Product Description
Product Description:
Coupling is used to link the 2 different organizations shaft (driving shaft and driven shaft) to rotate to common transmission torque of mechanical parts.The overloaded power transmission at high speed, some coupling and buffer, vibration and enhance the role of shaft system dynamic performance.Coupling consists of 2 parts, respectively, and the driving shaft and driven shaft connection.
| Brand | SHAC |
| Raw material | Aluminum |
| Inner Diameter | 4-60MM |
| Length | 25-140MM |
| Model number | JM1,JM2,JDM,JM-T,JH,TM1/TM2/TM3/TM4,JB,JG,JT |
| Packing | Plastic bag+inner box.According to customer’s request |
| Sample | Free sample and catalogue available |
| Certification | ISO 9001 , ISO 14001 , ISO 14000 |
| Application | CNC machines, medical and food machinery, fitness machinery, packaging machinery, printing machinery, and other machinery supporting equipment. |
Detailed Photos
Company Profile
Certifications
Our Advantages
Service:
1,Our Team:
We have experienced and qualified team of marketing and sales representatives to serve our valued customers with the finest products and unsurpassed service.And have professional engineers team to assessment and development the new precision products,and make the OEM customized more easily,experienced QC team to test the products quaity ensure the goods quality before delivery out.
2,Our products:
Quality is the life .We use only the best quality material to ensure the precision of our
Product.All products we sold out are strictly selected and tested by our QC department.
3,Payment:
We accept payment via TT (Bank transfer), L/C,Western Union.
4,Shipping method:
Including DHL, UPS, TNT, FEDEX,EMS, Airfreight and by Sea,as customer required.
To get sample or price list of linear gudies,ball screw, please contact us.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

How to Properly Install a Rigid Shaft Coupling for Optimal Performance and Reliability
Proper installation of a rigid shaft coupling is essential to ensure optimal performance and reliability in mechanical systems. Here are the steps to follow for a successful installation:
- Shaft Preparation: Ensure that the shafts to be connected are clean, smooth, and free from any burrs or contaminants that could affect the coupling’s performance.
- Alignment: Align the two shafts accurately to minimize misalignment during installation. The alignment process is critical as any misalignment can lead to premature wear and reduced coupling efficiency.
- Fitment: Choose the appropriate size of the rigid shaft coupling that matches the shaft diameters. Carefully slide the coupling onto one shaft at a time.
- Fastening: For one-piece rigid couplings, ensure that the coupling is fitted snugly onto both shafts. For two-piece couplings, bolt the two halves together securely around the shafts.
- Tightening: Use the recommended torque value and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to tighten the coupling bolts properly. Over-tightening can cause distortion, while under-tightening can lead to slippage and reduced torque transmission.
- Inspection: After installation, inspect the coupling to ensure that it is centered and aligned correctly. Check for any signs of misalignment or interference during rotation.
- Lubrication: Some rigid couplings may require lubrication at the friction points to reduce wear and friction. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and types.
- Load Testing: Perform load testing on the system to verify the coupling’s performance and check for any unusual vibrations or noises during operation.
- Regular Maintenance: Include the rigid coupling in your regular maintenance schedule. Periodically check for signs of wear, misalignment, or damage, and replace the coupling if necessary.
By following these installation steps and best practices, you can ensure that the rigid shaft coupling operates optimally, providing reliable torque transmission and contributing to the overall efficiency and longevity of the mechanical system.

Are there any safety considerations when using rigid shaft couplings in critical applications?
Yes, when using rigid shaft couplings in critical applications, several safety considerations should be taken into account:
- Torsional Stiffness: Rigid couplings have high torsional stiffness, which can lead to increased stresses and potential failures in the connected equipment. Proper analysis of torsional vibrations and stiffness compatibility with the connected components is crucial.
- Shaft Alignment: Inaccurate shaft alignment can lead to additional loads on the coupling and connected machinery. Precision alignment is essential to prevent premature wear, increased stress, and potential breakdowns.
- Overloading: Exceeding the rated torque capacity of the coupling can result in sudden failures and damage to machinery. It’s essential to operate within the coupling’s specified limits to ensure safe operation.
- Maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance are critical to identify signs of wear, fatigue, or misalignment. Neglecting maintenance can lead to unexpected failures and safety hazards.
- Environmental Factors: Harsh environments, extreme temperatures, and corrosive substances can impact the integrity of rigid couplings. Choosing appropriate materials and protective measures can mitigate these effects.
For critical applications, it’s recommended to work closely with experienced engineers, perform thorough risk assessments, and follow industry standards and best practices to ensure the safe and reliable use of rigid shaft couplings.

Can Rigid Shaft Couplings Handle Misalignment Between Shafts Effectively?
Rigid shaft couplings are not designed to accommodate misalignment between shafts effectively. Unlike flexible couplings, which can bend or flex to some degree to compensate for misalignment, rigid couplings are inflexible and require precise alignment for proper operation.
When using rigid shaft couplings, it is crucial to ensure that the two shafts being connected are aligned with high accuracy. Misalignment between the shafts can lead to various issues, including:
- Vibrations: Misalignment can cause vibrations and increase stress on the coupling and connected machinery, leading to premature wear and reduced performance.
- Increased Stress: Misalignment results in additional stress on the shafts and coupling, which may lead to fatigue failure over time.
- Reduced Efficiency: Misalignment can result in power loss and reduced overall system efficiency.
- Noise: Misalignment may generate noise during operation, leading to potential discomfort for operators and additional wear on components.
To ensure the effective functioning of rigid shaft couplings, it is crucial to align the shafts accurately during installation. The alignment process typically involves using precision tools and techniques to achieve the desired alignment tolerances.
For applications where misalignment is expected or unavoidable, flexible couplings such as beam couplings or jaw couplings may be more suitable as they can accommodate slight misalignments and reduce the transmission of shock and vibration between shafts.
Overall, rigid shaft couplings are best suited for applications where precise shaft alignment is feasible and necessary for optimal performance. Proper alignment and regular maintenance are essential to maximize the life and efficiency of rigid couplings in mechanical systems.


editor by CX 2024-04-30
China manufacturer ISO 9001 Approved Customization Available Professional Roller Chains Type Shaft Pitch Flexible Chain Couplings for Rigid Connection
Product Description
FAQ
Q:Is your company a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We have our own factory.
Q:How long does the lead time take?
A: If the goods are in stock, it is generally 1-2 days; if the goods are not in stock, it is 5-10 days, depending on the quantity.
Q: Can I order shaft bore couplings that are not listed in the catalog?)(Additional machining service for coupling shaft hole
A:Of course.In addition, the recommended dimensional tolerance for the applicable shaft diameter is H7.
Q: How to handle when the received parts are of poor quality?
A:If there is any non-conformity of the product, please contact us immediately, we will check the problem in the first time, and rework or repair.
Q: Why choose XingHe Precision Transmission ?
A:As a professional manufacturer of coupling , we possess a skillful team of workers and designers To provide our customers with first-class services.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
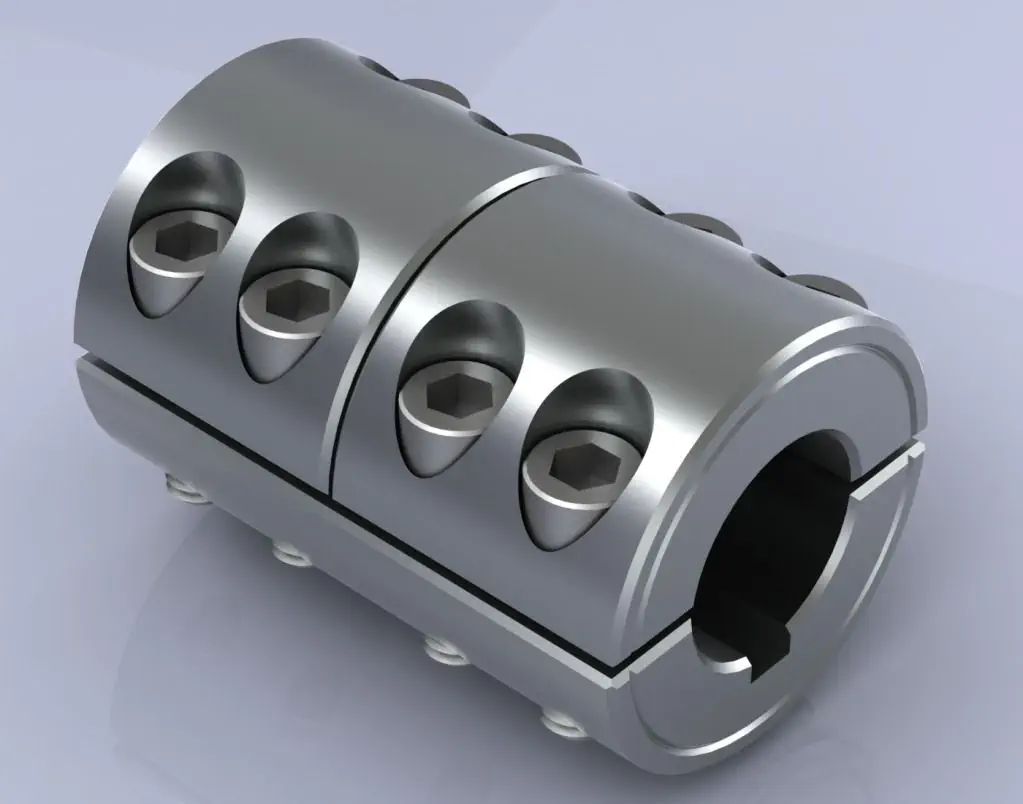

Industry Standards and Certifications for Rigid Shaft Couplings
Yes, there are industry standards and certifications that apply to rigid shaft couplings to ensure their quality, performance, and safety. Some of the common standards and certifications include:
- ISO 14691: This International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standard specifies the requirements and dimensions for metallic straight-toothed rigid couplings with external clamping for shaft connections.
- ANSI/AGMA 9002-C16: The American Gear Manufacturers Association (AGMA) standard covers measurement methods for evaluating the torsional stiffness of rigid couplings.
- API 671: This American Petroleum Institute (API) standard applies to special-purpose couplings used in petroleum, chemical, and gas industry services, ensuring reliable operation and safety.
- DNV GL: Rigid couplings used in marine and offshore applications may require certification from DNV GL, an international accredited registrar and classification society.
- ATEX: For couplings used in explosive atmospheres, compliance with the ATEX directive is crucial to ensure that the coupling does not become a source of ignition.
When selecting a rigid shaft coupling, it is essential to look for products that comply with these relevant industry standards and certifications. Meeting these standards guarantees that the couplings have undergone rigorous testing and adhere to recognized quality and safety guidelines.

