16.1 | 13.5 | M6 | 12 |
| GFC-55X78 | 8,10,12,12.7,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,24,25,28,30,32 | 55 | 78 | 46.4 | 16.1 | 19 | M6 | 12 |
| GFC-65X80 | 14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,24,25,28,30,32,35,38,40 | 65 | 80 | 48.5 | 17.3 | 14 | M8 | 20 |
| GFC-65X90 | 14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,24,25,28,30,32,35,38,40 | 65 | 90 | 53.5 | 17.3 | 22.5 | M8 | 20 |
| GFC-80X114 | 19,20,22,24,25,28,30,32,35,38,40,42,45 | 80 | 114 | 68 | 22.5 | 16 | M8 | 20 |
| GFC-95X126 | 19,20,22,24,25,28,30,32,35,38,40,42,45,50,55 | 95 | 126 | 74.5 | 24 | 18 | M10 | 30 |
| model parameter | Rated torque (N.M)* |
allowable eccentricity (mm)* |
allowable deflection angle (°)* |
allowable axial deviation (mm)* |
maximum speed rpm |
static torsional stiffness (N.M/rad) |
moment of inertia (Kg.M2) |
Material of shaft sleeve | Material of shrapnel | surface treatment | weight (g) |
| GFC-14X22 | 5.0 | 0.1 | 1 | ±02 | 10000 | 50 | 1.0×10-6 | High strength aluminum alloy | Polyurethane imported from Germany | Anodizing treatment | 10 |
| GFC-20X25 | 5.0 | 0.1 | 1 | ±02 | 10000 | 50 | 1.0×10-6 | 15 | |||
| GFC-20X30 | 5.0 | 0.1 | 1 | ^02 | 10000 | 53 | 1.1×10-6 | 19 | |||
| GFC-25X30 | 10 | 0.1 | 1 | 10000 | 90 | 5.2X10-6 | 33 | ||||
| GFC-25X34 | 10 | 0.1 | 1 | £)2 | 10000 | 90 | 5.2×10-6 | 42 | |||
| GFC-30X35 | 12.5 | 0.1 | 1 | ±02 | 10000 | 123 | 6.2×10-6 | 50 | |||
| GFC-30×40 | 12.5 | 0.1 | 1 | 102 | 10000 | 123 | 6.2×10-6 | 60 | |||
| GFC-40X50 | 17 | 0.1 | 1 | 8000 | 1100 | 3.8×10-5 | 115 | ||||
| GFC-40X55 | 17 | 0.1 | 1 | ±02 | 8000 | 1100 | 3.8×10-5 | 127 | |||
| GFC-40X66 | 17 | 0.1 | 1 | 7000 | 1140 | 3.9×10-5 | 154 | ||||
| GFC-55X49 | 45 | 0.1 | 1 | ±02 | 6500 | 2350 | 1.6×10-3 | 241 | |||
| GFC-55X78 | 45 | 0.1 | 1 | 102 | 6000 | 2500 | 1.6×10-3 | 341 | |||
| GFC-65X80 | 108 | 0.1 | 1 | ±02 | 5500 | 4500 | 3.8×10-3 | 433 | |||
| GFC-65X90 | 108 | 0.1 | 1 | ±02 | 5500 | 4800 | 3.8×10-3 | 583 | |||
| GFC-80X114 | 145 | 0.1 | 1 | £)2 | 4500 | 5000 | 1.8×10-3 | 1650 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can Shaft Couplings Compensate for Angular, Parallel, and Axial Misalignments?
Yes, shaft couplings are designed to compensate for different types of misalignments between rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. They can handle the following types of misalignments:
- Angular Misalignment: This occurs when the shafts are not parallel and have an angle between them. Flexible couplings, such as elastomeric, beam, or Oldham couplings, can accommodate angular misalignments by allowing slight angular movement between the shafts while transmitting torque.
- Parallel Misalignment: This happens when the shafts are not collinear, resulting in axial displacement. Flexible couplings with lateral flexibility, like elastomeric or bellows couplings, can handle parallel misalignment by allowing limited lateral movement between the shafts.
- Radial Misalignment: Radial misalignment occurs when the shafts have lateral displacement but remain parallel. Flexible couplings, such as jaw or grid couplings, can absorb radial misalignment by permitting some lateral deflection while transmitting torque.
It is essential to note that while shaft couplings can compensate for misalignments to some extent, they do have their limits. The magnitude of misalignment they can handle depends on the type and design of the coupling. Exceeding the specified misalignment capabilities of a coupling can lead to premature wear, reduced efficiency, and possible coupling failure.
Therefore, when selecting a shaft coupling for an application, it is crucial to consider the expected misalignment and choose a coupling that can accommodate the anticipated misalignment range. Additionally, maintaining proper alignment through regular maintenance and periodic inspections is essential to ensure the coupling’s optimal performance and extend its service life.
“`
Comparing Shaft Couplings with Other Types of Couplings in Performance
Shaft couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, and their performance characteristics vary depending on the coupling type. Let’s compare shaft couplings with other common types of couplings:
1. Shaft Couplings:
Shaft couplings come in various designs, including flexible and rigid couplings. They are widely used in a broad range of applications due to their ability to transmit torque and accommodate misalignments between rotating shafts. Flexible shaft couplings, with elastomeric or metallic elements, offer good misalignment compensation and damping characteristics. Rigid couplings, on the other hand, provide precise torque transmission and are ideal for applications where shafts are well-aligned.
2. Gear Couplings:
Gear couplings are robust and designed for heavy-duty applications. They consist of two external gear hubs with internal gear teeth that mesh together. Gear couplings can handle high torque, high-speed, and angular misalignment. They are often used in demanding industries such as steel, mining, and paper manufacturing.
3. Grid Couplings:
Grid couplings feature a flexible grid element between the two halves of the coupling. They provide excellent shock absorption and misalignment compensation. Grid couplings are commonly used in pumps, compressors, and other industrial machinery.
4. Disc Couplings:
Disc couplings utilize flexible metallic discs to transmit torque and compensate for misalignment. They offer high torsional stiffness, making them suitable for applications requiring precise motion control, such as robotics and CNC machines.
5. Jaw Couplings:
Jaw couplings consist of two hubs with elastomeric spider inserts. They are easy to install, have good misalignment capabilities, and offer electrical isolation between shafts. Jaw couplings are widely used in light to medium-duty applications.
6. Oldham Couplings:
Oldham couplings have three discs—two outer discs with slots and a central disc with a tongue that fits into the slots. They provide excellent angular misalignment compensation while maintaining constant velocity between shafts. Oldham couplings are commonly used in printing machines and conveyors.
7. Beam Couplings:
Beam couplings are made from a single piece of flexible material with spiral cuts. They offer good misalignment compensation and torsional flexibility, making them suitable for precision equipment like encoders and servo motors.