Are there any real-world case studies or success stories of using rigid shaft couplings in various engineering projects?
While specific case studies might not be readily available, there are numerous real-world examples of using rigid shaft couplings in various engineering projects across industries. These projects highlight the versatility and benefits of rigid shaft couplings in different applications:
- Industrial Machinery: Rigid shaft couplings are commonly used in industrial machinery such as conveyor systems, pumps, compressors, and machine tools. They ensure precise torque transmission, alignment, and stability in these critical applications, contributing to reliable and efficient operation.
- Robotics: Robotics often require accurate and repeatable motion control. Rigid couplings provide a rigid connection between robotic joints and actuators, ensuring precise movement and positioning.
- Aerospace: In aerospace applications, where safety and reliability are paramount, rigid shaft couplings play a role in connecting various components, such as engine components and control surfaces, ensuring consistent and reliable performance.
- Medical Equipment: Rigid couplings are used in medical devices such as diagnostic equipment, laboratory instruments, and surgical tools. They contribute to accurate motion control and sample manipulation.
- Automotive: Rigid shaft couplings can be found in automotive systems, including drivetrains and transmission systems. They ensure efficient torque transmission and alignment in components such as steering columns.
- Printing and Packaging: Printing presses and packaging machinery rely on rigid couplings to maintain precise alignment between rollers and components, ensuring consistent print quality and packaging accuracy.
While these examples illustrate the broad range of applications where rigid shaft couplings are used, it’s important to note that the success of each project is influenced by factors beyond just the coupling. Proper installation, maintenance, and integration into the overall system are crucial for achieving optimal results.
When considering the implementation of rigid shaft couplings in a project, engineers should collaborate with coupling manufacturers, suppliers, and experienced professionals to ensure proper selection, installation, and operation. By leveraging the advantages of rigid couplings, engineering projects can benefit from improved efficiency, reliability, and performance.

What are the Materials Commonly Used to Manufacture Rigid Shaft Couplings, and How Do They Impact Performance?
Rigid shaft couplings are typically made from a variety of materials, and the choice of material can significantly impact the performance of the coupling in specific applications. Some common materials used in manufacturing rigid shaft couplings include:
- Steel: Steel is one of the most commonly used materials for rigid shaft couplings. It offers excellent strength and durability, making it suitable for high-torque and heavy-duty applications. Steel couplings can withstand significant stresses and provide reliable torque transmission.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel couplings offer the same benefits as regular steel couplings but with the added advantage of corrosion resistance. They are commonly used in applications where the coupling may be exposed to harsh environments or moisture.
- Aluminum: Aluminum couplings are lightweight and have good corrosion resistance. They are often used in applications where weight reduction is essential, such as in aerospace and automotive industries.
- Brass: Brass couplings are known for their excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. They are commonly used in applications where electrical conductivity is required.
- Cast Iron: Cast iron couplings are robust and offer good resistance to wear and tear. They are commonly used in industrial machinery and equipment.
The choice of material depends on various factors, including the application’s operating conditions, such as torque requirements, temperature, and environmental conditions. For example, in high-torque applications, steel or stainless steel couplings are often preferred due to their high strength. On the other hand, aluminum couplings are favored in applications where weight reduction is critical.
It is essential to consider the specific needs of the application and the coupling’s material properties to ensure optimal performance, longevity, and reliability of the rigid shaft coupling.


editor by CX 2024-04-24
China wholesaler FCL Flexible Shaft Couplings for Reducer and Motor
Product Description
SC Transmission FCL Flexible Shaft Couplings for Reducer and Motor
Product Description
FCL Coupling/Shaft Coupling /Pin & Bush Coupling /FCL Flexible Coupling/NBK FCL Coupling is widely used for its compacts designing, easy installation, convenient maintenance, small and light weight.
As long as the relative displacement between shafts is kept within the specified tolerance, couplings will operate the best function and have a longer working life.
Thus it is greatly demanded in medium and minor power transmission systems driven by motors, such as speed reducers, hoists, compressors, conveyors, spinning and weaving machines and ball mills.
Product Parameters
| SIZE | D | D1 | d1 | L | C | n-M | kg | |||
| r/min | ||||||||||
| N.m | ||||||||||
| FCL90 | 4 | 4000 | 90 | 35.5 | 11 | 28 | 3 | 4-M8 | 1.7 | |
| FCL100 | 10 | 4000 | 100 | 40 | 11 | 35.5 | 3 | 4-M10 | 2.3 | |
| FCL112 | 16 | 4000 | 112 | 45 | 13 | 40 | 3 | 4-M10 | 2.8 | |
| FCL125 | 25 | 4000 | 125 | 65 | 50 | 13 | 45 | 3 | 4-M12 | 4 |
| FCL140 | 50 | 4000 | 140 | 71 | 63 | 13 | 50 | 3 | 6-M12 | 5.4 |
| FCL160 | 110 | 4000 | 160 | 80 | 15 | 56 | 3 | 8-M12 | 8 | |
| FCL180 | 157 | 3500 | 180 | 90 | 15 | 63 | 3 | 8-M12 | 10.5 | |
| FCL200 | 245 | 3200 | 200 | 100 | 21 | 71 | 4 | 8-M20 | 16.2 | |
| FCL224 | 392 | 2850 | 224 | 112 | 21 | 80 | 4 | 8-M20 | 21.3 | |
| FCL250 | 618 | 2550 | 250 | 125 | 25 | 90 | 4 | 8-M24 | 31.6 | |
| FCL280 | 980 | 2300 | 280 | 140 | 34 | 100 | 4 | 8-M24 | 44 | |
| FCL315 | 1568 | 2050 | 315 | 160 | 41 | 112 | 4 | 10-M24 | 57.7 | |
| FCL355 | 2450 | 1800 | 355 | 180 | 60 | 125 | 5 | 8-M30 | 89.5 | |
| FCL400 | 3920 | 1600 | 400 | 200 | 60 | 125 | 5 | 10-M30 | 113 | |
| FCL450 | 6174 | 1400 | 450 | 224 | 65 | 140 | 5 | 12-M30 | 145 | |
| FCL560 | 9800 | 1150 | 560 | 250 | 85 | 160 | 5 | 14-M30 | 229 | |
| FCL630 | 15680 | 1000 | 630 | 280 | 95 | 180 | 5 | 18-M30 | 296 | |
Company Profile
FAQ
Shipping
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
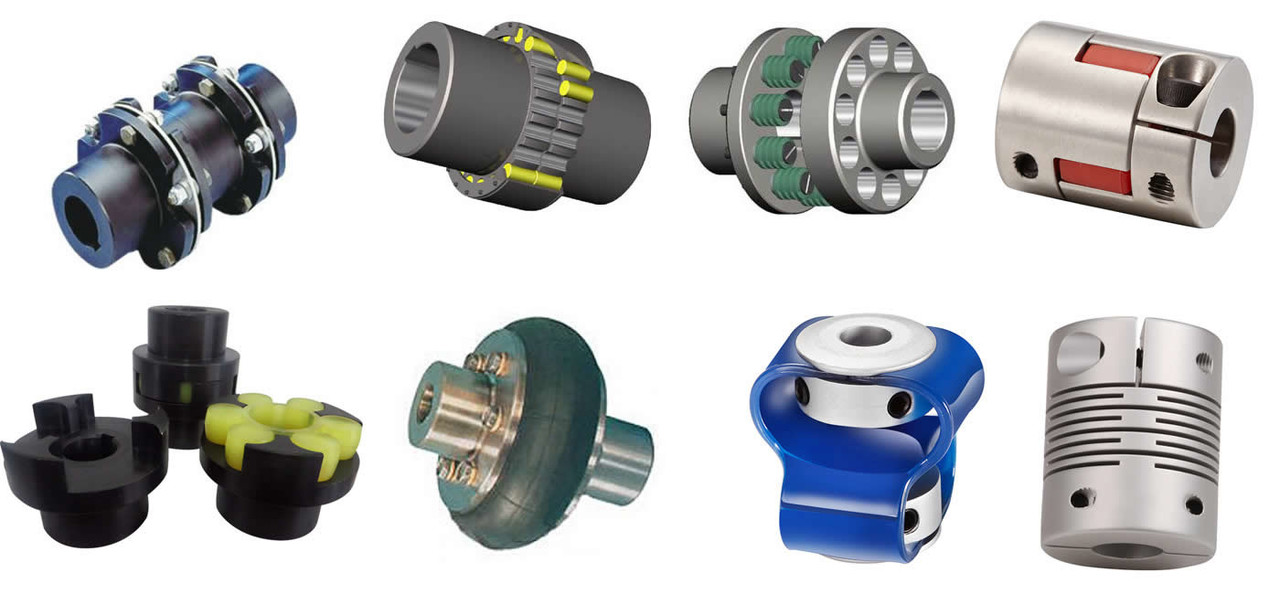

Understanding the Torque and Misalignment Capabilities of Shaft Couplings
Shaft couplings play a critical role in transmitting torque and accommodating misalignment between rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. Understanding their torque and misalignment capabilities is essential for selecting the right coupling for a specific application. Here’s an overview:
Torque Transmission:
The torque capacity of a shaft coupling refers to its ability to transmit rotational force from one shaft to another. It is typically specified in torque units, such as Nm (Newton-meters) or lb-ft (pound-feet). The coupling’s torque capacity depends on its design, size, and material.
When selecting a coupling, it’s crucial to ensure that its torque capacity meets or exceeds the torque requirements of the application. Overloading a coupling beyond its torque capacity can lead to premature failure or damage to the coupling and connected equipment.
Misalignment Compensation:
Shaft misalignment can occur due to various factors, including thermal expansion, manufacturing tolerances, or foundation settling. Misalignment puts additional stress on the coupling and connected components, potentially leading to increased wear and reduced efficiency.
Shaft couplings are designed to compensate for different types of misalignment:
- Angular Misalignment: Occurs when the shafts are not parallel and have an angle between them.
- Parallel Misalignment: Occurs when the shafts are not collinear, resulting in axial displacement.
- Radial Misalignment: Occurs when the shafts have lateral displacement but remain parallel.
The coupling’s misalignment capabilities are specified in terms of angular and axial misalignment values, usually in degrees or millimeters. Different coupling designs can accommodate varying degrees of misalignment, and the choice depends on the specific application and operating conditions.
Flexible Couplings:
Flexible couplings, such as elastomeric or jaw couplings, offer good misalignment compensation. They can handle a combination of angular, parallel, and axial misalignments. However, their torque capacity may be limited compared to rigid couplings.
Rigid Couplings:
Rigid couplings, such as clamp or sleeve couplings, have high torque transmission capabilities but offer minimal misalignment compensation. They are best suited for applications where shafts are well-aligned and precise torque transmission is critical.
Torsional Stiffness:
Another factor to consider is the coupling’s torsional stiffness, which determines how much torsional deflection or twist occurs under load. Some applications, like precision systems, may require couplings with high torsional stiffness to maintain accurate positioning and avoid torsional backlash.
By understanding the torque and misalignment capabilities of shaft couplings, engineers can make informed decisions when selecting a coupling to ensure efficient power transmission and reliable performance in their mechanical systems.
“`
Temperature and Speed Limits for Different Shaft Coupling Types
The temperature and speed limits of shaft couplings vary depending on the materials and design of the coupling. Manufacturers provide specific guidelines and ratings for each coupling type. Below are general temperature and speed limits for some common shaft coupling types:
1. Elastomeric Couplings:
Elastomeric couplings, such as jaw couplings and tire couplings, typically have temperature limits ranging from -40°C to 100°C (-40°F to 212°F). The speed limits for elastomeric couplings are generally up to 5,000 RPM, but some designs may allow higher speeds.
2. Metallic Couplings:
Metallic couplings, like gear couplings and disc couplings, can handle a wider temperature range, typically from -50°C to 200°C (-58°F to 392°F). The speed limits for metallic couplings vary based on the size and design, but they can range from 3,000 RPM to over 10,000 RPM.
3. Grid Couplings:
Grid couplings have temperature limits similar to metallic couplings, ranging from -50°C to 200°C (-58°F to 392°F). The speed limits for grid couplings are typically in the range of 3,000 to 5,000 RPM.
4. Oldham Couplings:
Oldham couplings usually have temperature limits from -30°C to 100°C (-22°F to 212°F) and speed limits ranging from 1,000 to 5,000 RPM.
5. Beam Couplings:
Beam couplings generally have temperature limits from -40°C to 120°C (-40°F to 248°F) and speed limits between 5,000 to 10,000 RPM.
6. Fluid Couplings:
Fluid couplings are suitable for a wide range of temperatures, often from -50°C to 300°C (-58°F to 572°F). The speed limits depend on the size and design of the fluid coupling but can extend to several thousand RPM.
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines, and the actual temperature and speed limits may vary based on the specific coupling manufacturer, material quality, and application requirements. Always refer to the manufacturer’s documentation and technical specifications for accurate and up-to-date temperature and speed limits for a particular shaft coupling model.
“`
Best Practices for Installing a Shaft Coupling for Optimal Performance
Proper installation of a shaft coupling is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and preventing premature wear or failure. Follow these best practices to install a shaft coupling correctly:
1. Shaft Alignment:
Ensure that both the driving and driven shafts are properly aligned before installing the coupling. Misalignment can lead to increased stress on the coupling and other connected components, reducing efficiency and causing premature wear. Use alignment tools, such as dial indicators or laser alignment systems, to achieve accurate shaft alignment.
2. Cleanliness:
Before installation, clean the shaft ends and the coupling bore thoroughly. Remove any dirt, debris, or residue that could interfere with the coupling’s fit or cause misalignment.
3. Lubrication:
Apply the recommended lubricant to the coupling’s contact surfaces, such as the bore and shaft ends. Proper lubrication ensures smooth installation and reduces friction during operation.
4. Correct Fit:
Ensure that the coupling is the correct size and type for the application. Use couplings with the appropriate torque and speed ratings to match the equipment’s requirements.
5. Fastening:
Use the recommended fastening methods, such as set screws or keyways, to securely attach the coupling to the shafts. Make sure the fasteners are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications to prevent loosening during operation.
6. Spacer or Adapter:
If required, use a spacer or adapter to properly position the coupling on the shafts and maintain the desired distance between the driving and driven components.
7. Avoid Shaft Damage:
Be careful during installation to avoid damaging the shaft ends, especially when using set screws or other fastening methods. Shaft damage can lead to stress concentrations and eventual failure.
8. Check Runout:
After installation, check the coupling’s runout using a dial indicator to ensure that it rotates smoothly and without wobbling. Excessive runout can indicate misalignment or improper fit.
9. Periodic Inspection:
Regularly inspect the coupling and its components for signs of wear, misalignment, or damage. Perform routine maintenance as recommended by the manufacturer to prevent issues from worsening over time.
10. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Always follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions and guidelines. Different types of couplings may have specific installation requirements that need to be adhered to for optimal performance and safety.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your shaft coupling is installed correctly, maximizing its efficiency and reliability in your mechanical power transmission system.
“`

editor by CX 2024-04-23
China OEM Two Piece Clamp on Rigid Shaft Couplings
Product Description
CHINAMFG Rigid Shaft Coupling:
Design available: one-piece or two-piece or set screw
With keyway or without keyway
Material available: Aluminum
Carbon Steel Black Oxidized
Stainless Steel
Size available: 6mm to 50mm shaft fit
1/4” to 2” shaft fit
Features: Cost saving for economy
High torque capacity
Zero backlash
Without the shaft damage and fretting
Misalignment free
Clamp Style Rigid Couplings for applications where alignment is critical, no backlash is desired, and flexibility is not required. The one-piece rigid coupling wraps around the shaft, providing high torsional holding power without the shaft damage and fretting. The two-piece rigid coupling has the additional benefit of allowing for disassembly and maintenance without removal of other components.
| Black Oxide Steel | Stainless Steel | Inner Dia mm | Outer Dia mm | Length mm | Clamp Screw | Weight g |
| RSC1-6-ST | RSC1-6-SS | 6 | 18 | 30 | M 3 x 8 | 47 |
| RSC1-8-ST | RSC1-8-SS | 8 | 24 | 35 | M 3 x 10 | 102 |
| RSC1-10-ST | RSC1-10-SS | 10 | 29 | 45 | M 4 x 12 | 185 |
| RSC1-12-ST | RSC1-12-SS | 12 | 29 | 45 | M 4 x 12 | 180 |
| RSC1-14-ST | RSC1-14-SS | 14 | 34 | 50 | M 5 x 16 | 272 |
| RSC1-15-ST | RSC1-15-SS | 15 | 34 | 50 | M 5 x 16 | 266 |
| RSC1-16-ST | RSC1-16-SS | 16 | 34 | 50 | M 5 x 16 | 261 |
| RSC1-20-ST | RSC1-20-SS | 20 | 42 | 65 | M 6 x 16 | 518 |
| RSC1-25-ST | RSC1-25-SS | 25 | 45 | 75 | M 6 x 16 | 623 |
| RSC1-30-ST | RSC1-30-SS | 30 | 53 | 83 | M 6 x 18 | 920 |
| RSC1-35-ST | RSC1-35-SS | 35 | 67 | 95 | M 8 x 25 | 1880 |
| RSC1-40-ST | RSC1-40-SS | 40 | 77 | 108 | M 8 x 25 | 2710 |
| RSC1-50-ST | RSC1-50-SS | 50 | 85 | 124 | M 10 x 25 | 3520 |
| Black Oxide Steel | Stainless Steel | Inner Dia mm | Outer Dia mm | Length mm | Clamp Screw | Weight g |
| RSC2-6-ST | RSC2-6-SS | 6 | 18 | 30 | M 3 x 8 | 47 |
| RSC2-8-ST | RSC2-8-SS | 8 | 24 | 35 | M 3 x 10 | 102 |
| RSC2-10-ST | RSC2-10-SS | 10 | 29 | 45 | M 4 x 12 | 185 |
| RSC2-12-ST | RSC2-12-SS | 12 | 29 | 45 | M 4 x 12 | 180 |
| RSC2-14-ST | RSC2-14-SS | 14 | 34 | 50 | M 5 x 16 | 272 |
| RSC2-15-ST | RSC2-15-SS | 15 | 34 | 50 | M 5 x 16 | 266 |
| RSC2-16-ST | RSC2-16-SS | 16 | 34 | 50 | M 5 x 16 | 261 |
| RSC2-20-ST | RSC2-20-SS | 20 | 42 | 65 | M 6 x 16 | 518 |
| RSC2-25-ST | RSC2-25-SS | 25 | 45 | 75 | M 6 x 16 | 623 |
| RSC2-30-ST | RSC2-30-SS | 30 | 53 | 83 | M 6 x 18 | 920 |
| RSC2-35-ST | RSC2-35-SS | 35 | 67 | 95 | M 8 x 25 | 1880 |
| RSC2-40-ST | RSC2-40-SS | 40 | 77 | 108 | M 8 x 25 | 2710 |
| RSC2-50-ST | RSC2-50-SS | 50 | 85 | 124 | M 10 x 25 | 3520 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

How to Properly Install a Rigid Shaft Coupling for Optimal Performance and Reliability
Proper installation of a rigid shaft coupling is essential to ensure optimal performance and reliability in mechanical systems. Here are the steps to follow for a successful installation:
- Shaft Preparation: Ensure that the shafts to be connected are clean, smooth, and free from any burrs or contaminants that could affect the coupling’s performance.
- Alignment: Align the two shafts accurately to minimize misalignment during installation. The alignment process is critical as any misalignment can lead to premature wear and reduced coupling efficiency.
- Fitment: Choose the appropriate size of the rigid shaft coupling that matches the shaft diameters. Carefully slide the coupling onto one shaft at a time.
- Fastening: For one-piece rigid couplings, ensure that the coupling is fitted snugly onto both shafts. For two-piece couplings, bolt the two halves together securely around the shafts.
- Tightening: Use the recommended torque value and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to tighten the coupling bolts properly. Over-tightening can cause distortion, while under-tightening can lead to slippage and reduced torque transmission.
- Inspection: After installation, inspect the coupling to ensure that it is centered and aligned correctly. Check for any signs of misalignment or interference during rotation.
- Lubrication: Some rigid couplings may require lubrication at the friction points to reduce wear and friction. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and types.
- Load Testing: Perform load testing on the system to verify the coupling’s performance and check for any unusual vibrations or noises during operation.
- Regular Maintenance: Include the rigid coupling in your regular maintenance schedule. Periodically check for signs of wear, misalignment, or damage, and replace the coupling if necessary.
By following these installation steps and best practices, you can ensure that the rigid shaft coupling operates optimally, providing reliable torque transmission and contributing to the overall efficiency and longevity of the mechanical system.
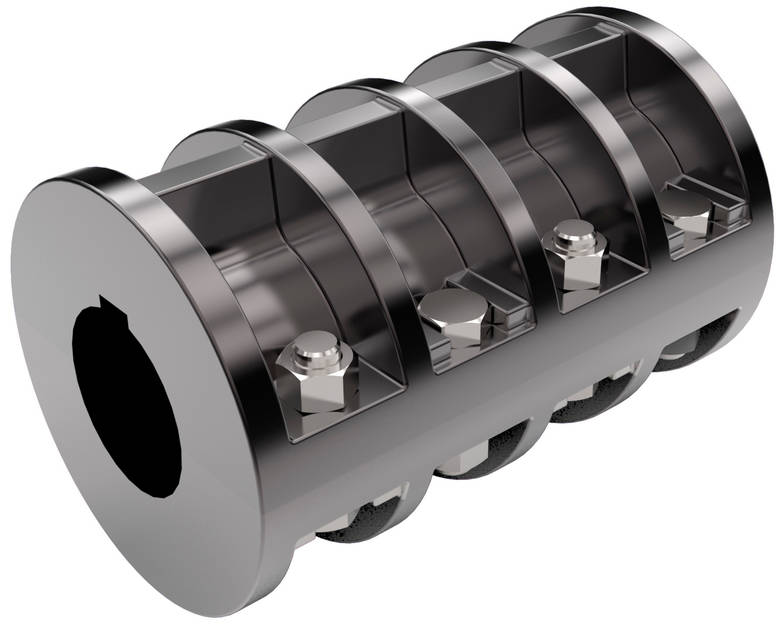

How do rigid shaft couplings contribute to the overall efficiency of rotating machinery?
Rigid shaft couplings play a crucial role in enhancing the overall efficiency and performance of rotating machinery by ensuring precise torque transmission, accurate shaft alignment, and reduced power losses. Their contribution to efficiency can be understood through the following points:
- Accurate Torque Transmission: Rigid couplings provide a direct and efficient connection between two shafts, allowing torque to be transmitted without significant losses. Unlike flexible couplings that can absorb some energy through flexibility, rigid couplings minimize energy dissipation, leading to efficient power transfer.
- Minimized Misalignment: Proper alignment of shafts is essential for efficient operation. Rigid couplings maintain accurate shaft alignment, reducing friction, wear, and energy losses that can occur due to misaligned shafts.
- Reduced Vibrations: By preventing misalignment and maintaining shaft stability, rigid couplings help minimize vibrations. Reduced vibrations lead to smoother operation, less wear and tear, and a decrease in energy losses associated with friction and oscillations.
- Consistent Performance: Rigid couplings ensure consistent and reliable torque transmission throughout the machinery’s operation. This stability helps maintain optimal operating conditions and prevents sudden disruptions or fluctuations in performance.
- Enhanced System Integrity: A stable and secure connection between shafts provided by rigid couplings reduces the risk of equipment failures and breakdowns. This enhances the machinery’s overall reliability and uptime, contributing to improved efficiency.
- Minimized Power Losses: With their rigid construction, these couplings have minimal flexibility, reducing power losses associated with elastic deformation. As a result, more of the input power is effectively utilized for productive work.
- Reduced Maintenance Needs: Rigid couplings, when properly installed and maintained, experience fewer wear-related issues compared to flexible couplings. This translates to reduced downtime and maintenance requirements, further enhancing machinery efficiency.
Efficient rotating machinery is critical for various industries, as it leads to cost savings, improved productivity, and extended equipment lifespan. Rigid shaft couplings contribute significantly to achieving these goals by ensuring reliable torque transmission, stable operation, and minimized energy losses.
It’s important to note that while rigid couplings offer advantages in terms of efficiency, they might not be suitable for applications requiring flexibility to accommodate misalignment or shock absorption. Engineers should carefully consider the specific requirements of their machinery and select couplings that best align with the desired balance of efficiency, flexibility, and other operational needs.