The choice of coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application, including torque, speed, misalignment compensation, environmental conditions, and space limitations. Each coupling type has its strengths and limitations, and selecting the right coupling is crucial to ensure optimal performance and reliability in the mechanical system.
“`
Diagnosing and Fixing Common Issues with Shaft Couplings
Regular inspection and maintenance of shaft couplings are essential to detect and address common issues that may arise during operation. Here are steps to diagnose and fix some common coupling problems:
1. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:
If you notice unusual noise or excessive vibration during equipment operation, it may indicate misalignment, wear, or damage in the coupling. Check for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks or deformations, and inspect the coupling for proper alignment.
Diagnosis:
Use a vibration analysis tool to measure the vibration levels and identify the frequency of the abnormal vibrations. This can help pinpoint the source of the problem.
Fix:
If misalignment is the cause, adjust the coupling to achieve proper alignment between the shafts. Replace any damaged or worn coupling components, such as spiders or elastomeric inserts, as needed.
2. Excessive Heat:
Feeling excessive heat on the coupling during operation can indicate friction, improper lubrication, or overload conditions.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the coupling and surrounding components for signs of rubbing, lack of lubrication, or overloading.
Fix:
Ensure proper lubrication of the coupling, and check for any interference between the coupling and adjacent parts. Address any overloading issues by adjusting the equipment load or using a coupling with a higher torque capacity.
3. Shaft Movement:
If you observe axial or radial movement in the connected shafts, it may indicate wear or improper installation of the coupling.
Diagnosis:
Check the coupling’s set screws, keyways, or other fastening methods to ensure they are secure and not causing the shaft movement.
Fix:
If the coupling is worn or damaged, replace it with a new one. Ensure proper installation and use appropriate fastening methods to secure the coupling to the shafts.
4. Sheared Shear Pin:
In shear pin couplings, a sheared shear pin indicates overloading or shock loads that exceeded the coupling’s torque capacity.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the shear pin for damage or breakage.
Fix:
Replace the sheared shear pin with a new one of the correct specifications. Address any overloading issues or adjust the equipment to prevent future shearing.
5. Coupling Wear:
Regular wear is normal for couplings, but excessive wear may lead to decreased performance and increased misalignment.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the coupling components for signs of wear, such as worn elastomeric elements or damaged teeth.
Fix:
Replace the worn or damaged components with new ones of the appropriate specifications.
Remember, regular maintenance and periodic inspection are key to diagnosing issues early and preventing severe problems. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and replacement schedules to ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the shaft coupling.
“`

editor by CX 2024-04-02
China best Custom Coupler Connector Flexible Split Flange Rigid Motor Guide Drive Shaft Coupling
Product Description
| Certification | ISO9001:2018;SGS;TS16949 |
| Quality |
CNC machine, CNC Turning, CNC Milling, CNC center machine, auto lathe machine, Wire-cutting Machine CNC punching machines, CNC bending machines CNT stamping machine, CNC/auto lathe machine, Drilling machine, Hydraulic machine, Riveting machine, Tapping machine, welding machine, Film attaching machine, etc. |
| Materials |
Aluminum, Steel, SPCC, SGCC,SECC, SPTE, Stainless steel, Brass, Copper, Bronze, ABS, PC, PO, POM, Nylon, etc. |
| Surface finish |
Anodized, Oxide, Plating, Brushing, Polishing, Blackened, Powder coating, Sandblasting, Laser engraving Zn-plating, Ni-plating, Cr-plating, Tin-plating, copper-plating, the wreath oxygen resin spraying, the heat disposing, hot-dip galvanizing, black oxide coating, painting, powdering, color zinc-plated, blue-black zinc-plated, rust preventive oil, titanium alloy galvanized, silver plating, plastic, electroplating, anodizing, etc |
| Inspection Equipment |
CMM, Projection, Calipers, Micro caliper, Thread Micro caliper, Pin gauge, Caliper gauge, Pass meter, Pass meter, etc. |
| Drawing formation | PDF, CAD/DWG/DXF, IGS/STP etc. |
HangZhou CHINAMFG Industrial Co., Ltd. is a comprehensive factory that specialized in fasteners, CNC parts, stamping parts, machinery parts, and so on. Since the establishment of the company, we have passed ISO9001: 2018, SGS, TS16949.
Our factory covers an area of 5,000 square CHINAMFG and has 58 employees, including 5 R & D personnel and 5 quality inspection personnel.
Major areas of service include automotive, bicycle and motorcycle, industrial automation, agricultural equipment, digital electronics, medical equipment, and so on.
Looking CHINAMFG to your cooperation.
1. We have Specialized QC testers to check the products quality according to customers’ needs.
2. We have IQC to check the dimensions and surface of the incoming material.
3. We have PQC to inspect full-course during the processing.
4. We have FQC to inspect all the plating products from outsides and make the 100% inspection before the shipments.
FAQ:
Q1: Why choose ZheJiang n?
To provide our customers with first-class services in the supply of quality screws minimizing costs.
Q2: How is quality ensured?
All our processes strictly adhere to ISO9001:2018 procedures. We have strict quality control from producing to delivery. Our company had strong technology support, 80% of our colleagues are master or bachelor’s degree. We have cultivated a group of managers who are familiar with product quality , good at modern concept of management.
Q3: Can You Strictly Follow The Tolerance on The Drawing And Meet The High Precision?
Yes, we can, we can provide high precision parts and make the parts as your drawing.
Q4: How should I order and make payment?
By T/T, for samples 100% with the order; for production, 30% paid for deposit by T/T before production arrangement, the balance to be paid before shipment. negotiation accepted.
Q5: What’s your Delivery Time?
Standard parts: 7-20days
Non-standard parts: 15-25days
We will make the delivery as soon as possible with the guarantee quality
Q6:How to Custom-made (OEM/ODM)?
If you have a new product drawing or a sample, please send to us, and we can custom-made the as your required. We will also provide our professional advices of the products to make the design to be more realized & maximize the performance.
Q7:Which mode of transport would be better?