What is a Rigid Shaft Coupling and How Does It Work in Mechanical Systems?
A rigid shaft coupling is a type of coupling used to connect two shafts together in a mechanical system. As the name suggests, it is designed to provide a rigid and solid connection between the shafts, without any flexibility or misalignment compensation.
The primary function of a rigid shaft coupling is to transmit torque from one shaft to another efficiently and with minimal backlash. It achieves this by directly connecting the two shafts using a rigid mechanical interface.
Rigid shaft couplings typically consist of two halves with flanges that are bolted or clamped together around the shaft ends. The flanges are precision machined to ensure accurate alignment of the shafts. Some common types of rigid shaft couplings include:
- Sleeve Couplings: These are the simplest type of rigid couplings and consist of a cylindrical sleeve with a bore that fits over the shaft ends. The two shafts are aligned and then secured together using screws or pins.
- Clamp or Split Couplings: These couplings have two halves that are split and bolted together around the shafts. The split design allows for easy installation and removal without the need to disassemble other components of the system.
- Flanged Couplings: Flanged couplings have two flanges with precision machined faces that are bolted together, providing a robust connection.
- Tapered Bushing Couplings: These couplings use a tapered bushing to lock the coupling onto the shafts, creating a secure and concentric connection.
Rigid shaft couplings are commonly used in applications where precise alignment is critical, such as in high-speed machinery, precision instruments, and power transmission systems. Since they do not have any flexibility, they are best suited for applications where shaft misalignment is minimal or can be controlled through accurate alignment during installation.
One of the main advantages of rigid shaft couplings is their ability to provide a direct and efficient transfer of torque, making them suitable for high-torque and high-speed applications. Additionally, their simple design and solid connection make them easy to install and maintain.
However, it’s essential to ensure proper alignment during installation to prevent premature wear and stress on the shafts and other components. In cases where misalignment is expected or unavoidable, flexible couplings like beam couplings, bellows couplings, or jaw couplings are more appropriate, as they can compensate for small misalignments and provide some degree of shock absorption.


editor by CX 2024-04-19
China high quality Nl Nylon Sleeve Internal Gear Coupling Nl8 Shaft Couplings Rigid Continous Sleeve and Double Engagement Gearing
Product Description
NL Nylon sleeve internal gear coupling NL8 shaft Couplings Rigid Continous sleeve and double engagement gearing
Product Description
1. Completely interchangeable with the original
2. Suitable for various mechanical engineering and hydraulic fields
3. Nylon and steel material match, maintenance-free
4. Can compensate axial, radial, and angular installation deviation
Product Parameters
| SIZE | MOLD | TOOTH | TORQUE (H.) |
SPEED (r/min) |
MAIN SIZE | ||||||
| SHAFT DIA (d1, d2) |
SHAFT LENGTH (L1,L2) |
L | D | H | D1 D2 | E | |||||
| NL2 | 1.5/1 | 28/42 | 100 | 6000 | 9-22 | 20-45 | CUSTOMIZED | 55 | 40 | 36 | 4 |
| NL3 | 1.5/1 | 34/25 | 160 | 6000 | 9-28 | 20-60 | 66 | 41 | 38-50 | 4 | |
| NL4 | 1.5/2 | 45/32 | 250 | 6000 | 12-38 | 25-80 | 84 | 47 | 50-60 | 4 | |
| NL5 | 2 | 38/36 | 315 | 5000 | 15-42 | 30-110 | 93 | 50 | 60-67 | 4 | |
| NL6 | 2/2.5 | 40/32 | 400 | 5000 | 16-48 | 40-110 | 100 | 51 | 60-70 | 4 | |
| NL7 | 2.5/2 | 36/45 | 630 | 3600 | 16-55 | 45-110 | 115 | 56 | 70-82 | 4 | |
| NL8 | 2.5/3 | 36/45 | 1250 | 3600 | 20-65 | 50-140 | 140 | 70 | 85-95 | 4 | |
| NL9 | 3 | 45/46 | 2000 | 2000 | 20-80 | 60-170 | 175 | 91 | 120 | 6 | |
| NL10 | 4 | 44 | 3150 | 1800 | 38-100 | 70-210 | 220 | 105 | 157 | 8 | |
Related Products
Company Profile
FAQ
Q: Can you make the coupling with customization?
A: Yes, we can customize per your request.
Q: Do you provide samples?
A: Yes. The sample is available for testing.
Q: What is your MOQ?
A: It is 10pcs for the beginning of our business.
Q: What’s your lead time?
A: Standard products need 5-30 days, a bit longer for customized products.
Q: Do you provide technical support?
A: Yes. Our company has a design and development team, and we can provide technical support if you
need.
Q: How to ship to us?
A: It is available by air, sea, or by train.
Q: How to pay the money?
A: T/T and L/C are preferred, with different currencies, including USD, EUR, RMB, etc.
Q: How can I know if the product is suitable for me?
A: >1ST confirm drawing and specification >2nd test sample >3rd start mass production.
Q: Can I come to your company to visit?
A: Yes, you are welcome to visit us at any time.
Q: How shall we contact you?
A: You can send an inquiry directly, and we will respond within 24 hours. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

What are the potential drawbacks or limitations of using rigid shaft couplings in certain applications?
Rigid shaft couplings, while offering benefits in certain scenarios, also have limitations that should be considered when selecting them for specific applications:
- Minimal Misalignment Compensation: Rigid couplings have limited ability to compensate for shaft misalignment, making them less suitable for applications with significant misalignment.
- Transmits Vibrations: Rigid couplings do not dampen vibrations, which can lead to increased wear and fatigue in connected components and decrease overall system lifespan.
- Higher Stress Concentration: Due to their rigid nature, these couplings can result in higher stress concentrations at the coupling ends, potentially leading to premature failure.
- Noisy Operation: Rigid couplings can amplify noise generated by connected equipment, contributing to a noisier operating environment.
- Requires Precise Alignment: Proper alignment during installation is crucial to prevent excessive loads on equipment and ensure reliable operation.
- Less Torsional Damping: Rigid couplings lack the torsional damping capabilities of some other coupling types, which may be necessary in systems with varying loads.
- Less Forgiving: Rigid couplings can transmit shocks and impacts directly to connected equipment, which may not be suitable for applications with frequent starts, stops, or heavy loads.
It’s important to carefully assess the specific requirements of an application and consider factors such as misalignment, vibration, torque transmission, and environmental conditions when deciding whether to use a rigid shaft coupling. In cases where the limitations of rigid couplings may pose challenges, other coupling types such as flexible, torsionally soft, or damping couplings could be more appropriate alternatives.

How do rigid shaft couplings compare to flexible couplings in terms of torque transmission and misalignment handling?
Rigid shaft couplings and flexible couplings differ in their ability to handle torque transmission and misalignment. Here’s a comparison of these aspects:
- Torque Transmission: Rigid shaft couplings offer excellent torque transmission due to their solid construction. They efficiently transmit high torque loads without significant power loss. Flexible couplings, on the other hand, may have some inherent power loss due to their flexibility.
- Misalignment Handling: Flexible couplings excel in compensating for misalignment between shafts. They can accommodate angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, reducing stress on connected equipment. Rigid couplings are limited in their misalignment compensation, primarily handling minimal misalignments. Significant misalignment can lead to increased wear and premature failure.
The choice between rigid and flexible couplings depends on the specific requirements of the application. If precise torque transmission and minimal misalignment are priorities, rigid couplings may be suitable. However, if misalignment compensation and vibration dampening are crucial, flexible couplings are a better option.

What is a Rigid Shaft Coupling and How Does It Work in Mechanical Systems?
A rigid shaft coupling is a type of coupling used to connect two shafts together in a mechanical system. As the name suggests, it is designed to provide a rigid and solid connection between the shafts, without any flexibility or misalignment compensation.
The primary function of a rigid shaft coupling is to transmit torque from one shaft to another efficiently and with minimal backlash. It achieves this by directly connecting the two shafts using a rigid mechanical interface.
Rigid shaft couplings typically consist of two halves with flanges that are bolted or clamped together around the shaft ends. The flanges are precision machined to ensure accurate alignment of the shafts. Some common types of rigid shaft couplings include:
- Sleeve Couplings: These are the simplest type of rigid couplings and consist of a cylindrical sleeve with a bore that fits over the shaft ends. The two shafts are aligned and then secured together using screws or pins.
- Clamp or Split Couplings: These couplings have two halves that are split and bolted together around the shafts. The split design allows for easy installation and removal without the need to disassemble other components of the system.
- Flanged Couplings: Flanged couplings have two flanges with precision machined faces that are bolted together, providing a robust connection.
- Tapered Bushing Couplings: These couplings use a tapered bushing to lock the coupling onto the shafts, creating a secure and concentric connection.
Rigid shaft couplings are commonly used in applications where precise alignment is critical, such as in high-speed machinery, precision instruments, and power transmission systems. Since they do not have any flexibility, they are best suited for applications where shaft misalignment is minimal or can be controlled through accurate alignment during installation.
One of the main advantages of rigid shaft couplings is their ability to provide a direct and efficient transfer of torque, making them suitable for high-torque and high-speed applications. Additionally, their simple design and solid connection make them easy to install and maintain.
However, it’s essential to ensure proper alignment during installation to prevent premature wear and stress on the shafts and other components. In cases where misalignment is expected or unavoidable, flexible couplings like beam couplings, bellows couplings, or jaw couplings are more appropriate, as they can compensate for small misalignments and provide some degree of shock absorption.