In general, the product are heavy, we advice to make delivery by sea, Also we respect your views of other transportation as well.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

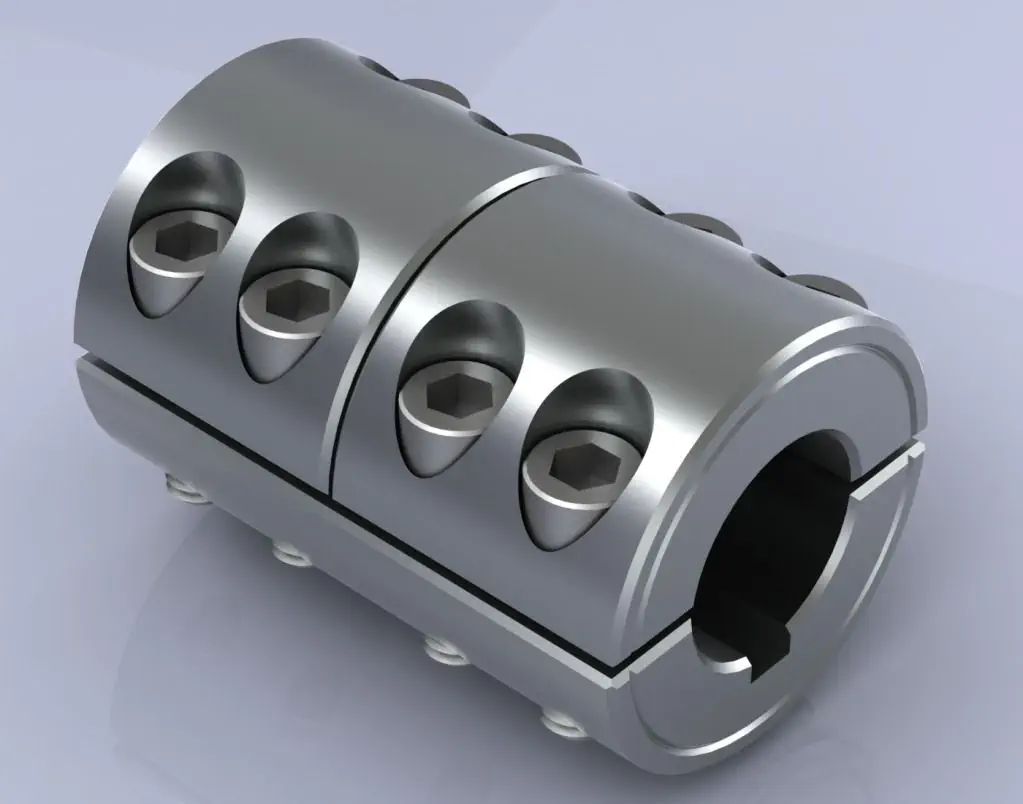
How Does a Rigid Coupling Protect Connected Equipment from Shock Loads and Vibrations?
Rigid couplings play a crucial role in protecting connected equipment from shock loads and vibrations by providing a direct and rigid connection between the shafts. The design and properties of rigid couplings contribute to their ability to mitigate the impact of shock loads and vibrations in the following ways:
– High Stiffness: Rigid couplings are constructed from materials with high stiffness, such as steel or aluminum. This high stiffness allows them to resist deformation and bending under load, ensuring that the coupling remains stable and maintains its shape. As a result, the shock loads and vibrations are not amplified or transferred to the connected equipment.
– Immediate Torque Transmission: Rigid couplings provide immediate torque transmission between the shafts without any backlash or play. When the connected machinery experiences a sudden shock load, the rigid coupling effectively transfers the torque to the other side of the coupling without delay. This rapid and precise torque transfer prevents the shock load from causing misalignment or damaging the equipment.
– Elimination of Damping: Unlike flexible couplings, which can dampen vibrations to some extent, rigid couplings do not have any damping properties. While damping can be beneficial in certain applications, it can also allow vibrations to persist, potentially affecting the performance and reliability of the connected equipment. Rigid couplings do not introduce any additional damping, ensuring that the vibrations are not prolonged.
– Stable Connection: Rigid couplings create a stable and unyielding connection between the shafts, limiting any relative movement. This stability prevents the propagation of vibrations from one shaft to another, reducing the potential for resonance and vibration amplification.
– Minimal Maintenance: Rigid couplings require minimal maintenance due to their simple and durable design. Unlike flexible couplings that may have wear-prone elements, rigid couplings do not have parts that need regular replacement. This reliability and low maintenance contribute to their ability to provide continuous protection against shock loads and vibrations.
In applications where shock loads and vibrations are prevalent, using a rigid coupling can help protect critical machinery and components from damage and premature failure. By providing a rigid and immediate torque transmission, rigid couplings effectively isolate the connected equipment from the harmful effects of shock loads and vibrations, ensuring smooth operation and enhanced reliability.

Impact of Rigid Coupling on the Overall Reliability of Connected Equipment
A rigid coupling plays a crucial role in enhancing the overall reliability of connected equipment in mechanical systems. Here’s how it positively impacts reliability:
1. Power Transmission Efficiency: Rigid couplings provide a direct and efficient connection between the shafts of the connected equipment. With no flexible elements, there is minimal power loss, ensuring efficient power transmission from one shaft to another.
2. Elimination of Backlash: Rigid couplings have zero backlash, which is crucial in precision applications. Backlash, which is the play or clearance between connected components, can cause inaccuracies in motion control systems. With a rigid coupling, any movement is directly transferred, maintaining precise positioning.
3. Zero-Maintenance Option: Some rigid couplings are designed to be maintenance-free. They do not require lubrication or periodic adjustments, reducing downtime and ensuring continuous operation.
4. High Torque Transmission: Rigid couplings can handle high torque loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Their robust construction ensures reliable torque transmission without failure or slippage.
5. Resistant to Misalignment: While rigid couplings offer no flexibility, they are excellent at handling axial misalignment and angular misalignment, provided it falls within their design limits. This ability to tolerate some misalignment enhances reliability and reduces the risk of component damage.
6. Vibration Damping: The stiffness of rigid couplings aids in damping vibrations generated during operation. By minimizing vibrations, the coupling helps protect connected equipment from excessive stress and fatigue failure.
7. Increased System Stiffness: Rigid couplings contribute to the overall stiffness of the mechanical system. This stiffness improves the dynamic response of the system and reduces the likelihood of resonance, leading to more reliable operation.
8. Simple and Compact Design: Rigid couplings have a straightforward and compact design, which reduces the chances of component failure or wear. Their simplicity makes them easy to install and maintain, further enhancing system reliability.
9. Suitable for High-Speed Applications: Rigid couplings are well-suited for high-speed applications due to their ability to maintain accurate shaft alignment and transmit torque efficiently.
10. Compatibility with Various Industries: Rigid couplings find applications in a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and more. Their versatility and reliability make them a popular choice in demanding industrial environments.
Overall, the use of a properly selected and installed rigid coupling enhances the reliability of connected equipment by providing a robust and efficient connection between shafts. It ensures precise power transmission, reduced maintenance requirements, and improved system performance, leading to increased overall reliability and uptime of the mechanical system.

Types of Rigid Coupling Designs:
There are several types of rigid coupling designs available, each designed to meet specific application requirements. Here are some common types of rigid couplings:
- 1. Sleeve Couplings: Sleeve couplings are the simplest type of rigid couplings. They consist of a cylindrical sleeve with a bore in the center that fits over the shaft ends. The coupling is secured in place using setscrews or keyways. Sleeve couplings provide a solid and rigid connection between shafts and are easy to install and remove.
- 2. Clamp or Split Couplings: Clamp couplings, also known as split couplings, are designed with two halves that fit around the shafts and are fastened together with bolts or screws. The split design allows for easy installation and removal without the need to disassemble other components in the system. These couplings are ideal for applications where the shafts cannot be easily moved.
- 3. Flanged Couplings: Flanged couplings have flanges on each end that are bolted together to form a rigid connection. The flanges add stability and strength to the coupling, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. They are commonly used in industrial machinery and equipment.
- 4. Tapered Couplings: Tapered couplings have a tapered inner diameter that matches the taper of the shaft ends. When the coupling is tightened, it creates a frictional fit between the coupling and the shafts, providing a rigid connection. These couplings are often used in applications where high torque transmission is required.
- 5. Marine or Clampshell Couplings: Marine couplings, also known as clampshell couplings, consist of two halves that encase the shaft ends and are bolted together. These couplings are commonly used in marine applications, such as propeller shafts in boats and ships.
- 6. Diaphragm Couplings: Diaphragm couplings are a type of rigid coupling that provides some flexibility to accommodate misalignment while maintaining a nearly torsionally rigid connection. They consist of thin metal diaphragms that transmit torque while compensating for minor shaft misalignments.
The choice of rigid coupling design depends on factors such as shaft size, torque requirements, ease of installation, and the level of misalignment that needs to be accommodated. It is essential to select the appropriate coupling design based on the specific needs of the application to ensure optimal performance and reliability.


editor by CX 2024-04-02
China supplier Original Excavator Parts Coupling CF-a Series Rubber Flexible Torsionally Steel Universal Shaft Coupling for Centaflex
Product Description
Original Excavator Parts Coupling CF-a Series Rubber Flexible Torsionally Steel Universal Shaft Coupling for Centafle
Product Display:
| Model | Outer Diameter(mm) | Inner Diameter(mm) | Hight(mm) | Diameter from Hole to Hole(mm) | Weight(kg) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4A/4AS | 103 | 53 | 28 | 68 | 0.18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8A/8AS | 134 | 71 | 32 | 88 | 0.26 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16A/16AS | 160 | 80 | 41 | 110 | 0.54 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22A/22AS | 165 | 86 | 41 | 128 | 0.66 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25A/25AS | 183 | 102 | 46 | 123 | 0.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28A/AS | 0.88 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30A/30AS | 213 | 117 | 57 | 145 | 1.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 50A/50AS | 220 | 123 | 57 | 165 | 1.48 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 80A/80As | 225 | 120 | 65 | 167 | 1.92 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 90A/90As | 278 | 148 | 70 | 190 | 3.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 140A/140AS | 285 | 151 | 71 | 215 | 3.42 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 250A/250AS | 6.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 284B | 6.34 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4, 4655134, EX3, ZAX460MTH, ZAX480MTH, 4636444, ZX470-3, EX470, ZAX470, ZAX450-3, ZAX450-3F, ZAX5, Atlas Copco,,
AC 385, AC 396, AC415, AC416, AC 455, AC485, AC 486, AC86, AC836, AC976, AC 6-712, 4DNV98 Chinese Brand Excavators: LGK: 6085, 200 CLG 60, 205, 220, 906, 907, 908, 920, 925, 936, CLG906C, CLG922LG YC50-8, YC60-8, YC60-8, YC135-8, YC230, YC230-8, YC230LC-8, YC360, YC85, YC50, YC85-7, YC60-7, YC135 SW50, 60, 70, 150 FR85-7, FR65, FR80, FR150-7, ZL 60, 205, 230, 360 SY55, SY60, SY215, SY230, SY210, SY220, SY310 /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Can Shaft Couplings Compensate for Angular, Parallel, and Axial Misalignments?Yes, shaft couplings are designed to compensate for different types of misalignments between rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. They can handle the following types of misalignments:
It is essential to note that while shaft couplings can compensate for misalignments to some extent, they do have their limits. The magnitude of misalignment they can handle depends on the type and design of the coupling. Exceeding the specified misalignment capabilities of a coupling can lead to premature wear, reduced efficiency, and possible coupling failure. Therefore, when selecting a shaft coupling for an application, it is crucial to consider the expected misalignment and choose a coupling that can accommodate the anticipated misalignment range. Additionally, maintaining proper alignment through regular maintenance and periodic inspections is essential to ensure the coupling’s optimal performance and extend its service life. “` Explaining the Concept of Backlash and How It Affects Shaft Coupling PerformanceBacklash is the angular movement or play between the mating components of a mechanical system when the direction of motion is reversed. In the context of shaft couplings, backlash refers to the free rotational movement between the connected shafts before the coupling transmits torque from one shaft to the other. Backlash occurs in certain coupling designs that have features allowing relative movement between the coupling’s mating parts. Common coupling types that may exhibit some degree of backlash include elastomeric couplings (such as jaw couplings), gear couplings, and Oldham couplings. How Backlash Affects Shaft Coupling Performance:1. Loss of Precision: In applications requiring precise motion control, backlash can lead to inaccuracies and reduced positional accuracy. For example, in CNC machines or robotics, any rotational play due to backlash can result in positioning errors and decreased machining or movement precision. 2. Reversal Impact: When a reversing load is applied to a coupling, the presence of backlash can lead to a brief period of rotational play before the coupling re-engages, causing a momentary jolt or impact. This impact can lead to increased stress on the coupling and connected components, potentially reducing their lifespan. 3. Dynamic Response: Backlash can affect the dynamic response of the mechanical system. In systems requiring rapid acceleration or deceleration, the initial play due to backlash may create a delay in torque transmission, affecting the system’s responsiveness. 4. Noise and Vibration: Backlash can cause noise and vibration in the system, leading to increased wear and potential fatigue failure of components. 