editor by CX 2024-04-16
China Good quality Auto Parts Multi Sizes Spline Coupler Motor Connector Spiral Beam Shaft Couplings
Product Description
|
Product Name |
Auto Parts Multi Sizes Spline Coupler Motor Connector Spiral Beam Shaft Couplings |
|
Material |
Aluminum alloy |
|
Surface treatment |
Natural color anode |
|
Customized service |
Support light customization and logo customization |
|
Remarks |
The default engraving brand name and size of the product. If you need not engraving, please contact the customer service for comments |
| Packaging Details | Carton box with anti-static package,carton plus with wooden case. |
| Main Products | Shaft Parts, Timing Belt Pulley, Gears, CNC Machining Parts, Sheet Metal Fabrication |
| Certifications(2) | ISO9001:2015, IPMS |
| Applicable Industries | Building Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Food & Beverage Factory, Farms |
| Supply Ability | 100000 Piece/Pieces per Month |
| Dimension | oem provided |
| Surface finish | anodized |
| Lead Time | 25 days |
| Application | Furniture,cabinet |
| Custom | OEM and ODM services are welcome,we can make cutom LOGO and products according to customer’s requests. |
| Quality control Our | Finished product inspection,Warranty available |
| service | Swiss machining;deburring;lathe/turning;5 axis;micromachining |
| Color |
silver,gold,black,red,bulue,and according to the customer requests. |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Exploring the Use of Elastomeric Materials in Flexible Shaft Couplings
Elastomeric materials play a crucial role in the design and function of flexible shaft couplings. These materials, commonly known as elastomers, are rubber-like substances that exhibit high elasticity and flexibility. They are widely used in various types of flexible couplings due to their unique properties and benefits:
1. Damping and Vibration Absorption:
Elastomeric materials have excellent damping characteristics, meaning they can absorb and dissipate vibrations and shocks. This property is particularly useful in applications where vibration control is essential to protect sensitive equipment and improve overall system performance.
2. Misalignment Compensation:
Flexible shaft couplings with elastomeric elements can accommodate different types of misalignments, including angular, parallel, and radial misalignments. The elasticity of the material allows for limited movement between the shafts while still transmitting torque efficiently.
3. Torsional Flexibility:
Elastomers offer torsional flexibility, which allows them to twist and deform under torque loads. This feature helps to minimize torsional stresses and torsional backlash, making them suitable for applications requiring precise motion control.
4. Shock and Impact Resistance:
Due to their high resilience, elastomers can withstand sudden shocks and impacts without permanent deformation. This property makes them ideal for use in machinery subjected to varying loads or rapid changes in torque.
5. No Lubrication Requirement:
Elastomeric couplings are often maintenance-free because the elastomer material does not require additional lubrication. This reduces maintenance costs and simplifies the overall system upkeep.
6. Electric Isolation:
In certain applications, elastomeric materials can provide electrical isolation between the driving and driven components. This can help prevent the transmission of electrical currents or static charges through the coupling.
7. Corrosion Resistance:
Many elastomers used in couplings are resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for use in challenging environments where exposure to chemicals or moisture is a concern.
8. Easy Installation:
Elastomeric couplings are often designed for ease of installation and replacement. Their flexibility allows for simple and quick assembly onto the shafts without the need for special tools or complex procedures.
Given these advantages, elastomeric materials are popular choices for various flexible shaft couplings, including jaw couplings, tire couplings, and spider couplings. However, it is essential to select the right elastomer material based on the specific application requirements, such as temperature range, chemical compatibility, and torque capacity.
“`
How to Identify Signs of Wear or Failure in a Shaft Coupling
Regular inspection and monitoring are essential to identify signs of wear or potential failure in a shaft coupling. Detecting issues early can help prevent costly downtime and equipment damage. Here are common signs to look for:
1. Visible Damage:
Inspect the coupling for visible signs of damage, such as cracks, chips, or deformation. These can indicate mechanical stress or overload.
2. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:
Unusual noise or excessive vibration during operation may indicate misalignment, worn-out components, or a coupling nearing its failure point.
3. Increased Temperature:
If the coupling becomes noticeably hotter during operation than usual, it could be a sign of friction or misalignment issues.
4. Shaft Misalignment:
Check for misalignment between the shafts connected by the coupling. Misalignment can lead to increased stress on the coupling and its components.
5. Excessive Backlash:
If the coupling exhibits too much free play or rotational play before torque transmission, it might indicate wear or fatigue in the coupling’s components.
6. Lubrication Issues:
Inspect the coupling for lubrication leaks or insufficient lubrication, which can lead to increased friction and wear.
7. Elastomeric Element Deterioration:
If the coupling uses elastomeric elements (e.g., rubber or polyurethane), check for signs of deterioration, such as cracking, softening, or deformation.
8. Bolts and Fasteners:
Examine the bolts and fasteners connecting the coupling components. Loose or damaged bolts can lead to misalignment and coupling failure.
9. Age and Service Life:
Consider the age and service life of the coupling. If it has been in use for a long time or exceeds the manufacturer’s recommended service life, it may be more susceptible to wear and failure.
10. Abnormal Performance:
Monitor the overall performance of the connected equipment. Any abnormal behavior, such as reduced power transmission or erratic operation, could be indicative of coupling issues.
If any of these signs are observed, it’s crucial to take immediate action. Depending on the severity of the issue, this may involve replacing worn components, realigning the shafts, or replacing the entire coupling. Regular maintenance and periodic inspections are key to identifying these signs early and ensuring the coupling operates optimally and safely.
“`
What is a Shaft Coupling and Its Role in Mechanical Power Transmission?
A shaft coupling is a mechanical device used to connect two shafts together at their ends, allowing for the transmission of mechanical power from one shaft to another. It serves as an essential component in various machinery and industrial applications where rotational motion needs to be transmitted between two shafts that are not perfectly aligned or are separated by a distance.
The role of a shaft coupling in mechanical power transmission includes the following:
1. Power Transmission:
The primary function of a shaft coupling is to transmit power from a driving shaft to a driven shaft. When the driving shaft rotates, the coupling transfers the rotational motion to the driven shaft, enabling the driven equipment to perform its intended function.
2. Misalignment Compensation:
In real-world applications, it is often challenging to achieve perfect alignment between two shafts due to manufacturing tolerances or dynamic conditions. Shaft couplings are designed to accommodate different types of misalignment, such as angular, parallel, and axial misalignment, allowing the equipment to function smoothly even when the shafts are not perfectly aligned.
3. Vibration Damping:
Shaft couplings can help dampen vibrations and shocks caused by uneven loads or sudden changes in the operating conditions. This vibration damping feature protects the connected components from damage and contributes to the overall system’s reliability.
4. Overload Protection:
In some cases, a shaft coupling can act as a safety device by providing overload protection. When the connected machinery experiences excessive torque or shock loads, certain types of couplings can disengage or shear to prevent damage to the equipment.
5. Torque and Speed Conversion:
Shaft couplings can be designed to provide torque and speed conversion between the driving and driven shafts. This allows for adaptation to different operating conditions and varying torque requirements in the connected machinery.
6. Flexible Connection:
Shaft couplings with flexible elements, such as elastomeric inserts or flexible discs, provide a flexible connection that can absorb shocks and misalignments. This flexibility helps reduce stress on the connected equipment and extends its lifespan.
Overall, shaft couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, enabling the efficient transfer of rotational motion between shafts while accommodating misalignments and providing protection against overloads and vibrations. The selection of the appropriate coupling type and design depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the type of misalignment, torque capacity, and operating conditions.
“`

editor by CX 2024-04-16
China Best Sales CHINAMFG Gy Type Flange Rigid Coupling Transmission Connection Shaft Couplings
Product Description
GY Type Flange Coupling(GB/T5843-2003)
Product Description
♦Description
Flange Type Couplings are multi-piece mechanical couplings used to transmit torque and rotation between shafts in mechanical power transmission assemblies. Their design allows them to accommodate slight alignment changes that occur between connecting shafts, while also absorbing shock loads. Huading is a leading grid coupling manufacturer in China, a grid coupling supplier in China offering the latest and modern Grid Type Couplings.
Grid Coupling is widely used in metallurgy, mining, lifting, transportation, petroleum, chemical, ships, textile, light industry, agricultural machinery, printing machines and pumps, fans, compressors, machine tools and other mechanical equipment and industry shaft transmission.
♦Feature
1.The serpentine spring as the elastic element, the elastic strong at the same time, greatly improves the grid coupling torque, widely used in heavy machinery and general machinery.The serpentine spring special technology department, has long service life, allowing higher speed, has good ability to compensate in the axial, radial and angle
2.High transmission efficiency, start safety. Transmission efficiency of up to 99.47%, short-time overload capacity is 2 times the rated torque, operation safety.
3.Simple structure, convenient assembly and disassembly, long service life
4.Damping effect is good to avoid the resonance.
♦Basic Parameter and Main Dimension
Note:
N.m=Norminal Torque; r/min= Allowable speed of rotation;d=Diameter of shaft hole ;
Y L=Length of shaft hole; kg.m²=Rotational inertia; kg= Mass
The weight and rotation are calculated according to the combination type and minimum diameter of the Y/J shaft hole of GY type coupling.
Other products
| Transmission Machinery Parts Name |
Model |
| Universal Coupling | WS,WSD,WSP |
| Cardan Shaft | SWC,SWP,SWZ |
| Tooth Coupling | CL,CLZ,GCLD,GIICL, GICL,NGCL,GGCL,GCLK |
| Disc Coupling | JMI,JMIJ,JMII,JMIIJ |
| High Flexible Coupling | LM |
| Chain Coupling | GL |
| Jaw Coupling | LT |
| Grid Coupling | JS |
Company Profile
Our company supplies different kinds of transmission products, such as cardan shaft, gear coupling, grid coupling and so on. High quality and reasonable price. We stick to the principle of “quality first, service first, continuous improvement and innovation to meet the customers” for the management and “zero defect, zero complaints” as the quality objective. To perfect our service, we provide the products with good quality at the reasonable price.
Welcome to customize products from our factory and please provide your design drawings or contact us if you need other requirements.
Our service
1.Design Services
Our design team has experience in cardan shaft relating to product design and development. If you have any needs for your new product or wish to make further improvements, we are here to offer our support.
2.Product Services
Raw materials → Cutting → Forging →Rough machining →Shot blasting →Heat treatment →Testing →Fashioning →Cleaning→ Assembly→ Packing→Shipping
3.Samples Procedure
We could develop the sample according to your requirement and amend the sample constantly to meet your need.
4.Research & Development
We usually research the new needs of the market and develop the new model when there is new cars in the market.
5.Quality Control
Every step should be special test by Professional Staff according to the standard of ISO9001 and TS16949.
FAQ
Q 1: Are you trading company or manufacturer?
A: We are a professional manufacturer specializing in manufacturing various series of couplings.
Q 2: Can you do OEM?
Yes, we can. We can do OEM & ODM for all the customers with customized artworks of PDF or AI format.
Q 3: How long is your delivery time?
Generally it is 20-30 days if the goods are not in stock. It is according to quantity.
Q 4: Do you provide samples ? Is it free or extra ?
Yes, we could offer the sample but not for free.Actually we have a very good price principle, when you make the bulk order then cost of sample will be deducted.
Q 5: How long is your warranty?
A: Our Warranty is 12 months under normal circumstance.
Q 6: What is the MOQ?
A: Usually our MOQ is 1 pcs.
Q 7: Do you have inspection procedures for coupling ?
A: 100% self-inspection before packing.
Q 8: Can I have a visit to your factory before the order?
A: Sure,welcome to visit our factory.
Q 9: What’s your payment?
A: T/T.
♦Contact Us
Web: huadingcoupling
Add: No.11 HangZhou Road,Chengnan park,HangZhou City,ZheJiang Province,China /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can Rigid Shaft Couplings Accommodate Different Shaft Sizes and Handle High Torque Loads?
Yes, rigid shaft couplings are designed to accommodate different shaft sizes and are capable of handling high torque loads. One of the key advantages of rigid couplings is their ability to provide a solid and strong connection between two shafts.
Rigid shaft couplings come in various designs, such as one-piece and two-piece configurations. The one-piece couplings have a solid construction with no moving parts and are ideal for applications where precise alignment and torque transmission are essential.
The two-piece rigid couplings consist of two halves that are bolted together around the shafts, creating a tight and secure connection. These couplings allow for easier installation and removal without the need to move the connected shafts. They are commonly used in applications where frequent maintenance is required.
The design of rigid shaft couplings enables them to handle high torque loads efficiently. The solid and rigid construction allows for the direct transfer of torque from one shaft to another, minimizing power loss and ensuring precise torque transmission.
Moreover, rigid couplings can accommodate different shaft sizes by offering various bore diameters and keyway options. This adaptability allows users to connect shafts of different diameters without the need for additional modifications or couplings.
However, it is crucial to select the appropriate size and type of rigid coupling based on the specific application’s torque requirements and shaft sizes. Properly sized rigid couplings will ensure reliable and efficient power transmission while preventing issues such as misalignment, vibration, and premature wear.