5. Misalignment Compensation: In some flexible coupling designs, a certain amount of backlash is intentionally incorporated to allow for misalignment compensation. While this is a beneficial feature, excessive backlash can compromise the coupling’s performance. Minimizing Backlash:Manufacturers often design couplings with specific features to minimize backlash. For instance, some gear couplings employ crowned gear teeth to reduce clearance, while elastomeric couplings may have preloaded elastomeric elements. Precision couplings like zero-backlash or torsionally rigid couplings are engineered to eliminate or minimize backlash for applications requiring high accuracy and responsiveness. When selecting a coupling, it’s essential to consider the application’s specific requirements regarding precision, speed, reversing loads, and misalignment compensation, as these factors will determine the acceptable level of backlash for optimal performance. “` Can a Damaged Shaft Coupling Lead to Equipment Failure and Downtime?Yes, a damaged shaft coupling can lead to equipment failure and downtime in mechanical power transmission systems. Shaft couplings play a critical role in connecting rotating shafts and transmitting power between them. When a coupling becomes damaged or fails to function properly, several negative consequences can arise: 1. Misalignment Issues:A damaged coupling may no longer be able to compensate for misalignments between the connected shafts. Misalignment can cause excessive vibration, increased wear, and premature failure of bearings and other connected components. Over time, these issues can lead to equipment breakdown and unplanned downtime. 2. Vibration and Shock Loads:Without the damping properties of a functional coupling, vibrations and shock loads from the driven equipment can transmit directly to the driving shaft and other parts of the system. Excessive vibrations can lead to fatigue failure, cracking, and damage to the equipment, resulting in reduced operational efficiency and increased downtime. 3. Overloading and Torque Transmission:A damaged coupling may not effectively transmit the required torque between the driving and driven shafts. In applications where the coupling is a safety device (e.g., shear pin couplings), failure to disengage during overloading situations can lead to equipment overload and damage. 4. Increased Wear and Tear:A damaged coupling can lead to increased wear on other parts of the system. Components such as bearings, seals, and gears may experience higher stress and wear, reducing their lifespan and increasing the likelihood of breakdowns. 5. Reduced System Reliability:A functional shaft coupling contributes to the overall reliability of the mechanical system. A damaged coupling compromises this reliability, making the system more prone to failures and unplanned maintenance. 6. Downtime and Production Loss:When a shaft coupling fails, it often results in unscheduled downtime for repairs or replacement. Downtime can be costly for industries that rely on continuous production processes and can lead to production losses and missed delivery deadlines. 7. Safety Hazards:In certain applications, such as heavy machinery or industrial equipment, a damaged coupling can create safety hazards for workers and surrounding equipment. Sudden failures or uncontrolled movements may pose risks to personnel and property. Regular inspection, maintenance, and prompt replacement of damaged shaft couplings are essential to prevent equipment failure, minimize downtime, and ensure safe and efficient operation of mechanical systems. It is crucial to address any signs of coupling wear or damage immediately to avoid potential catastrophic failures and costly disruptions to operations. “` China Professional Customized Steel Rigid Plum-Shaped Positioning Motor Shaft CouplingProduct Description
How do We Work with Our Clients 2. For a start-up company owner or green hand for engineering: just send an idea that you want to try, you don’t even need to know what casting is; 3. Our sales will reply you within 24 hours to confirm further details and give the estimated quote time; 4. Our engineering team will evaluate your inquiry and provide our offer within next 1~3 working days. 5. We can arrange a technical communication meeting with you and our engineers together anytime if required.
The Advantage of Powder Metallurgy Process 1. Cost effective 2. Complex shapes 3. High precision 4. Self-lubrication 5. Green technology FAQ Q2: How to guarantee the high quality? Q3: How long will you give me the reply? Q4. How about your delivery time? Q5. Can you produce according to the samples or drawings? Q6: How about tooling Charge? Q7: What is your sample policy? Q8: How do you make our business long-term and good relationship?
How to Properly Install a Rigid Shaft Coupling for Optimal Performance and ReliabilityProper installation of a rigid shaft coupling is essential to ensure optimal performance and reliability in mechanical systems. Here are the steps to follow for a successful installation:
By following these installation steps and best practices, you can ensure that the rigid shaft coupling operates optimally, providing reliable torque transmission and contributing to the overall efficiency and longevity of the mechanical system.
Are there any safety considerations when using rigid shaft couplings in critical applications?Yes, when using rigid shaft couplings in critical applications, several safety considerations should be taken into account:
For critical applications, it’s recommended to work closely with experienced engineers, perform thorough risk assessments, and follow industry standards and best practices to ensure the safe and reliable use of rigid shaft couplings.
How Rigid Shaft Couplings Ensure Precise and Torque-Resistant Shaft ConnectionsRigid shaft couplings are designed to provide a solid and inflexible connection between two shafts, ensuring precise alignment and efficient torque transmission. The key features that enable rigid couplings to achieve this include:
By combining these design elements, rigid shaft couplings ensure that the connected shafts remain in perfect alignment during operation. This precise alignment reduces the risk of misalignment-related issues such as vibrations, premature wear, and decreased efficiency. Additionally, the rigid nature of these couplings allows them to transmit torque without any backlash, providing immediate and accurate responsiveness to changes in torque and rotational direction. Overall, rigid shaft couplings are an excellent choice for applications that demand precise shaft connections and reliable torque transmission. However, it’s essential to consider factors such as shaft alignment, load capacity, and environmental conditions when selecting the appropriate coupling for a specific application. “` China Professional Sintered Alloy Iron/Copper-Iron CNC Machinery Auto Car Motorcycle Electrical Tools Textile Engine Gearbox Transmission Reducer Flexible Shaft Jaw CouplingProduct Description
How do We Work with Our Clients 2. For a start-up company owner or green hand for engineering: just send an idea that you want to try, you don’t even need to know what casting is; 3. Our sales will reply you within 24 hours to confirm further details and give the estimated quote time; 4. Our engineering team will evaluate your inquiry and provide our offer within next 1~3 working days. 5. We can arrange a technical communication meeting with you and our engineers together anytime if required.
The Advantage of Powder Metallurgy Process 1. Cost effective 2. Complex shapes 3. High precision 4. Self-lubrication 5. Green technology FAQ Q2: How to guarantee the high quality? Q3: How long will you give me the reply? Q4. How about your delivery time? Q5. Can you produce according to the samples or drawings? Q6: How about tooling Charge? Q7: What is your sample policy? Q8: How do you make our business long-term and good relationship?