How do rigid shaft couplings compare to flexible couplings in terms of torque transmission and misalignment handling?
Rigid shaft couplings and flexible couplings differ in their ability to handle torque transmission and misalignment. Here’s a comparison of these aspects:
- Torque Transmission: Rigid shaft couplings offer excellent torque transmission due to their solid construction. They efficiently transmit high torque loads without significant power loss. Flexible couplings, on the other hand, may have some inherent power loss due to their flexibility.
- Misalignment Handling: Flexible couplings excel in compensating for misalignment between shafts. They can accommodate angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, reducing stress on connected equipment. Rigid couplings are limited in their misalignment compensation, primarily handling minimal misalignments. Significant misalignment can lead to increased wear and premature failure.
The choice between rigid and flexible couplings depends on the specific requirements of the application. If precise torque transmission and minimal misalignment are priorities, rigid couplings may be suitable. However, if misalignment compensation and vibration dampening are crucial, flexible couplings are a better option.

Are There Different Types of Rigid Shaft Couplings Available, and What Are Their Specific Applications?
Yes, there are different types of rigid shaft couplings available, each with its own specific applications. Some common types of rigid shaft couplings include:
- Sleeve Couplings: Sleeve couplings are simple and cost-effective couplings that connect two shafts together using a solid sleeve or tube. They are commonly used in applications with moderate torque requirements and where shaft alignment can be maintained with high precision.
- Clamp or Split Couplings: Clamp or split couplings consist of two halves that are clamped together around the shafts using screws or bolts. They are easy to install and suitable for applications where frequent maintenance or disassembly is required.
- Flanged Couplings: Flanged couplings have flanges on both ends that are bolted together. They are used in applications where shafts need to be rigidly connected and where some degree of axial movement is expected.
- Tapered Shaft Couplings: Tapered shaft couplings have tapered bores that fit tightly onto tapered shafts, creating a friction-based connection. They are often used in applications where precise alignment and torque transmission are essential.
- Keyed Shaft Couplings: Keyed shaft couplings use a key and keyway arrangement to connect the shafts securely. They are commonly used in heavy-duty applications where high torque transmission is required.
The choice of rigid shaft coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application. Factors such as torque transmission, shaft size, alignment precision, ease of installation, and maintenance needs play a crucial role in selecting the appropriate coupling type.
Rigid shaft couplings are widely used in various industries, including manufacturing, power generation, robotics, aerospace, and automotive. They are often employed in applications such as pumps, compressors, conveyors, and high-precision machinery.
It is essential to consider the specific demands of the application and consult with coupling manufacturers or experts to determine the most suitable rigid coupling type for optimal performance and reliability.


editor by CX 2024-04-16
China manufacturer Rigid Shaft Coupling Magnetic Couple Motor Couplings
Product Description
Hot sale: low noise,no leakage, no additional cost for rigid shaft coupling magnetic couple motor couplings
Introduction of rigid shaft coupling magnetic couple motor couplings
Magnetic shaft coupling is a new kind of coupling, which connects motor and machine by permanent magnetic force.
They are consisted of external rotor, internal rotor and isolating covers.
They work in the sealed magnetic drive pumps, which transporting volatile, flammable, explosive and toxic solutions with no leakage.
These magnetic shaft couplings can be used to connect gear pumps , screw pumps, centrifugal pumps, etc. with all types of electric motor or gear box.
Magnetic shaft coupling are widely used in various industries and fields, such as chemical, papermaking, foodstuff, pharmacy, and so on.
Advantages of rigid shaft coupling magnetic couple motor couplings
» Elimination of fluid leakage from the pump shaft.
» Vibrations are not transmitted to the pump.
» No maintenance required for magnetic couplings.
» Using magnetic couplings allows use of standard pumps without expensive mechanical seals.
» No additional cost for purchasing mechanical seal spare parts and maintenance.
Technical drawing of rigid shaft coupling magnetic couple motor couplings
Specification of rigid shaft coupling magnetic couple motor couplings
| Item | Internal Rotor(mm) | External Rotor(mm) | Isolating Covering(mm) | |||||||||||||||||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | Shaft Pin | H | I | J | L | N | M | P | Q | R | S | T | U | |
| GME03-3LM00 | Φ35 | – | Φ10 | 26 | – | 18 | – | M6X12 | Φ42 | Φ60 | Φ50 | 46 | 6-M4 | Φ40 | Φ50 | 4-Φ5.4 | Φ38 | Φ60 | 6 | 6 |
| GME03-5MM00 | Φ42 | – | Φ12 | 27 | 4 | 18 | 13.8 | M6X16 | Φ49 | Φ72 | Φ60 | 46 | 4-Φ6.7 | Φ52 | Φ60 | 4-Φ6.7 | Φ44 | Φ74 | 8 | 8 |
| GME03-16LM00 | Φ56 | – | Φ12 | 45 | 4 | 25 | 13.8 | M6X16 | Φ63 | Φ89 | Φ80 | 75 | 6-M5 | Φ70 | Φ75 | 4-Φ6.7 | Φ58 | Φ89 | 8 | 8 |
| GME03-16LM01 | Φ56 | – | Φ12 | 45 | 4 | 25 | 13.8 | M6X16 | Φ63 | Φ89 | Φ80 | 75 | 4-M5 | Φ70 | Φ75 | 4-Φ6.7 | Φ58 | Φ89 | 6 | 10 |
| GME03-16MM00 | Φ56 | – | Φ12 | 45 | 4 | 25 | 13.8 | M6X16 | Φ63 | Φ89 | Φ80 | 75 | 6-M5 | Φ70 | Φ75 | 4-Φ6.7 | Φ58 | Φ89 | 8 | 8 |
| GME03-22LM00 | Φ88 | – | Φ20 | 29 | 6 | 25 | 22.8 | M8X20 | Φ97 | Φ122 | Φ110 | 70 | 8-M6 | Φ98 | Φ108 | 6-Φ6.7 | Φ91 | Φ122 | 8 | 8 |
| GME03-30LM00 | Φ88 | – | Φ20 | 48 | 6 | 30 | 22.8 | M8X20 | Φ97 | Φ122 | Φ110 | 81 | 8-M6 | Φ98 | Φ108 | 6-Φ6.7 | Φ91 | Φ122 | 8 | 8 |
| GME03-40LM00 | Φ101 | – | Φ25 | 49 | 8 | 28 | 28.3 | M10X20 | Φ109 | Φ140 | Φ124 | 83 | 8-M8 | Φ110 | Φ126 | 8-Φ6.7 | Φ103 | Φ140 | 12 | 6 |
| GME03-50LM00 | Φ107 | – | Φ20 | 70 | 6 | 30 | 22.8 | M6X16 | Φ113.4 | Φ145 | Φ135 | 80 | 4-M6 | Φ126 | Φ133 | 12-Φ8.7 | Φ109 | Φ153 | 12 | 15 |
| GME03-65LM00 | Φ101 | – | Φ25 | 77 | 8 | 45 | 28.3 | M10X20 | Φ109 | Φ140 | Φ124 | 111 | 8-M8 | Φ110 | Φ126 | 8-Φ6.7 | Φ103 | Φ140 | 12 | 6 |
| GME03-80LM00 | Φ106 | – | Φ32 | 65 | 10 | 21 | 36.5 | M6X25 | Φ115 | Φ145 | Φ135 | 82 | 4-M6 | Φ127 | Φ135 | 6-Φ8.7 | Φ110 | Φ153 | 13 | 18 |
| GME03-80LM00 | Φ141 | Φ92 | Φ40 | 65 | 12 | 45 | 43.3 | M12X25 | Φ152 | Φ180 | Φ168 | 100 | 8-M8 | Φ154 | Φ164 | 8-Φ6.7 | Φ145 | Φ180 | 12 | 8 |
| GME03-100LM00 | Φ131 | Φ82 | Φ32 | 80 | 10 | 24.5 | 35.3 | M8X35 | Φ139 | Φ170 | Φ160 | 100 | 4-M6 | Φ152 | Φ158 | 8-Φ8.7 | Φ133 | Φ178 | 14 | 21 |
| GME03-110LH00 | Φ141 | Φ92 | Φ40 | 85 | 10 | 50 | 43.3 | M12X25 | Φ152 | Φ184 | Φ168 | 115 | 12-M8 | Φ156 | Φ164 | 12-Φ6.7 | Φ145 | Φ180 | 12 | 3 |
| GME03-110LM00 | Φ141 | Φ92 | Φ35 | 80 | 10 | 55 | 38.3 | M12X25 | Φ152 | Φ180 | Φ168 | 115 | 12-M8 | Φ154 | Φ164 | 12-Φ6.7 | Φ145 | Φ180 | 12 | 3 |
| GME03-140LM00 | Φ141 | Φ92 | Φ40 | 110 | 12 | 80 | 43.3 | M12X25 | Φ152 | Φ190 | Φ170 | 145 | 12-M10 | Φ154 | Φ164 | 12-Φ6.7 | Φ145 | Φ180 | 12 | 3 |
| GME03-180LM00 | Φ141 | Φ92 | Φ40 | 140 | 12 | 95 | 43.3 | M12X25 | Φ152 | Φ190 | Φ170 | 175 | 12-M10 | Φ154 | Φ164 | 12-Φ6.7 | Φ145 | Φ180 | 12 | 3 |
| GME03-220LM00 | Φ141 | Φ92 | Φ48 | 160 | 14 | 110 | 51.8 | M12X25 | Φ152 | Φ190 | Φ170 | 195 | 12-M10 | Φ154 | Φ164 | 12-Φ6.7 | Φ145 | Φ180 | 12 | 3 |
| GME03-300LM00 | Φ162 | – | Φ65 | 100 | 18 | 60 | 69.4 | Φ170 | Φ198 | Φ188 | 123 | 12-M6 | Φ180 | Φ192 | 12-Φ11 | Φ163.5 | Φ218 | 16 | 10 | |
| GME03-400LH00 | Φ195 | – | Φ70 | 127 | 20 | 107 | 79.9 | M12X25 | Φ203 | Φ234 | Φ222 | 152 | 6-M6 | Φ212 | Φ164 | 12-Φ11 | Φ198 | Φ278 | 16 | 22 |
Application of rigid shaft coupling magnetic couple motor couplings
The ability to hermetically separate 2 areas whilst continuing to transmit mechanical power from one to the other makes these couplings ideal for applications where prevention of cross contamination is essential. For instance: hydraulic sectors, dosing systems, compressors, sterilizers, industrial ovens, biotechnology, subsea equipment, pharmaceutical industry, chemical industry, food industry, generators and mixers.
Operation principles of rigid shaft coupling magnetic couple motor couplings
The magnetic coupling works by using the power generated by permanent magnets. No external power supply is needed. These are permanent magnets not electro magnets.
Packing Method of rigid shaft coupling magnetic couple motor couplings
Double strength corrugated Carton and Wood case Sea Packing.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can rigid shaft couplings operate in high-temperature or corrosive environments?
Rigid shaft couplings can be designed and manufactured using materials that are suitable for high-temperature or corrosive environments. Common materials used for such applications include stainless steel, nickel alloys, and other corrosion-resistant materials. These materials can withstand elevated temperatures and resist the effects of corrosive substances. When selecting a rigid shaft coupling for high-temperature or corrosive environments, it is essential to consider factors such as the operating temperature range, the specific corrosive substances present, and the overall environmental conditions. Additionally, proper lubrication and maintenance are crucial to ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of rigid couplings in these demanding environments. It is essential to consult with coupling manufacturers or suppliers who specialize in providing solutions for high-temperature or corrosive applications. They can help identify the appropriate materials and designs that will meet the specific requirements of the intended environment.