How to Select the Right Shaft Coupling for Specific Torque and Speed RequirementsSelecting the appropriate shaft coupling involves considering the specific torque and speed requirements of the application. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the right coupling: 1. Determine Torque and Speed:Identify the torque and speed requirements of the application. Torque is the rotational force required to transmit power between the shafts, usually measured in Nm (Newton-meters) or lb-ft (pound-feet). Speed refers to the rotational speed of the shafts, typically measured in RPM (revolutions per minute). 2. Calculate Torque Capacity:Check the torque capacity of various shaft couplings. Manufacturers provide torque ratings for each coupling type and size. Ensure that the selected coupling has a torque capacity that exceeds the application’s torque requirements. 3. Consider Misalignment:If the application involves significant shaft misalignment due to thermal expansion, vibration, or other factors, consider flexible couplings with good misalignment compensation capabilities. Elastomeric or beam couplings are popular choices for such applications. 4. Assess Operating Speed:For high-speed applications, choose couplings with high rotational speed ratings to avoid resonance issues and potential coupling failure. High-speed couplings may have specialized designs, such as disk or diaphragm couplings. 5. Evaluate Environmental Conditions:If the coupling will operate in harsh environments with exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures, select couplings made from corrosion-resistant materials or with protective coatings. 6. Check Torsional Stiffness:In applications requiring precision motion control, consider couplings with high torsional stiffness to minimize torsional backlash and maintain accurate positioning. Bellows or Oldham couplings are examples of couplings with low torsional backlash. 7. Size and Space Constraints:Ensure that the selected coupling fits within the available space and aligns with the shaft dimensions. Be mindful of any installation limitations, especially in confined spaces or applications with limited radial clearance. 8. Consult Manufacturer’s Data:Refer to the manufacturer’s catalogs and technical data sheets for detailed information on each coupling’s torque and speed ratings, misalignment capabilities, materials, and other relevant specifications. 9. Consider Cost and Maintenance:Compare the costs and maintenance requirements of different couplings. While some couplings may have higher upfront costs, they could offer longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in the long run. By following these steps and considering the specific torque and speed requirements of your application, you can select the right shaft coupling that will ensure efficient power transmission and reliable performance for your mechanical system. “` Do Shaft Couplings Require Regular Maintenance, and if so, What Does it Involve?Yes, shaft couplings do require regular maintenance to ensure their optimal performance, extend their service life, and prevent unexpected failures. The maintenance frequency may vary based on factors such as the coupling type, application, operating conditions, and the manufacturer’s recommendations. Here’s what regular maintenance for shaft couplings typically involves: 1. Visual Inspection:Regularly inspect the coupling for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Check for cracks, corrosion, and worn-out elastomeric elements (if applicable). Look for any abnormal movement or rubbing between the coupling components during operation. 2. Lubrication:If the shaft coupling requires lubrication, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the appropriate lubricant type and frequency. Lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and noise in the coupling. 3. Alignment Check:Monitor shaft alignment periodically. Misalignment can lead to premature coupling failure and damage to connected equipment. Make adjustments as needed to keep the shafts properly aligned. 4. Torque Check:For bolted couplings, periodically check the torque on the bolts to ensure they remain securely fastened. Loose bolts can lead to misalignment and reduce coupling performance. 5. Replace Worn Components:If any coupling components show signs of wear or damage beyond acceptable limits, replace them promptly with genuine replacement parts from the manufacturer. 6. Environmental Considerations:In harsh environments with exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures, take additional measures to protect the coupling, such as applying corrosion-resistant coatings or using special materials. 7. Monitoring Coupling Performance:Implement a monitoring system to track coupling performance and detect any changes or abnormalities early on. This could include temperature monitoring, vibration analysis, or other condition monitoring techniques. 8. Professional Inspection:Periodically have the coupling and connected machinery inspected by qualified professionals to identify any potential issues that may not be apparent during regular inspections. By adhering to a regular maintenance schedule and taking proactive measures to address potential issues, you can ensure that your shaft couplings operate reliably and efficiently throughout their service life, minimizing downtime and improving overall system performance. “` What is a Shaft Coupling and Its Role in Mechanical Power Transmission?A shaft coupling is a mechanical device used to connect two shafts together at their ends, allowing for the transmission of mechanical power from one shaft to another. It serves as an essential component in various machinery and industrial applications where rotational motion needs to be transmitted between two shafts that are not perfectly aligned or are separated by a distance. The role of a shaft coupling in mechanical power transmission includes the following: 1. Power Transmission:The primary function of a shaft coupling is to transmit power from a driving shaft to a driven shaft. When the driving shaft rotates, the coupling transfers the rotational motion to the driven shaft, enabling the driven equipment to perform its intended function. 2. Misalignment Compensation:In real-world applications, it is often challenging to achieve perfect alignment between two shafts due to manufacturing tolerances or dynamic conditions. Shaft couplings are designed to accommodate different types of misalignment, such as angular, parallel, and axial misalignment, allowing the equipment to function smoothly even when the shafts are not perfectly aligned. 3. Vibration Damping:Shaft couplings can help dampen vibrations and shocks caused by uneven loads or sudden changes in the operating conditions. This vibration damping feature protects the connected components from damage and contributes to the overall system’s reliability. 4. Overload Protection:In some cases, a shaft coupling can act as a safety device by providing overload protection. When the connected machinery experiences excessive torque or shock loads, certain types of couplings can disengage or shear to prevent damage to the equipment. 5. Torque and Speed Conversion:Shaft couplings can be designed to provide torque and speed conversion between the driving and driven shafts. This allows for adaptation to different operating conditions and varying torque requirements in the connected machinery. 6. Flexible Connection:Shaft couplings with flexible elements, such as elastomeric inserts or flexible discs, provide a flexible connection that can absorb shocks and misalignments. This flexibility helps reduce stress on the connected equipment and extends its lifespan. Overall, shaft couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, enabling the efficient transfer of rotational motion between shafts while accommodating misalignments and providing protection against overloads and vibrations. The selection of the appropriate coupling type and design depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the type of misalignment, torque capacity, and operating conditions. “` China supplier Gr-55X57 Aluminum Alloy Gr Rigid Shaft Coupling Bellows Setscrew CouplingProduct Description
GR-55×57 Aluminum Alloy GR Rigid Shaft Coupling Bellows Setscrew Coupling Description of GR-55×57 Aluminum Alloy GR Rigid Shaft Coupling Bellows Setscrew Coupling
Catalogue of GR-55×57 Aluminum Alloy GR Rigid Shaft Coupling Bellows Setscrew Coupling
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Common Industries and Use Cases for Rigid Shaft CouplingsRigid shaft couplings find applications in various industries where precise and torque-resistant shaft connections are required. Some of the common industries that use rigid shaft couplings include:
Rigid shaft couplings are versatile and can be found in numerous other industries where precise and efficient power transmission is critical for smooth operation and high-performance machinery.
What are the maintenance requirements for rigid shaft couplings to extend their lifespan?Rigid shaft couplings are mechanical components used to connect two shafts and transmit torque between them. While rigid couplings are known for their durability and minimal maintenance needs, proper care and maintenance can further extend their lifespan and ensure optimal performance. Here are key maintenance considerations:
Proper maintenance practices not only extend the lifespan of rigid shaft couplings but also contribute to the overall reliability and efficiency of the connected machinery. Regular inspections and maintenance can help identify potential issues early, preventing costly downtime and repairs. It’s important to note that maintenance requirements can vary based on the specific design and material of the rigid coupling. Consulting the manufacturer’s documentation and seeking professional advice can help establish a suitable maintenance schedule tailored to the coupling’s characteristics and the application’s demands.
What is a Rigid Shaft Coupling and How Does It Work in Mechanical Systems?A rigid shaft coupling is a type of coupling used to connect two shafts together in a mechanical system. As the name suggests, it is designed to provide a rigid and solid connection between the shafts, without any flexibility or misalignment compensation. The primary function of a rigid shaft coupling is to transmit torque from one shaft to another efficiently and with minimal backlash. It achieves this by directly connecting the two shafts using a rigid mechanical interface. Rigid shaft couplings typically consist of two halves with flanges that are bolted or clamped together around the shaft ends. The flanges are precision machined to ensure accurate alignment of the shafts. Some common types of rigid shaft couplings include:
Rigid shaft couplings are commonly used in applications where precise alignment is critical, such as in high-speed machinery, precision instruments, and power transmission systems. Since they do not have any flexibility, they are best suited for applications where shaft misalignment is minimal or can be controlled through accurate alignment during installation. One of the main advantages of rigid shaft couplings is their ability to provide a direct and efficient transfer of torque, making them suitable for high-torque and high-speed applications. Additionally, their simple design and solid connection make them easy to install and maintain. However, it’s essential to ensure proper alignment during installation to prevent premature wear and stress on the shafts and other components. In cases where misalignment is expected or unavoidable, flexible couplings like beam couplings, bellows couplings, or jaw couplings are more appropriate, as they can compensate for small misalignments and provide some degree of shock absorption.
China high quality Sintered Alloy Iron/Copper-Iron CNC Machinery Auto Car Motorcycle Electrical Tools Textile Engine Gearbox Transmission Reducer Flexible Shaft Jaw CouplingProduct Description
How do We Work with Our Clients 2. For a start-up company owner or green hand for engineering: just send an idea that you want to try, you don’t even need to know what casting is; 3. Our sales will reply you within 24 hours to confirm further details and give the estimated quote time; 4. Our engineering team will evaluate your inquiry and provide our offer within next 1~3 working days. 5. We can arrange a technical communication meeting with you and our engineers together anytime if required.
The Advantage of Powder Metallurgy Process 1. Cost effective 2. Complex shapes 3. High precision 4. Self-lubrication 5. Green technology FAQ Q2: How to guarantee the high quality? Q3: How long will you give me the reply? Q4. How about your delivery time? Q5. Can you produce according to the samples or drawings? Q6: How about tooling Charge? Q7: What is your sample policy? Q8: How do you make our business long-term and good relationship?
Is It Possible to Replace a Shaft Coupling Without Professional Assistance?Yes, it is possible to replace a shaft coupling without professional assistance, especially if you have some mechanical knowledge and the necessary tools. However, the ease of replacement can vary depending on the type of coupling and the complexity of the equipment. Here are some general steps to guide you through the process: 1. Safety First:Before starting any work, ensure that the equipment is turned off and disconnected from the power source. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to protect yourself from potential hazards. 2. Assess the Coupling Type:Different types of couplings may have specific installation and removal methods. Identify the type of coupling you need to replace, and consult the manufacturer’s documentation or online resources for guidance. 3. Gather Tools and Materials:Collect the necessary tools, such as wrenches, sockets, and a puller (if required), to safely remove the old coupling. Have the new coupling ready for installation, ensuring it matches the specifications of the old one. 4. Disassembly:If your coupling is a split or clamp-style coupling, you may be able to replace it without fully disassembling the connected equipment. Otherwise, you may need to remove other components to access the coupling. 5. Remove Fasteners:Loosen and remove any fasteners, such as set screws, that secure the old coupling to the shafts. Take care not to damage the shafts during this process. 6. Extraction:If the old coupling is tightly fitted on the shafts, you may need to use a coupling puller or other appropriate extraction tools to safely remove it. 7. Clean and Inspect:After removing the old coupling, clean the shaft ends and inspect them for any signs of damage or wear. Also, check for any misalignment issues that may have contributed to the old coupling’s failure. 8. Install New Coupling:Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installing the new coupling. Apply appropriate lubrication and ensure the coupling is correctly aligned with the shafts. 9. Fasten Securely:Tighten the fasteners to the manufacturer’s recommended torque values to securely attach the new coupling to the shafts. 10. Test Run:After installation, perform a test run of the equipment to ensure the new coupling operates smoothly and without issues. While it is possible to replace a shaft coupling without professional assistance, keep in mind that some couplings and equipment may require specialized knowledge and tools for safe and proper replacement. If you are uncertain about the process or encounter any difficulties, it is advisable to seek help from a qualified professional or technician to avoid potential damage to the equipment or injury to yourself. “` Comparing Shaft Couplings with Other Types of Couplings in PerformanceShaft couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, and their performance characteristics vary depending on the coupling type. Let’s compare shaft couplings with other common types of couplings: 1. Shaft Couplings:Shaft couplings come in various designs, including flexible and rigid couplings. They are widely used in a broad range of applications due to their ability to transmit torque and accommodate misalignments between rotating shafts. Flexible shaft couplings, with elastomeric or metallic elements, offer good misalignment compensation and damping characteristics. Rigid couplings, on the other hand, provide precise torque transmission and are ideal for applications where shafts are well-aligned. 2. Gear Couplings:Gear couplings are robust and designed for heavy-duty applications. They consist of two external gear hubs with internal gear teeth that mesh together. Gear couplings can handle high torque, high-speed, and angular misalignment. They are often used in demanding industries such as steel, mining, and paper manufacturing. 3. Grid Couplings:Grid couplings feature a flexible grid element between the two halves of the coupling. They provide excellent shock absorption and misalignment compensation. Grid couplings are commonly used in pumps, compressors, and other industrial machinery. 4. Disc Couplings:Disc couplings utilize flexible metallic discs to transmit torque and compensate for misalignment. They offer high torsional stiffness, making them suitable for applications requiring precise motion control, such as robotics and CNC machines. 5. Jaw Couplings:Jaw couplings consist of two hubs with elastomeric spider inserts. They are easy to install, have good misalignment capabilities, and offer electrical isolation between shafts. Jaw couplings are widely used in light to medium-duty applications. 6. Oldham Couplings:Oldham couplings have three discs—two outer discs with slots and a central disc with a tongue that fits into the slots. They provide excellent angular misalignment compensation while maintaining constant velocity between shafts. Oldham couplings are commonly used in printing machines and conveyors. 7. Beam Couplings:Beam couplings are made from a single piece of flexible material with spiral cuts. They offer good misalignment compensation and torsional flexibility, making them suitable for precision equipment like encoders and servo motors. The choice of coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application, including torque, speed, misalignment compensation, environmental conditions, and space limitations. Each coupling type has its strengths and limitations, and selecting the right coupling is crucial to ensure optimal performance and reliability in the mechanical system. “` Advantages of Using Shaft Couplings in Connecting Rotating ShaftsShaft couplings offer several advantages in connecting rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. These advantages contribute to the efficiency, reliability, and versatility of various industrial applications. Here are the key benefits of using shaft couplings: 1. Misalignment Compensation:Shaft couplings can accommodate different types of misalignment, including angular, parallel, and axial misalignments. This capability ensures that the connected shafts can continue to operate smoothly even if they are not perfectly aligned, reducing stress on the equipment and minimizing premature wear. 2. Vibration Damping:Some types of shaft couplings, particularly those with flexible elements, offer vibration damping properties. They can absorb shocks and vibrations caused by uneven loads or sudden changes in operating conditions, improving the overall reliability and lifespan of the connected machinery. 3. Shock Absorption:Shaft couplings with flexible elements can also absorb and cushion shock loads, protecting the connected components from damage and preventing system failures in high-impact situations. 4. Torque Transmission:Shaft couplings are designed to transmit torque from one shaft to another efficiently. They ensure that the rotational motion of the driving shaft is effectively transferred to the driven shaft, allowing the equipment to perform its intended function. 5. Overload Protection:Certain types of shaft couplings, such as shear pin couplings, act as safety devices by providing overload protection. In case of excessive torque or shock loads, the shear pin in the coupling will fail, disconnecting the driving and driven shafts and preventing damage to the equipment. 6. Angular Flexibility:Shaft couplings with angular flexibility can handle small angular misalignments between the shafts, compensating for shaft deflection or movement due to external forces. 7. Easy Installation and Maintenance:Shaft couplings are generally easy to install and require minimal maintenance. They are available in various designs, sizes, and materials to suit different applications and operating conditions. 8. Versatility:Shaft couplings are versatile components used in a wide range of industries and applications. They can be found in machinery for material handling, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and more. 9. Cost-Effectiveness:Using shaft couplings eliminates the need for rigid connections between shafts, which can be costly and difficult to implement, especially in situations where misalignment is prevalent. Shaft couplings provide a cost-effective solution for efficient power transmission. Overall, shaft couplings play a crucial role in connecting rotating shafts, ensuring smooth power transmission, protecting equipment from misalignment-related issues, and enhancing the overall performance and reliability of mechanical systems. “` China high quality Customized Steel Rigid Plum-Shaped Positioning Motor Shaft CouplingProduct Description
How do We Work with Our Clients 2. For a start-up company owner or green hand for engineering: just send an idea that you want to try, you don’t even need to know what casting is; 3. Our sales will reply you within 24 hours to confirm further details and give the estimated quote time; 4. Our engineering team will evaluate your inquiry and provide our offer within next 1~3 working days. 5. We can arrange a technical communication meeting with you and our engineers together anytime if required.