What are the maintenance requirements for rigid shaft couplings to extend their lifespan?
Rigid shaft couplings are mechanical components used to connect two shafts and transmit torque between them. While rigid couplings are known for their durability and minimal maintenance needs, proper care and maintenance can further extend their lifespan and ensure optimal performance. Here are key maintenance considerations:
- Lubrication: Some rigid couplings, especially those with moving parts like set screws, may require periodic lubrication to reduce friction and wear. Use appropriate lubricants as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the coupling for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Look for cracks, dents, or any other abnormalities that could affect its performance. Address any issues promptly.
- Tightening Fasteners: If the rigid coupling is secured using fasteners such as set screws or bolts, ensure they are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications. Loose fasteners can lead to misalignment and reduced coupling effectiveness.
- Alignment Check: Periodically check the alignment of the connected shafts. Misalignment can lead to increased stress on the coupling and premature wear. Realign the shafts if necessary.
- Coupling Integrity: Make sure the coupling is securely fastened and properly seated on both shafts. Any looseness or improper fitting can lead to vibrations and wear.
- Cleanliness: Keep the coupling and surrounding area clean from dirt, debris, and contaminants. Foreign particles can lead to increased wear and reduced performance.
- Environmental Factors: Consider the operating environment. If the coupling is exposed to harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures or corrosive substances, take appropriate measures to protect the coupling’s surfaces and materials.
- Replacement of Worn Parts: If any components of the coupling show significant wear or damage, consider replacing them as per the manufacturer’s recommendations. This can prevent further issues and maintain coupling integrity.
- Manufacturer Guidelines: Always follow the maintenance recommendations provided by the coupling manufacturer. They can provide specific guidelines based on the coupling’s design and materials.
Proper maintenance practices not only extend the lifespan of rigid shaft couplings but also contribute to the overall reliability and efficiency of the connected machinery. Regular inspections and maintenance can help identify potential issues early, preventing costly downtime and repairs.
It’s important to note that maintenance requirements can vary based on the specific design and material of the rigid coupling. Consulting the manufacturer’s documentation and seeking professional advice can help establish a suitable maintenance schedule tailored to the coupling’s characteristics and the application’s demands.

How Rigid Shaft Couplings Ensure Precise and Torque-Resistant Shaft Connections
Rigid shaft couplings are designed to provide a solid and inflexible connection between two shafts, ensuring precise alignment and efficient torque transmission. The key features that enable rigid couplings to achieve this include:
- One-Piece Construction: Rigid shaft couplings are typically made from a single piece of material, often metal, without any moving parts or flexible elements. This one-piece construction eliminates the risk of component failure and ensures a stable connection between the shafts.
- Accurate Machining: Rigid couplings undergo precise machining processes to achieve tight tolerances and accurate dimensions. This precision machining ensures that the coupling fits perfectly onto the shafts without any gaps or misalignments.
- High-Quality Materials: Rigid couplings are commonly manufactured from materials such as steel or aluminum, which offer excellent strength and durability. These high-quality materials contribute to the coupling’s ability to handle high torque loads without deformation or wear.
- Keyways and Set Screws: Many rigid shaft couplings feature keyways and set screws for additional security. Keyways are slots on the coupling and shafts that allow the transmission of torque without slippage. Set screws, when tightened against the shafts, create a firm grip, preventing axial movement and enhancing torque resistance.
- Clamping Force: Rigid couplings rely on a clamping force to hold the shafts firmly together. When the coupling is fastened around the shafts, the clamping force creates a strong bond between the coupling and shafts, minimizing any relative movement.
By combining these design elements, rigid shaft couplings ensure that the connected shafts remain in perfect alignment during operation. This precise alignment reduces the risk of misalignment-related issues such as vibrations, premature wear, and decreased efficiency. Additionally, the rigid nature of these couplings allows them to transmit torque without any backlash, providing immediate and accurate responsiveness to changes in torque and rotational direction.
Overall, rigid shaft couplings are an excellent choice for applications that demand precise shaft connections and reliable torque transmission. However, it’s essential to consider factors such as shaft alignment, load capacity, and environmental conditions when selecting the appropriate coupling for a specific application.
“`

editor by CX 2024-04-15
China factory FCL Flexible Shaft Couplings for Reducer and Motor
Product Description
SC Transmission FCL Flexible Shaft Couplings for Reducer and Motor
Product Description
FCL Coupling/Shaft Coupling /Pin & Bush Coupling /FCL Flexible Coupling/NBK FCL Coupling is widely used for its compacts designing, easy installation, convenient maintenance, small and light weight.
As long as the relative displacement between shafts is kept within the specified tolerance, couplings will operate the best function and have a longer working life.
Thus it is greatly demanded in medium and minor power transmission systems driven by motors, such as speed reducers, hoists, compressors, conveyors, spinning and weaving machines and ball mills.
Product Parameters
| SIZE | D | D1 | d1 | L | C | n-M | kg | |||
| r/min | ||||||||||
| N.m | ||||||||||
| FCL90 | 4 | 4000 | 90 | 35.5 | 11 | 28 | 3 | 4-M8 | 1.7 | |
| FCL100 | 10 | 4000 | 100 | 40 | 11 | 35.5 | 3 | 4-M10 | 2.3 | |
| FCL112 | 16 | 4000 | 112 | 45 | 13 | 40 | 3 | 4-M10 | 2.8 | |
| FCL125 | 25 | 4000 | 125 | 65 | 50 | 13 | 45 | 3 | 4-M12 | 4 |
| FCL140 | 50 | 4000 | 140 | 71 | 63 | 13 | 50 | 3 | 6-M12 | 5.4 |
| FCL160 | 110 | 4000 | 160 | 80 | 15 | 56 | 3 | 8-M12 | 8 | |
| FCL180 | 157 | 3500 | 180 | 90 | 15 | 63 | 3 | 8-M12 | 10.5 | |
| FCL200 | 245 | 3200 | 200 | 100 | 21 | 71 | 4 | 8-M20 | 16.2 | |
| FCL224 | 392 | 2850 | 224 | 112 | 21 | 80 | 4 | 8-M20 | 21.3 | |
| FCL250 | 618 | 2550 | 250 | 125 | 25 | 90 | 4 | 8-M24 | 31.6 | |
| FCL280 | 980 | 2300 | 280 | 140 | 34 | 100 | 4 | 8-M24 | 44 | |
| FCL315 | 1568 | 2050 | 315 | 160 | 41 | 112 | 4 | 10-M24 | 57.7 | |
| FCL355 | 2450 | 1800 | 355 | 180 | 60 | 125 | 5 | 8-M30 | 89.5 | |
| FCL400 | 3920 | 1600 | 400 | 200 | 60 | 125 | 5 | 10-M30 | 113 | |
| FCL450 | 6174 | 1400 | 450 | 224 | 65 | 140 | 5 | 12-M30 | 145 | |
| FCL560 | 9800 | 1150 | 560 | 250 | 85 | 160 | 5 | 14-M30 | 229 | |
| FCL630 | 15680 | 1000 | 630 | 280 | 95 | 180 | 5 | 18-M30 | 296 | |
Company Profile
FAQ
Shipping
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

How to Select the Right Shaft Coupling for Specific Torque and Speed Requirements
Selecting the appropriate shaft coupling involves considering the specific torque and speed requirements of the application. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the right coupling:
1. Determine Torque and Speed:
Identify the torque and speed requirements of the application. Torque is the rotational force required to transmit power between the shafts, usually measured in Nm (Newton-meters) or lb-ft (pound-feet). Speed refers to the rotational speed of the shafts, typically measured in RPM (revolutions per minute).
2. Calculate Torque Capacity:
Check the torque capacity of various shaft couplings. Manufacturers provide torque ratings for each coupling type and size. Ensure that the selected coupling has a torque capacity that exceeds the application’s torque requirements.
3. Consider Misalignment:
If the application involves significant shaft misalignment due to thermal expansion, vibration, or other factors, consider flexible couplings with good misalignment compensation capabilities. Elastomeric or beam couplings are popular choices for such applications.
4. Assess Operating Speed:
For high-speed applications, choose couplings with high rotational speed ratings to avoid resonance issues and potential coupling failure. High-speed couplings may have specialized designs, such as disk or diaphragm couplings.
5. Evaluate Environmental Conditions:
If the coupling will operate in harsh environments with exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures, select couplings made from corrosion-resistant materials or with protective coatings.
6. Check Torsional Stiffness:
In applications requiring precision motion control, consider couplings with high torsional stiffness to minimize torsional backlash and maintain accurate positioning. Bellows or Oldham couplings are examples of couplings with low torsional backlash.
7. Size and Space Constraints:
Ensure that the selected coupling fits within the available space and aligns with the shaft dimensions. Be mindful of any installation limitations, especially in confined spaces or applications with limited radial clearance.
8. Consult Manufacturer’s Data:
Refer to the manufacturer’s catalogs and technical data sheets for detailed information on each coupling’s torque and speed ratings, misalignment capabilities, materials, and other relevant specifications.
9. Consider Cost and Maintenance:
Compare the costs and maintenance requirements of different couplings. While some couplings may have higher upfront costs, they could offer longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in the long run.
By following these steps and considering the specific torque and speed requirements of your application, you can select the right shaft coupling that will ensure efficient power transmission and reliable performance for your mechanical system.
“`
Do Shaft Couplings Require Regular Maintenance, and if so, What Does it Involve?
Yes, shaft couplings do require regular maintenance to ensure their optimal performance, extend their service life, and prevent unexpected failures. The maintenance frequency may vary based on factors such as the coupling type, application, operating conditions, and the manufacturer’s recommendations. Here’s what regular maintenance for shaft couplings typically involves:
1. Visual Inspection:
Regularly inspect the coupling for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Check for cracks, corrosion, and worn-out elastomeric elements (if applicable). Look for any abnormal movement or rubbing between the coupling components during operation.
2. Lubrication:
If the shaft coupling requires lubrication, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the appropriate lubricant type and frequency. Lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and noise in the coupling.
3. Alignment Check:
Monitor shaft alignment periodically. Misalignment can lead to premature coupling failure and damage to connected equipment. Make adjustments as needed to keep the shafts properly aligned.
4. Torque Check:
For bolted couplings, periodically check the torque on the bolts to ensure they remain securely fastened. Loose bolts can lead to misalignment and reduce coupling performance.
5. Replace Worn Components:
If any coupling components show signs of wear or damage beyond acceptable limits, replace them promptly with genuine replacement parts from the manufacturer.
6. Environmental Considerations:
In harsh environments with exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures, take additional measures to protect the coupling, such as applying corrosion-resistant coatings or using special materials.
7. Monitoring Coupling Performance:
Implement a monitoring system to track coupling performance and detect any changes or abnormalities early on. This could include temperature monitoring, vibration analysis, or other condition monitoring techniques.
8. Professional Inspection:
Periodically have the coupling and connected machinery inspected by qualified professionals to identify any potential issues that may not be apparent during regular inspections.
By adhering to a regular maintenance schedule and taking proactive measures to address potential issues, you can ensure that your shaft couplings operate reliably and efficiently throughout their service life, minimizing downtime and improving overall system performance.
“`
What is a Shaft Coupling and Its Role in Mechanical Power Transmission?
A shaft coupling is a mechanical device used to connect two shafts together at their ends, allowing for the transmission of mechanical power from one shaft to another. It serves as an essential component in various machinery and industrial applications where rotational motion needs to be transmitted between two shafts that are not perfectly aligned or are separated by a distance.
The role of a shaft coupling in mechanical power transmission includes the following:
1. Power Transmission:
The primary function of a shaft coupling is to transmit power from a driving shaft to a driven shaft. When the driving shaft rotates, the coupling transfers the rotational motion to the driven shaft, enabling the driven equipment to perform its intended function.
2. Misalignment Compensation:
In real-world applications, it is often challenging to achieve perfect alignment between two shafts due to manufacturing tolerances or dynamic conditions. Shaft couplings are designed to accommodate different types of misalignment, such as angular, parallel, and axial misalignment, allowing the equipment to function smoothly even when the shafts are not perfectly aligned.
3. Vibration Damping:
Shaft couplings can help dampen vibrations and shocks caused by uneven loads or sudden changes in the operating conditions. This vibration damping feature protects the connected components from damage and contributes to the overall system’s reliability.
4. Overload Protection:
In some cases, a shaft coupling can act as a safety device by providing overload protection. When the connected machinery experiences excessive torque or shock loads, certain types of couplings can disengage or shear to prevent damage to the equipment.
5. Torque and Speed Conversion:
Shaft couplings can be designed to provide torque and speed conversion between the driving and driven shafts. This allows for adaptation to different operating conditions and varying torque requirements in the connected machinery.
6. Flexible Connection:
Shaft couplings with flexible elements, such as elastomeric inserts or flexible discs, provide a flexible connection that can absorb shocks and misalignments. This flexibility helps reduce stress on the connected equipment and extends its lifespan.
Overall, shaft couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, enabling the efficient transfer of rotational motion between shafts while accommodating misalignments and providing protection against overloads and vibrations. The selection of the appropriate coupling type and design depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the type of misalignment, torque capacity, and operating conditions.
“`

editor by CX 2024-04-11
China Custom Auto Parts Multi Sizes Spline Coupler Motor Connector Spiral Beam Shaft Couplings
Product Description
|
Product Name |
Auto Parts Multi Sizes Spline Coupler Motor Connector Spiral Beam Shaft Couplings |
|
Material |
Aluminum alloy |
|
Surface treatment |
Natural color anode |
|
Customized service |
Support light customization and logo customization |
|
Remarks |
The default engraving brand name and size of the product. If you need not engraving, please contact the customer service for comments |
| Packaging Details | Carton box with anti-static package,carton plus with wooden case. |
| Main Products | Shaft Parts, Timing Belt Pulley, Gears, CNC Machining Parts, Sheet Metal Fabrication |
| Certifications(2) | ISO9001:2015, IPMS |
| Applicable Industries | Building Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Food & Beverage Factory, Farms |
| Supply Ability | 100000 Piece/Pieces per Month |
| Dimension | oem provided |
| Surface finish | anodized |
| Lead Time | 25 days |
| Application | Furniture,cabinet |
| Custom | OEM and ODM services are welcome,we can make cutom LOGO and products according to customer’s requests. |
| Quality control Our | Finished product inspection,Warranty available |
| service | Swiss machining;deburring;lathe/turning;5 axis;micromachining |
| Color |
silver,gold,black,red,bulue,and according to the customer requests. |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Is It Possible to Replace a Shaft Coupling Without Professional Assistance?
Yes, it is possible to replace a shaft coupling without professional assistance, especially if you have some mechanical knowledge and the necessary tools. However, the ease of replacement can vary depending on the type of coupling and the complexity of the equipment. Here are some general steps to guide you through the process:
1. Safety First:
Before starting any work, ensure that the equipment is turned off and disconnected from the power source. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to protect yourself from potential hazards.
2. Assess the Coupling Type:
Different types of couplings may have specific installation and removal methods. Identify the type of coupling you need to replace, and consult the manufacturer’s documentation or online resources for guidance.
3. Gather Tools and Materials:
Collect the necessary tools, such as wrenches, sockets, and a puller (if required), to safely remove the old coupling. Have the new coupling ready for installation, ensuring it matches the specifications of the old one.
4. Disassembly:
If your coupling is a split or clamp-style coupling, you may be able to replace it without fully disassembling the connected equipment. Otherwise, you may need to remove other components to access the coupling.
5. Remove Fasteners:
Loosen and remove any fasteners, such as set screws, that secure the old coupling to the shafts. Take care not to damage the shafts during this process.
6. Extraction:
If the old coupling is tightly fitted on the shafts, you may need to use a coupling puller or other appropriate extraction tools to safely remove it.
7. Clean and Inspect:
After removing the old coupling, clean the shaft ends and inspect them for any signs of damage or wear. Also, check for any misalignment issues that may have contributed to the old coupling’s failure.
8. Install New Coupling:
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installing the new coupling. Apply appropriate lubrication and ensure the coupling is correctly aligned with the shafts.
9. Fasten Securely:
Tighten the fasteners to the manufacturer’s recommended torque values to securely attach the new coupling to the shafts.
10. Test Run:
After installation, perform a test run of the equipment to ensure the new coupling operates smoothly and without issues.
While it is possible to replace a shaft coupling without professional assistance, keep in mind that some couplings and equipment may require specialized knowledge and tools for safe and proper replacement. If you are uncertain about the process or encounter any difficulties, it is advisable to seek help from a qualified professional or technician to avoid potential damage to the equipment or injury to yourself.
“`
How to Identify Signs of Wear or Failure in a Shaft Coupling
Regular inspection and monitoring are essential to identify signs of wear or potential failure in a shaft coupling. Detecting issues early can help prevent costly downtime and equipment damage. Here are common signs to look for:
1. Visible Damage:
Inspect the coupling for visible signs of damage, such as cracks, chips, or deformation. These can indicate mechanical stress or overload.
2. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:
Unusual noise or excessive vibration during operation may indicate misalignment, worn-out components, or a coupling nearing its failure point.
3. Increased Temperature:
If the coupling becomes noticeably hotter during operation than usual, it could be a sign of friction or misalignment issues.
4. Shaft Misalignment:
Check for misalignment between the shafts connected by the coupling. Misalignment can lead to increased stress on the coupling and its components.
5. Excessive Backlash:
If the coupling exhibits too much free play or rotational play before torque transmission, it might indicate wear or fatigue in the coupling’s components.
6. Lubrication Issues:
Inspect the coupling for lubrication leaks or insufficient lubrication, which can lead to increased friction and wear.
7. Elastomeric Element Deterioration:
If the coupling uses elastomeric elements (e.g., rubber or polyurethane), check for signs of deterioration, such as cracking, softening, or deformation.
8. Bolts and Fasteners:
Examine the bolts and fasteners connecting the coupling components. Loose or damaged bolts can lead to misalignment and coupling failure.
9. Age and Service Life:
Consider the age and service life of the coupling. If it has been in use for a long time or exceeds the manufacturer’s recommended service life, it may be more susceptible to wear and failure.
10. Abnormal Performance:
Monitor the overall performance of the connected equipment. Any abnormal behavior, such as reduced power transmission or erratic operation, could be indicative of coupling issues.
If any of these signs are observed, it’s crucial to take immediate action. Depending on the severity of the issue, this may involve replacing worn components, realigning the shafts, or replacing the entire coupling. Regular maintenance and periodic inspections are key to identifying these signs early and ensuring the coupling operates optimally and safely.
“`
Can a Damaged Shaft Coupling Lead to Equipment Failure and Downtime?
Yes, a damaged shaft coupling can lead to equipment failure and downtime in mechanical power transmission systems. Shaft couplings play a critical role in connecting rotating shafts and transmitting power between them. When a coupling becomes damaged or fails to function properly, several negative consequences can arise:
1. Misalignment Issues:
A damaged coupling may no longer be able to compensate for misalignments between the connected shafts. Misalignment can cause excessive vibration, increased wear, and premature failure of bearings and other connected components. Over time, these issues can lead to equipment breakdown and unplanned downtime.
2. Vibration and Shock Loads:
Without the damping properties of a functional coupling, vibrations and shock loads from the driven equipment can transmit directly to the driving shaft and other parts of the system. Excessive vibrations can lead to fatigue failure, cracking, and damage to the equipment, resulting in reduced operational efficiency and increased downtime.
3. Overloading and Torque Transmission:
A damaged coupling may not effectively transmit the required torque between the driving and driven shafts. In applications where the coupling is a safety device (e.g., shear pin couplings), failure to disengage during overloading situations can lead to equipment overload and damage.
4. Increased Wear and Tear:
A damaged coupling can lead to increased wear on other parts of the system. Components such as bearings, seals, and gears may experience higher stress and wear, reducing their lifespan and increasing the likelihood of breakdowns.
5. Reduced System Reliability:
A functional shaft coupling contributes to the overall reliability of the mechanical system. A damaged coupling compromises this reliability, making the system more prone to failures and unplanned maintenance.
6. Downtime and Production Loss:
When a shaft coupling fails, it often results in unscheduled downtime for repairs or replacement. Downtime can be costly for industries that rely on continuous production processes and can lead to production losses and missed delivery deadlines.
7. Safety Hazards:
In certain applications, such as heavy machinery or industrial equipment, a damaged coupling can create safety hazards for workers and surrounding equipment. Sudden failures or uncontrolled movements may pose risks to personnel and property.
Regular inspection, maintenance, and prompt replacement of damaged shaft couplings are essential to prevent equipment failure, minimize downtime, and ensure safe and efficient operation of mechanical systems. It is crucial to address any signs of coupling wear or damage immediately to avoid potential catastrophic failures and costly disruptions to operations.
“`

editor by CX 2024-04-04