The Advantage of Powder Metallurgy Process 1. Cost effective 2. Complex shapes 3. High precision 4. Self-lubrication 5. Green technology FAQ Q2: How to guarantee the high quality? Q3: How long will you give me the reply? Q4. How about your delivery time? Q5. Can you produce according to the samples or drawings? Q6: How about tooling Charge? Q7: What is your sample policy? Q8: How do you make our business long-term and good relationship?
How Do Rigid Couplings Compare to Other Types of Couplings in Terms of Performance?Rigid couplings offer specific advantages and disadvantages compared to other types of couplings, and their performance depends on the requirements of the application: 1. Performance: Rigid couplings provide excellent torque transmission capabilities and are best suited for applications that demand precise and efficient power transfer. They have minimal backlash and high torsional stiffness, resulting in accurate motion control. 2. Misalignment Tolerance: Rigid couplings cannot tolerate misalignment between shafts. They require precise shaft alignment during installation, which can be time-consuming and may result in increased downtime during maintenance or repairs. 3. Vibration Damping: Rigid couplings offer no damping of vibrations, which means they may not be suitable for systems that require vibration isolation or shock absorption. 4. Maintenance: Rigid couplings are generally low maintenance since they have no moving parts or flexible elements that can wear out over time. Once properly installed, they can provide reliable performance for extended periods. 5. Space Requirements: Rigid couplings are compact and do not add much length to the shaft, making them suitable for applications with limited space. 6. Cost: Rigid couplings are usually more economical compared to some advanced and specialized coupling types. Their simpler design and lower manufacturing costs contribute to their affordability. 7. Application: Rigid couplings are commonly used in applications where shafts are precisely aligned and no misalignment compensation is necessary. They are prevalent in precision machinery, robotics, and applications that require accurate motion control. In contrast, flexible couplings, such as elastomeric, jaw, or beam couplings, are designed to accommodate misalignment, dampen vibrations, and provide some degree of shock absorption. Their performance is ideal for systems where shafts may experience misalignment due to thermal expansion, shaft deflection, or dynamic loads. In summary, rigid couplings excel in applications that demand precise alignment and high torque transmission, but they may not be suitable for systems that require misalignment compensation or vibration damping.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Rigid Coupling for a Specific SystemChoosing the right rigid coupling for a specific system is crucial to ensure proper functionality and reliable performance. Several factors should be considered when making this decision: 1. Shaft Size and Compatibility: The most fundamental factor is ensuring that the rigid coupling is compatible with the shaft sizes of the connected components. The coupling should have the appropriate bore size and keyway dimensions to fit securely onto the shafts. 2. Operating Torque: Consider the torque requirements of the application. The rigid coupling should have a torque rating that exceeds the maximum torque expected during operation to prevent failures and ensure safety. 3. Speed: Determine the rotational speed (RPM) of the connected shafts. Rigid couplings have maximum RPM limits, and the selected coupling should be capable of handling the system’s operating speed. 4. Misalignment Tolerance: Assess the potential misalignment between the shafts. Rigid couplings provide no flexibility, so the system must have minimal misalignment to prevent excessive forces on the components. 5. Temperature and Environment: Consider the operating temperature range and the environment where the coupling will be used. Ensure the chosen material can withstand the temperature and any corrosive or harsh conditions present. 6. Space Limitations: Evaluate the available space for the coupling. Rigid couplings have a compact design, but ensure that there is enough clearance for installation and maintenance. 7. Backlash and Torsional Stiffness: In some precision systems, backlash must be minimized to maintain accurate positioning. Additionally, the torsional stiffness of the coupling can impact system response and stability. 8. Keyway or Keyless Design: Decide between a coupling with a keyway or a keyless design based on the specific application requirements and ease of installation. 9. Material Selection: Consider the material properties of the rigid coupling. Common materials include steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, each with its own advantages and limitations. 10. Maintenance: Determine the maintenance requirements of the coupling. Some couplings may need periodic lubrication or inspections, while others may be maintenance-free. 11. Cost: While cost should not be the sole consideration, it is essential to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of the coupling, taking into account its performance and longevity. By carefully considering these factors, you can select the most suitable rigid coupling for your specific system, ensuring optimal performance, and longevity of your mechanical setup.
Advantages of Using Rigid Couplings in Mechanical Systems:Rigid couplings offer several advantages when used in mechanical systems. These advantages make them a preferred choice in certain applications where precise alignment and high torque transmission are essential. Here are the key advantages of using rigid couplings:
Rigid couplings are commonly used in various industries and applications, including high-precision machinery, robotics, automation systems, precision motion control, and machine tools. They are especially beneficial in scenarios where misalignment needs to be minimized or avoided altogether. It’s important to note that while rigid couplings offer these advantages, they are not suitable for applications where shaft misalignment or shock absorption is required. In such cases, flexible couplings or other specialized coupling types may be more appropriate.
|




